Meninges of BrainYour brain and spinal cord (central nervous system) are surrounded and safeguarded by three layers of membrane called meninges. Your brain is held in place, protected, and has blood arteries, nerves, lymphatics, and cerebrospinal fluid maintained by three membranes:
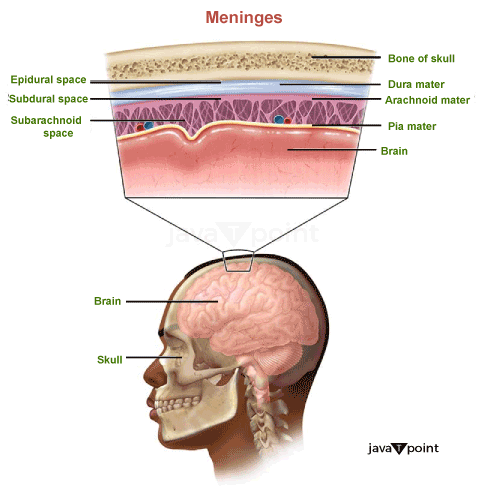
Meninges: What exactly are they?Your brain and spinal cord, collectively referred to as your Central Nervous System (CNS), are covered and shielded by three layers of membrane called the meninges. Their other names are:
Leptomeninges are the collective name for the arachnoid and pia maters. There are three spaces in the meninges:
What purpose do the Meninges fulfil?The Meninges means-
What features does Dura Mater have?The thick, durable membrane layer directly underneath your skull and vertebral column is called the dura mater. Dura mater is Latin for "hard mother." This structure is comprised of two layers of connective tissue. On one side, the dura is connected to your skull, and on the other, to the arachnoid mater, your middle membrane layer. Cerebrospinal fluid can return to the bloodstream and blood can leave your brain thanks to a drainage system in your dura mater called the dural venous sinuses. Your middle meningeal artery and vein provide your dura mater with blood, and your trigeminal nerve passes through it. Four thin membrane layers known as dural reflections are produced as a result of the dura mater folding inward. Each dural reflection encircles a particular hemisphere of your brain. What features does Arachnoid Tissue have?The arachnoid mater, the middle layer of your meninges, is located just beneath the dura mater. There is a thin layer separating your dura mater from your pia mater. There are no blood vessels or nerves. It resembles a spiderweb because of connective tissue projections that connect to your alma mater (the term "arachnoid" refers to a spider). The cerebrospinal fluid, which serves as the brain's cushion, is found in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater. What Sets the Pia Mater Apart?Your brain and spinal cord are covered in a thin layer called your pia mater, or deepest layer, which sticks to them like shrink wrap. This layer has numerous blood vessels that carry blood to the brain tissue. Cerebrospinal fluid retention is also facilitated by it. The spinal cord's rigidity is maintained by the pia mater. What Medical Conditions Affect the Meninges?The two most prevalent conditions that impact your meninges are as follows:
Doctor's SuggestionThree layers of meninges surround and protect your spinal cord and brain. Pia mater, arachnoid mater, and dura mater are the three membrane layers. The layers, which also contain cerebrospinal fluid, among other things, protect your brain tissue from rubbing up against your skull. Contrarily, bleeding into any of your meninges and/or the brain tissue itself (intracranial haemorrhage) can occur because of head trauma. Contact your doctor right away if you get a blow to the head because of trauma (like a car accident), a sports injury, or a fall.
Next TopicNitrogen Cycle
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









