Brain HematomaA brain hematoma is a form of brain bleed. It's a form of bleed that happens inside the skull but outside of the brain's tissue. The meninges are three membrane layers or coverings that lie between the bone skull and the brain's tissue. The meninges' function is to cover and protect the brain. 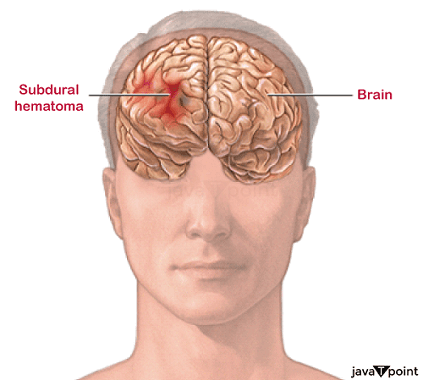
A brain hematoma is caused by a rip in a blood vessel, most commonly a vein, and blood leaks out of the injured vessel into the region beneath the dura mater membrane layer. Because it is beneath the dura, this space is known as the brain space. Abrain haemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding into this region. Subdural hematoma is also known as brain haemorrhage or intracranial hematoma. It is also a kind of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in general. How common are Brain Hematomas?Up to 25% of persons with head injuries develop brain hematomas. Are Brain Hematomas serious?Yes, a brain hematoma is a dangerous condition. The bleed can sometimes be gradual, and the body can absorb the collected blood. If the hematoma is significant, the blood buildup might create pressure on the brain. If not treated, this pressure can cause breathing issues, paralysis, and death. Because people don't know how bad a brain bleed is until additional testing, any trauma to the head should be treated seriously. Different types of Brain HematomasSubdural hematomas are classified by how quickly they grow, how much bleeding happens, and how much damage the bleeding produces. There are several forms of brain hematoma:
People more likely to get Brain HematomaAlthough anyone can develop a brain hematoma because of an accidental head injury, certain categories of people are more vulnerable. Brain hematomas are more common in children:
Babies-Babies do not have strong neck muscles to defend themselves from head injuries. When a baby is abused by shaking him or her, abrain hematoma might form. This is referred to as shaken baby syndrome. How do Brain Hematomas happen?The majority of brain hematomas are caused by head injuries. people are at risk of getting brain hematoma if he/she fall and strike the head, take a blow to the head in a car or bike accident, participate in an athletic activity or have another sort of head trauma. What are the symptoms of Brain Hematoma?Many symptoms are shared brain hematomas and traumatic brain injury (TBI). Symptoms of a brain hematoma may arise quickly after a head injury, or they may develop over time - even weeks or months. Signs and symptoms of a brain hematoma include:
Symptoms may worsen as the bleeding persists and the pressure in the brain rises. At this point, symptoms include:
Sometimes people have no symptoms just after a head injury. This is known as a lucid interval. They show symptoms several days later. It's also vital to understand that brain hematomas that develop slowly (the chronic type) can be misinterpreted for other diseases like a brain tumour or stroke. A word regarding head injuries and symptoms in seniors: Some symptoms of brain hematoma in elderly persons, such as memory loss, confusion, and personality changes, may be confused with dementia. The elderly individual may not recall being smacked on the head. People may forget because they are bewildered. In other cases, the injury was minimal and occurred weeks before symptoms manifested. They should still see their doctor for an examination. How are Brain Hematomas diagnosed?First, the physician will perform a complete physical and neurological examination. A doctor will inquire about the head injury (when and how it occurred, the symptoms and any medical problems, drugs that are taking, and other lifestyle choices). Blood pressure checks, vision testing, balance and strength testing, reflex tests, and a memory test will all be part of the neurology exam. If the doctor suspects patients have a brain hematoma, he or she will arrange a computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the head. These imaging procedures enable doctors to obtain clear images of the brain and pinpoint the location and extent of bleeding or other head and neck injuries. What are the treatments for Brain Hematoma?Decompression surgery is used by doctors to treat bigger hematomas. To drain the blood, a surgeon drills one or more holes in the skull. Draining the blood lessens the strain on the brain caused by blood accumulation. If large or thick blood clots are present, more surgery may be required to remove them. Typically, healthcare providers keep a drain in place for many days after surgery to allow the blood to drain. Sometimes hematomas cause few or no symptoms and are tiny enough that surgical treatment is unnecessary. Bed rest, medications, and close monitoring may be all that is required. Over time, usually a few months, the body can absorb a little amount of blood. What are the side effects of Brain Hematoma treatment?The risk of bleeding, infection, and blood clots is raised after decompression surgery. After surgery, the healthcare providers will keep a watchful eye on you. What are the complications of having a Brain Hematoma?Large hematomas can cause a coma and even death if left untreated. Additional issues include:
How can people prevent Brain Hematoma?Although a hematoma as a result of an accident may not be preventable, it's possible to lower the risk by:
What can a person expect if he/she have a Brain Hematoma?The prognosis if people have brain hematoma is determined by the age, the severity of the head injury, and how promptly it received care. Although 50% of persons with massive acute hematomas survive, the injury frequently causes irreversible brain damage. Younger people are more likely to survive than elderly persons. People with persistent brain hematomas typically have the greatest prognosis, particularly if they have few or no symptoms and have stayed awake and conscious following the head injury. After healing from a persistent brain hematoma, older persons are more likely to experience another bleed (haemorrhage). This is since older brains are unable to re-expand and fill the space where the blood was, making them more vulnerable to subsequent brain bleeds with even small head injuries.
Next TopicBrain Infection
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









