Brain Tumor SymptomsBrain tumors are developments that can occur in or closer to the brain, including on glands, nerves, and membranes. There are 2 kinds of brain tumors: primary (which initiate in the brain) and secondary (which result from cancer spreading from another part of the body to the brain). Plus, Secondary tumors are also regarded as metastatic tumors. There are different kinds of primary brain tumors - some benign (noncancerous) and others malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors do not spread throughout the body like cancer. However, they may grow over time and put pressure on surrounding tissues. Malignant or cancerous tumors grow more rapidly than benign ones and invade healthy tissues around them. Brain tumors can vary greatly in size. Some are smaller, while others can be quite larger before they are detected. People may notice signs right away if the tumor starts in an active part of their brain, however, if it begins in a less active area, it might not cause noticeable symptoms for some time. Let's discuss the brain tumor in depth. Brain Tumor Types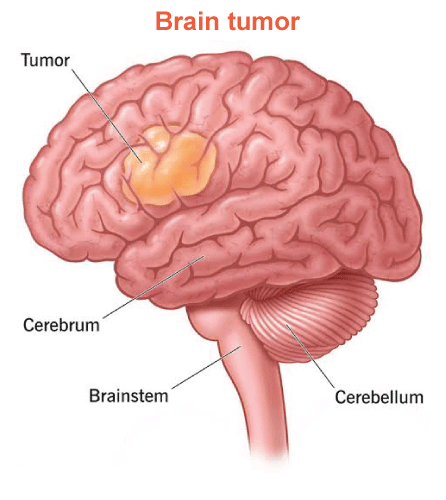
Brain tumors are divided based on the cells in tumor. Brain tumors can be either cancerous or noncancerous; Noncancerous brain tumors are also called benign brain tumors, whereas cancerous ones are known as malignant brain tumors. Benign brain tumors grow slowly, while malignant ones develop rapidly. There are numerous types of brain tumors, such as below.
Other TypesThere are various kinds of tumors that can occur, including those that produce from muscles and connective tissue surrounding the brain. Additionally, malignant brain tumors can grow from immune system cells in the brain and are known as primary central nervous system lymphoma. Risk Factors Associated with Brain Tumors
Symptoms of Brain Tumor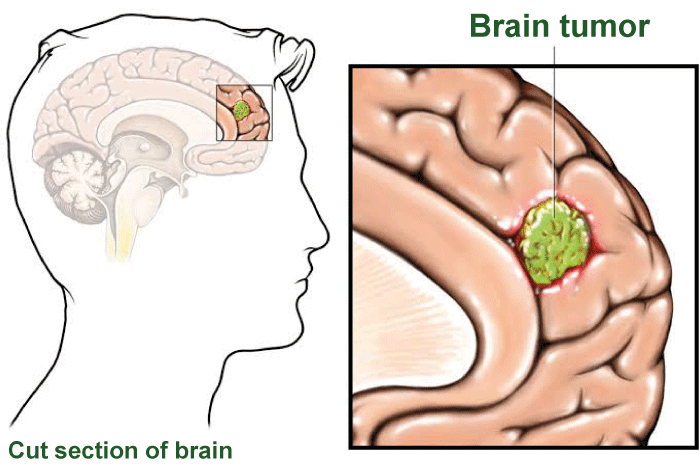
The symptoms of a brain tumor vary based on its size and growth rate (tumor grade). There are numerous symptoms of a potential brain tumor, including morning headaches or pressure in the head, frequent headaches (tension or migraines), nausea, vomiting, and eye issues like blurry vision or loss of peripheral sight.
Diagnosis of Brain TumorThe procedure of diagnosing brain tumors includes identifying the patient's medical history and conducting a physical examination. During a physical exam, physicians perform a detailed neurological examination to test the cranial nerves originating in the brain. Your specialist will utilize an ophthalmoscope to examine your eyes by shining a light via your pupils and onto your retinas. Doctors can check for modifications in the optic nerve caused by raised pressure inside the skull by examining a patient's pupils and looking directly into their eyes. The physician will assess muscle strength, coordination, memory, and mathematical capability during a physical exam. Following tests may be ordered depending on the outcome of the exam. 1. CT Scan CT scans provide detailed body scans for doctors, surpassing the capabilities of X-ray machines. It can be performed with or without contrast. A CT scan of the head uses a dye to create contrast and improve the visibility of certain structures, such as blood vessels. 2. MRI An MRI of the head can detect tumors with the use of a special dye without using radiation. It provides detailed pictures of brain structures compared to CT scans. 3. Angiography This study injects dye into the artery to see the blood supply of tumors during surgery. 4. Skull X-rays Brain tumors can lead to skull bone breaks and calcium deposits, which can be detected through specific X-rays. Calcium deposits may indicate cancer spreading to the bones. 5. Biopsy During a biopsy, a tiny piece of the tumor is examined by a neuropathologist to find out if the tumor cells are benign or malignant and whether it originated in the brain or another part of the body. Proper Treatment of Brain TumorBrain tumor treatment depends on factors such as type, size, location, and general health. Surgery is the most common option for malignant tumors to remove as much cancer without harming healthy brain tissue. Removing brain tumors can be challenging if they are located in certain areas, but partial removal can still provide some benefits. Brain surgery carries the risk of infection and bleeding but is necessary to remove dangerous benign tumors. Metastatic brain tumors are treated based on guidelines for the original cancer type. Surgery can be combined with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. ConclusionBrain tumors can be successfully treated and fully recovered from, but the outlook depends on factors such as tumor type, size, location, and general health. Early treatment can prevent complications and malignant spread to other tissues in the brain. A doctor can determine the best course of action for treatment and symptom management. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy may aid recovery after neurosurgery.
Next TopicGene Cloning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









