Bacterial meningitisWhat is bacterial meningitis?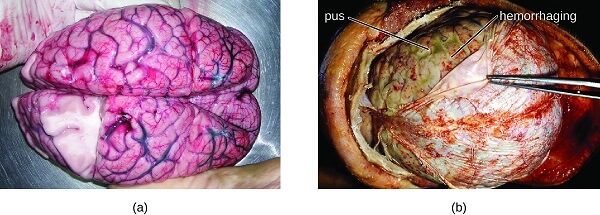
Generally, meningitis is an infection that occurred in the membranes that help in the protection of the spinal cord and brain. The infection on the membrane leads to swelling and pressing on the spinal cord and brain of the body. This can result in life-risking problems. The symptoms of meningitis occur suddenly and it gets worse with each passing day. Cause of bacterial meningitisBacterial meningitis can be caused by the attack of bacteria or viruses. Most common meningitis is caused by viruses however severe meningitis is caused by bacteria. It can result in serious damage to the brain, paralysis, or stroke. Sometimes, it can lead to the death of a person. Many types of bacterial strains are found to be causative of meningitis. However, vaccines are available that target pathogenic strains. To apply the right vaccine, it is important to identify the causative agent of meningitis, a bacterial strain that is causing the infection. Since all the types of bacteria affect the specific region of the body, they may have different symptoms and may require different treatments or vaccines. What are the risk factors for bacterial meningitis?The actual and exact reason for infection of meningitis is not always known. Some people induce it due to a weak immune system or when they have been sick. If a person has caught a head injury leads to a high risk of getting meningitis. Bacterial meningitis is very frequent in newborns or children under 1 year of age. Additionally, people between the ages of 16-21 years can also be infected with meningitis. Students living in forms or closed rooms are highly risked of getting infected with meningitis. Also, adults with particular medical issues are at high risk of getting infected. Especially the ones without a spleen in their body. What are the symptoms of bacterial meningitis?
Below are several symptoms that are common in children or infants.
These symptoms usually show up quickly in a couple of hours or up to a day or two. But if you think you or your child may have got meningitis, consult a doctor right away. How is bacterial meningitis diagnosed?For the diagnosis of this situation, a doctor or physician will perform a spinal tap which is also referred as a lumbar puncture. In this, doctors collect a sample of fluid from around the spinal cord region. The collected fluid is then observed for the presence of bacterial meningitis. Additionally, a physical test also takes place according to the symptoms of a person. Meningitis Rash glass testMeningococcal meningitis is a kind of bacterial meningitis that is caused by the bacterium strain of Neisseria meningitidis. M.meningitis can lead to the development of septicemia which is an infection of blood in the body. This is also called as Meningococcal septicemia or meningococcemia. This causes a weird rash on the skin surface which is characterized by small, non- bulged, purple reddish scrape. Meningococcemia causes bleeding outside the capillary tubes which results in the appearance of rashes on the skin. Meningococcal meningitis can result in rash or inflammation in about 50% of people with this problem. It is possible to detect the origin of rash that is from meningococcemia by pressing a glass tumbler against the rash. If the rash doesn't disappear after the test, it indicates that the person may have meningococcemia. Note - A person should not depend on the glass test for the identification of rash as it can also result from other factors. A proper consultation from a doctor is recommended for the disease.Prevention of MeningitisThe infection of meningitis may be prevented by avoiding in contact with viruses or bacteria that may cause it. The infection can be transmitted from one person to others by coughing, sneezing, kissing or sharing toothbrush or utensils. You may follow these steps to prevent meningitis.
Types of Meningitis1. Bacterial meningitisIt is the most dangerous and serious disease. It can be life-risking or lethal which leads to damage to the brain, and spinal cord. If you or your child get caught with bacterial meningitis, call for medical help immediately. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitis, and Listeria monocytogenes are some bacteria that cause meningitis. The Listeria monocytogenes cause meningitis in older people, pregnant women, or adults with weak immunity. These pathogens are very common in the United States. Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) bacteria is a common cause of meningitis in infants and young children. Since the Hub vaccine is not available for newborns, it is a very common infection. Moreover, Researchers have made vaccines for the pathogen Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae that cause serious life-threatening infections. Doctors recommend mandatory vaccines in children as well as adults with weak immunity or medical conditions. Most of the time, bacterial meningitis occurs when bacteria gets incorporated into your bloodstream from your nose, ears, or throat. This way bacteria travel through the bloodstream to the brain. 2. Viral meningitisIt is a form of meningitis that is more common than bacterial meningitis. It is usually less serious and life-threatening than bacterial meningitis. Several viruses can be responsible to trigger the infection including the ones that cause diarrhea. 3. Fungal meningitisFungal meningitis is usually rare than the bacterial or viral forms of meningitis. If a person has good immunity with low health problems, it is rare that fungal meningitis could occur in them. It is highly infectious in people with a weak immune system like AIDS patients. 4. Parasitic meningitisThis form of meningitis is also quite rare. It is primarily caused by the attack of parasites. It generally affects animals. A healthy person can also get it by consuming animals like snails, slugs, fishes, snakes, or chickens that are already contaminated by parasites. Eggs or parasitic eggs produced by infected parents are also dangerous to consume. Raw food or undercooked food products are the major sources of parasitic meningitis. It is not contagious, so no spreading rate. 5. Amoebic meningitisThis form of meningitis is also rarely found. It is dangerous as the infection is fatal. Amoebic meningitis is caused by a unicellular bug called Naegleria fowleri. The amoeba is found in areas like soil, and freshwater but they are not present in Saltwater like oceans. People get infected by swimming in water where the amoeba lives on the surface of pools or water banks. You do not get infected by drinking the same water. Hence it is not contagious. 6. Non-infectious meningitisNon-infectious meningitis is common in a person with head injury, brain surgery or on any medication. It is commonly occur in person with lupus or cancer. This class of meningitis is not contagious. 7. Chronic meningitisChronic meningitis has same symptoms as acute meningitis however chronic meningitis takes several weeks to develop and infect. It occurs from the infection with fungus or Mycobacterium that could lead to tuberculosis. These pathogen get incorporated into membrane and fluid around the brain to cause meningitis. .
Next TopicBacterial Growth Curve
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










