Brain LesionsBrain tissue damage is known as a lesion. Damage of this nature results from illnesses or brain injuries. A specific kind of brain injury is a stroke. The functioning of your brain can be disrupted by lesions, leading to a variety of symptoms include weakness, a disruption of one or more senses, and disorientation. How can Brain Lesions affect the BrainElectrical and chemical signals are used by your brain to communicate both inside it and with other parts of your body. A brain lesion can impair communication in the brain area or areas that are affected. The larger the interruption, the more serious the harm. 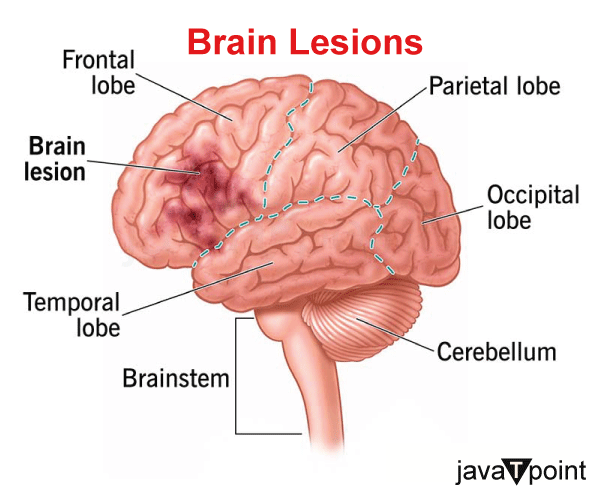
How Lesions affect different areas of the BrainThe symptoms of brain lesions differ depending on where they are in your brain since different parts of your brain govern various functions and activities. Your symptoms help a neurologist or other medical professional identify the part of your brain that is malfunctioning. The three major regions of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. CerebrumThe primary portion of your brain is called your cerebrum. Its two halves are the left and right hemispheres. Your brain has four lobe-like regions in each of its two hemispheres. Those areas are the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes. Under the frontal lobe, a secret internal region known as the insula exists. CerebellumAt the back of your skull's bottom, your cerebellum is a region of brain tissue that is closely packed. Cerebellar lesions can be identified by the following symptoms:
BrainstemYour brainstem, which resembles a stalk, joins your brain and spinal cord. Brainstem lesions can have an impact on your respiration, blood pressure, eye alignment, heart rhythm, and other functions. What are the Most Common Causes of Brain Lesions?Any ailment or scenario that can harm your brain can cause brain lesions. The following illnesses can result in brain lesions:
Brain lesions can occur as a result of an accident, trauma, or nonmedical factors such as:
How are Brain Lesions Diagnosed?Following a neurological exam, a healthcare provider may suspect a lesion. During this diagnose, a healthcare expert assesses muscle strength in your limbs, analyses your reflexes, and determines whether your senses are functioning properly. Imaging scans are used to discover a brain lesion after a neurologic assessment. The following are some of the most commonly used imaging tools for detecting various types of lesions:
Other tests may be performed, but they are often designed to discover or rule out another ailment that may be causing similar symptoms. Treatment of Brain LesionsThere are different therapy options for brain lesions because they can occur for a variety of reasons. Doctor's treatment recommendations will be based on the underlying cause of your brain damage. Some illnesses that result in brain lesions, such as a minor concussion, resolve on their own. Treatments are not required if the lesion is not serious. Rest and less activity are frequently all that is required. Other illnesses that cause brain lesions can be treated in various ways. Antibiotics or supportive care are frequently used to treat infections. Surgery may be used to remove growths or tumours, particularly those that are simple to reach. Some lesions are so tiny that they generate no symptoms or harm. Unfortunately, there are situations when brain lesions cannot be treated. This is most likely in cases with serious lesions. The same can be said for incurable disorders like Alzheimer's. How are Brain Lesions avoided?Brain lesions can occasionally be avoided depending on the source. The most avoidable types of lesions are those caused by concussions and traumatic brain traumas. Infections should be treated as soon as possible to avoid spreading to your brain and causing damage. The following are some of the most useful things you can do to avoid or reduce your risk of having brain lesions-
When to consult with the doctor?Signs of brain lesions that require immediate medical intervention include:
Doctor's NoteBrain lesions can occur for a variety of reasons, making them a common indicator of a brain-related illness. Some lesions are small and heal with little or no therapy. Others are more serious and may necessitate medical attention, such as surgery. Unfortunately, some lesions are serious, permanent, or occur for untreatable reasons. Medical imaging advances have improved healthcare practitioners' ability to detect and analyse brain abnormalities. These imaging technologies are also important in planning prospective therapies and anticipating possible or expected outcomes in your instance. Advances in medical understanding of the brain also open up new avenues for treating and recovering from brain lesions and the illnesses that produce them.
Next TopicClusters Headaches
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









