Bucket SortBucket Sort runs in linear time on average. Like Counting Sort, bucket Sort is fast because it considers something about the input. Bucket Sort considers that the input is generated by a random process that distributes elements uniformly over the intervalμ=[0,1]. To sort n input numbers, Bucket Sort
Bucket Sort considers that the input is an n element array A and that each element A [i] in the array satisfies 0≤A [i] <1. The code depends upon an auxiliary array B [0....n-1] of linked lists (buckets) and considers that there is a mechanism for maintaining such lists. BUCKET-SORT (A) 1. n ← length [A] 2. for i ← 1 to n 3. do insert A [i] into list B [n A[i]] 4. for i ← 0 to n-1 5. do sort list B [i] with insertion sort. 6. Concatenate the lists B [0], B [1] ...B [n-1] together in order. Example: Illustrate the operation of BUCKET-SORT on the array. Solution: 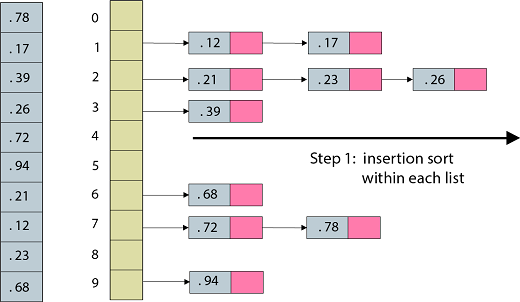
Fig: Bucket sort: step 1, placing keys in bins in sorted order 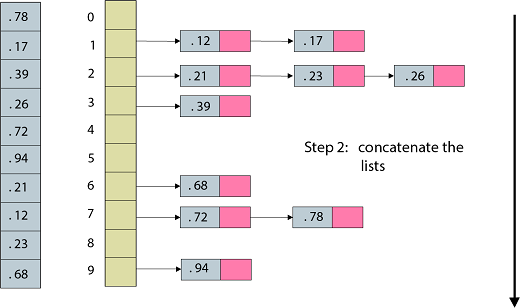
Fig: Bucket sort: step 2, concatenate the lists 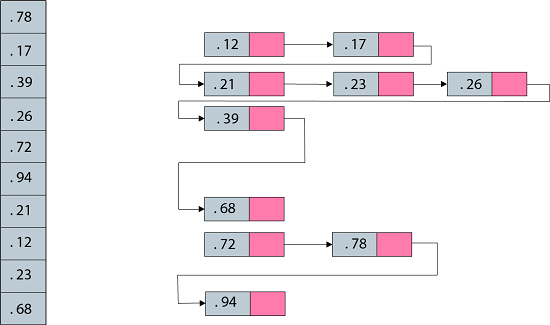
Fig: Bucket sort: the final sorted sequence
Next TopicRadix Sort
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










