ParenchymaIn the plural, the biological word parenchyma is called "parenchymatous" or "parenchymas". The parenchyma word is derived from 'parénkhyma' or 'parenkhein', which means 'beside', 'to pour in, and énkhuma means "the content of vessel". Parenchyma is a functional cell in the plants and animal body. It is an essential component of an organ. In-plant biology (botany), parenchyma is the simple permanent ground tissue used by the plant for photosynthesis and storage. These cells are present in bulk at the soft part of leaves, fruit pulp, and other plant organs. Parenchyma cells are present in both:-
Parenchyma cell in plantsIn plants, basic ground tissues combine three types of plant cells: parenchyma, sclerenchyma, and collenchyma.
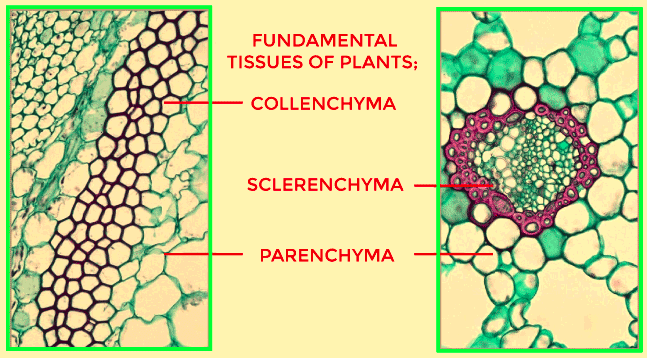
Function and characteristics of plant parenchyma cellPlant parenchyma cells make the ground tissues of the cell, which are the primary tissues for the plant. Parenchyma cells are used to store nutrients, proteins, starch, hormones, etc., that are necessary for the growth of a plant. Parenchyma cells help in the making of food in the plant as mesophyll cells under the epidermis capture the sunlight, and they are of two types:-
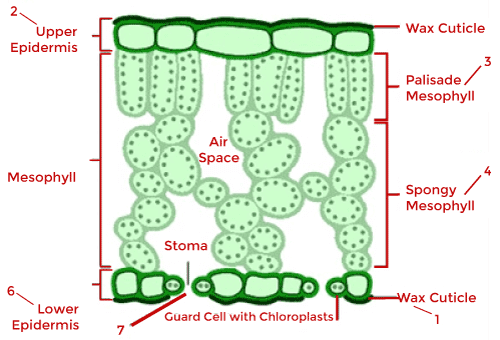
Diagram of palisade and spongy mesophyll parenchymatous cells Parenchymal cells structure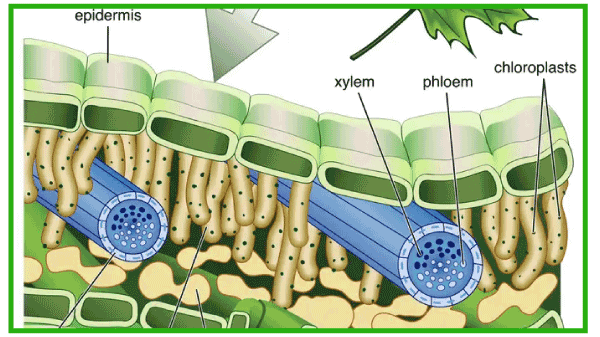
Parenchyma cells are the lifeline of the living organism; therefore, they are called living cells. They consist of the following:-
Various types of plant parenchyma cells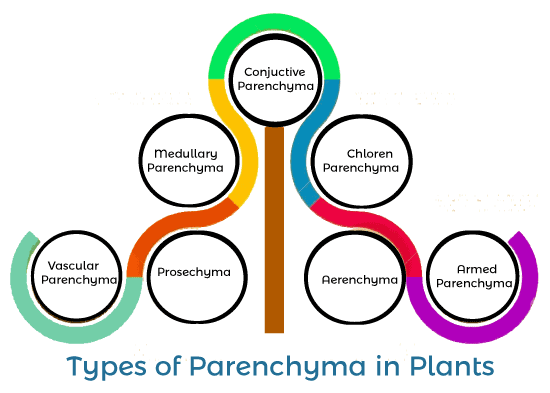
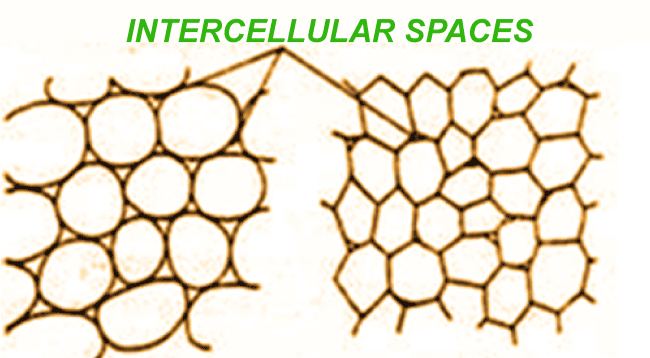
According to the shape and function, parenchyma cells are differentiated into the following types:- a. Chlorenchyma parenchyma cell This type of parenchymal cell resists in the mesophyll part of the leaves and cortex of the stem. The presence of chloroplast and chlorophyll gives green color to leaves and stems. Cells are loosely packed with intercellular space that allows the exchange of gases. These cells are mainly required for the process of photosynthesis. b. Conjunctive parenchyma cell These cells are present in conjunctive tissue, and on maturation, this tissue is converted into sclerenchymatous cells. c. Armed parenchyma cell These parenchyma cells are found in the mesophyll part of the gymnosperms. They are star-shaped cells also found in pine tree leaves. 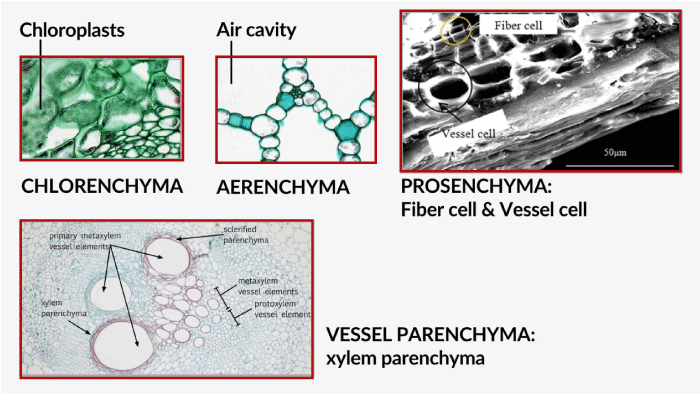
d. Medullary parenchyma cell These types of parenchyma cells are present in a medullary ray of the primary vascular tissue of the stem. These thin-walled elongated cells do the distribution of water and nutrients and store the starch grains. e. Vascular parenchyma cell This type of parenchyma cell is found in vascular tissues that provide nutrients to tissues. Type of vascular tissue are:-
f. Prosenchyma parenchyma cell Vascular tissues of plants address Prosenchyma parenchymal cells, and they have pointed end and elongated narrow cells. g. Aerenchyma cell These types of parenchymal cells are mainly found in aquatic plants. These cells are loosely packed, having large intercellular spaces that provide air pockets, buoying the plants as they can float. The plant uses stored gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide in Aerenchyma. According to the shape, plant parenchyma cells are classified into two types:
Parenchyma cells in AnimalsThe functional cell in the living organism are parenchymal cells tumor (neoplastic) cells are also part of them. In anatomy, parenchyma designates an organ's working elements and is distinguished from the stroma. In the brain, parenchyma cells are neuron and glial cells. In some vertebrates, parenchyma cells are the spongy connective tissues. Types of parenchyma cells in animals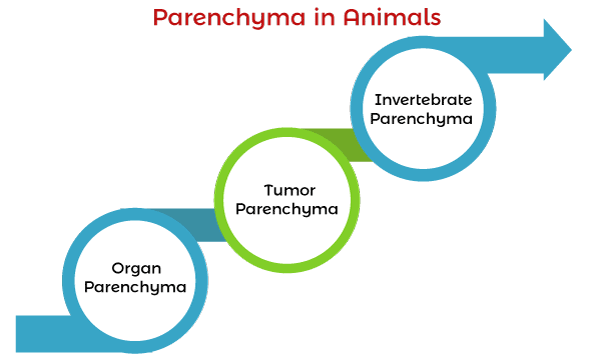
a. Organ parenchyma cell In a living organism, the biological organ is made of multiple tissues, and tissues are the combination of functional cells. Each tissue has to perform a particular function, and they are made of parenchyma cells, and supportive cells are called stromal cells (stroma). Parenchyma cells are the functional cells that make an organ work properly. List of organs that have parenchyma cells and are known as organ parenchyma cells:-
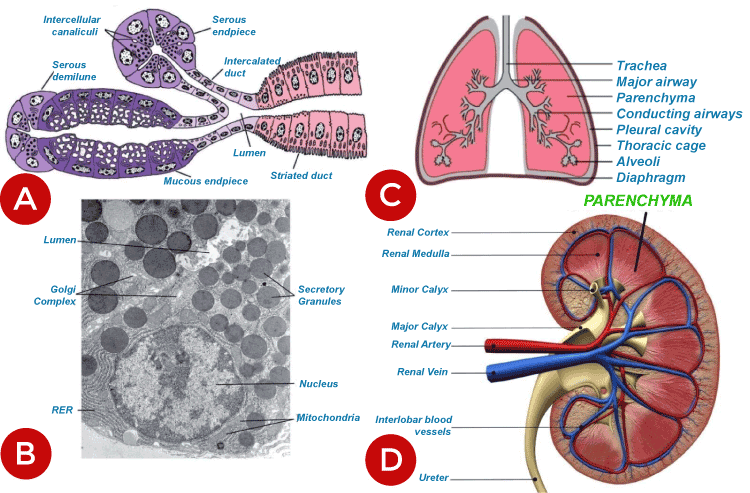
What does parenchyma cell function in animals?
b. Tumor parenchyma cell A tumor is defined in two parts:- Parenchyma or stromal cells These cells work with parenchyma cells in conjunction. Progression and invasiveness of the tumor depend on the functional parenchyma cells.
c. Invertebrate parenchyma cell Animals or insects like snails, flatworms, lobsters, and jellyfish are examples of invertebrate animals with no backbone or bone. Vice versa is vertebrates with backbone and bones like human beings and many animals. Invertebrates fall under the acoelomates that possess activity with the help of tissues only. Tissues carry the body's physiological function with the three layers (enclose the organism's gut). Layers are:-
In acoelomates, parenchymal cells provide motility, material transportation, regenerative cells reservoir, storage support (store nutrients), and skeletal support. 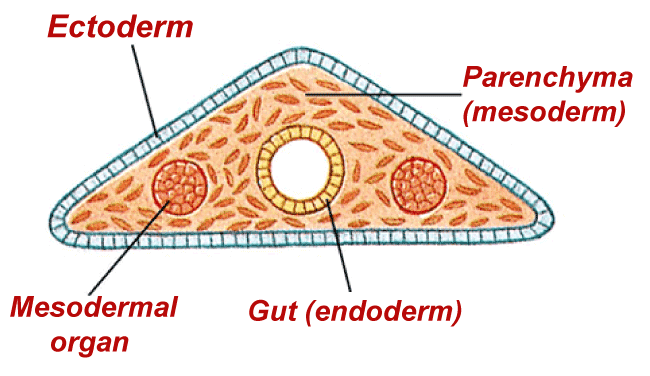
Next TopicTypes of plant Cell
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










