Composition of Blood
Blood
Blood is a circulatory tissue made up of fluid, plasma, and cells. It is a straw-coloured or pale yellow liquid containing suspended blood cells. Red blood cells contain a red color pigment called haemoglobin, which is rich in iron and transports oxygen from the alveoli of the lungs to the tissues of the body. Blood makes up a total of 8% of an adult's body weight. On average, a female's body consists of 4-5 litres of blood total body weight, whereas men have 5-6 litres of the blood total body weight. This difference arises because of different size and body structures.
Facts about blood
- Blood has an average temperature of 38 degrees Celsius.
- Blood has a pH of 7-7.5 which indicates that it is quiet basic in nature.
- The viscosity of blood is nearly 4 to 5 times higher in comparison to that of water, which indicates that it is more resistant to flow than water. This viscosity is basic basic blood property because the blood that flows too easily or with too much resistance can stress the heart and cause serious cardiac problems like heart strokes and heart attacks.
- Due to the higher levels of oxygen present in the artery walls, blood in the artery walls is bright red compared to the blood in the veins.
Main components of blood
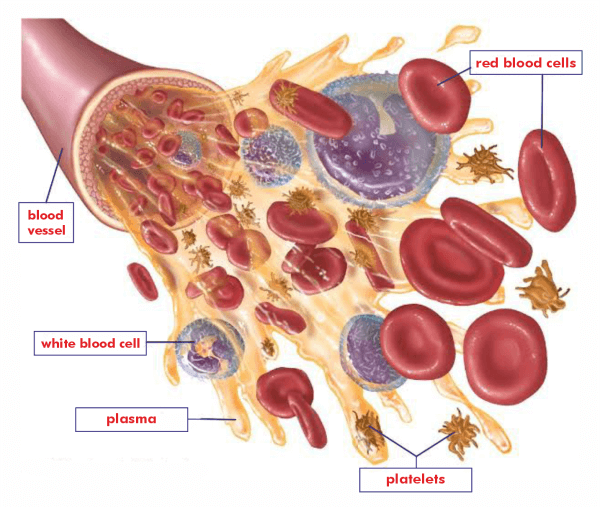
Blood is a connective tissue made up of two major components:
- Plasma: It is a clear extracellular viscous liquid.
- Formed Elements: Blood cells and platelets are called formed elements.
- The Formed elements may be distinguished from one another due to their distinct shape and structure and plasma membrane covering.
- Blood Platelets: They are microscopic pieces of bone marrow cells.
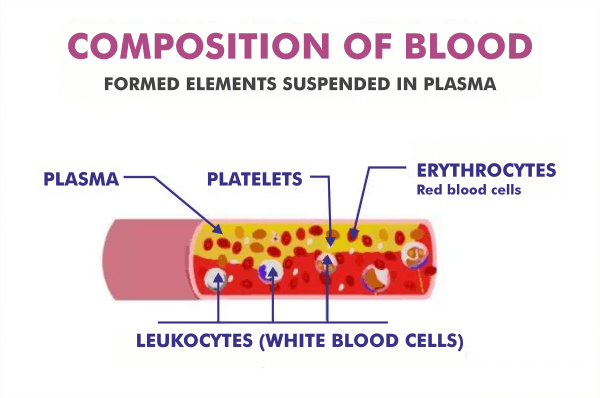
Blood consists of the following components:
- Blood Plasma
- Formed Elements
- Erythrocytes,
- Leukocytes,
- Platelets
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a complex combination of enzymes, nutrients, wastes, proteins, hormones, and gases. Some important functions of blood plasma are listed below:
Proteins
- Proteins are present in abundance in the plasma when we look at weight. They play a variety of roles within the body, including coagulation, protection, and transport.
- They serve as an important reserve of amino acids for the nutrition of cells.
- Macrophages in the digestive system, gastrointestinal, spleen, lungs, and the lymphoid system can degrade plasma proteins and release their amino acids. Other categories of cells use these amino acids to make new products.
- Plasma proteins help in transporting other molecules. Specific plasma proteins bind to different kinds of tiny molecules, which are then carried to various tissues for utilisation by the organs that absorb these proteins.
- Plasma proteins interact in unique ways to cause blood to clot, which is a core component of the body's response to blood vessel injury and helps in the prevention of blood loss and invasion by foreign microbes and pathogens.
- Plasma proteins facilitate the water distribution between blood and tissues by generating osmotic pressure.
Formed Elements
Erythrocytes
RBCs or Red Blood Cells also recognised as erythrocytes, have two important functions.
- RBCs help in transporting oxygen from the lungs to other tissues.
- They carry carbon dioxide from other tissues and expel it through the lungs.
An erythrocyte, often known as an RBC, is a ring cell with a wide rim and a thin hollow centre. The mature RBC's cell membrane contains polypeptides and glycolipids which help to identify a people's blood type. Actin and spectrin, are two proteins that make up the membrane's surface and are responsible for giving tensile and structural stability and are present in all living things. RBCs can thus bend, fold, and stretch as they move through smaller blood vessels while returning to their normal shape as they move over larger vessels.
Leukocytes
White blood cells or WBCs are also recognised as leukocytes. They are classified as granulocytes or agranulocytes. Granulocytes are made up of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes, in contrast, do not have granules. They are composed of lymphocytes and monocytes.
Platelets
Platelets are tiny fragments of bone marrow cells and perform the following functions:
- They secrete vasoconstrictors which constrict blood vessels, causing vascular spasms in broken blood vessels.
- Aids in blood clotting by secreting procoagulants which are clotting factors.
- Helps in dissolving blood clots when they are not needed.
- Causes complete destruction of bacteria.
- They secrete certain chemicals that attract neutrophils and monocytes at the sites of inflammation.
- Platelets also aid in the secretion of growth factors to maintain the linings of blood vessels.
|


 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










