5G Technology: Which Country is the First to Adapt?The 5G wireless communication standard has been developed in many countries, offering significant improvements over its predecessors. Telecom, healthcare, transportation, industrial and entertainment sectors are just some of the sectors that 5G has the potential to attract due to its unmatched speed, incredibly low latency, and vast device connectivity possibilities. Being the first country to implement 5G technology has huge implications for technological leadership, economic advantage, and global competitiveness. In this article, we discuss the 5G technology and know about the country which adopted it first and its importance. 
Introduction5G, a new global wireless standard following 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks, is the fifth generation of wireless cellular technology, which enables increased upload and download speeds, more consistent connections, and improved capacity than previous networks. Introducing 5G technology brings a new era of connection and creates possibilities for game-changing applications. It provides lightning-fast download and upload rates, enabling smooth HD multimedia streaming, quicker data transfers, and real-time interactions. The ultra-low latency of 5G enables near-instantaneous communication, which is a game-changer for applications such as driverless vehicles, remote surgery, and augmented reality experiences. The vast device connectivity capabilities of 5G also open up new opportunities for the Internet of Things (IoT). The technology enables intelligent cities, smart homes, and a wide range of interconnected systems and devices, all of which contribute to increased efficiency, automation, and improved quality of life. With 5G, it is possible to connect a vast number of devices at once. Significance of being the First Country to adopt 5G TechnologyBeing the first nation to use 5G technology has various benefits. With 5G, early access to cutting-edge infrastructure is made possible, allowing local firms to build cutting-edge goods and services that employ 5G technology. Being an early adopter also promotes technological developments, draws in foreign investment, and establishes the nation as a market leader. Being a leader in 5G adoption can also have huge economic ramifications. It can promote economic growth, increase industry competitiveness, and generate job creation. Due to its technological superiority in 5G, the nation has the potential to become a center for innovation and digital transformation by luring top talent and attracting Research and Development (RD) activity. The first nations to use 5G technology include South Korea, the US, China, and other significant competitors in this technological race, which are covered in this section in detail. Top Countries with Largest 5G Networks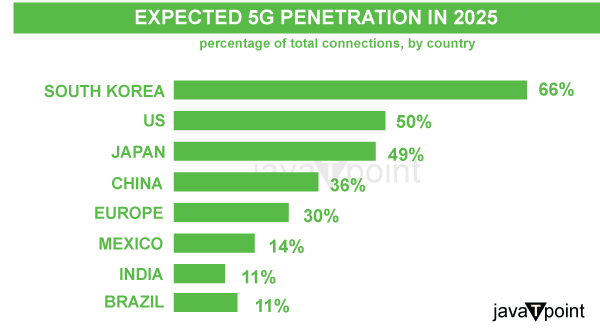
South KoreaIn the adoption and implementation of 5G technology, South Korea has emerged as a global leader. South Korea has grabbed the lead in advancing 5G because of a proactive attitude and large infrastructure expenditures. Leading telecom companies such as SK Telecom, KT Corporation, and LG Uplus have invested heavily in research and development as South Korea has rapidly moved towards 5G. In order to hasten the development and standardization of 5G technology, these corporations worked with equipment makers and governmental organizations. By 2026, according to government officials, 90% of Korea's mobile subscribers will be connected to a 5G network. As of January 2020, 85 cities across the country have already got 5G availability. A national commercial 5G service launch took place in South Korea for the first time in the world in April 2019. This accomplishment was made possible by quickly installing 5G infrastructure, which includes fiber-optic networks, base stations, and tiny cells. The advantages of 5G's fast speed and low latency were among the first to be felt in major cities like Seoul, Busan, and Incheon. By providing legislative backing and designating frequency bands for 5G networks, the South Korean government significantly contributed to adopting 5G. To advance the creation of 5G-powered applications and services, they also promoted collaborations between telecom firms and various industries. In the Taebaek Mountains, KT Corp (KT) completed testing of a system from NEC Corp., which used extremely high frequencies to transfer data at up to 3.2 Gbps (gigabits per second). Communication between LTE (long-term evolution) base stations is made possible by NEC's iPasolink EX ultra-compact microwave system. This is far simpler than installing fiber for the linkages. A method of encoding used by the microwave system, which transmits data at frequencies between 70 and 80 GHz, allows for transmitting more data while maintaining a stronger signal in the atmosphere than other systems. South Korea's proactive attitude, solid infrastructure, and cooperative efforts have positioned it as a global leader in adopting 5G technology, accelerating breakthroughs, and establishing an example for other nations to follow. The United States of AmericaIn an effort to position itself as a world leader in this revolutionary wireless communication standard, the United States has been actively seeking the adoption of 5G technology. The U.S. has made tremendous progress in establishing and utilizing 5G networks thanks to its sizable market, advanced technology, and creative ecosystem. Leading American telecom firms, including Verizon, ATT, and T-Mobile, have made significant investments in 5G infrastructure, including installing small cells, modernizing existing towers, and expanding coverage in metropolitan areas. These investments have enabled the rollout of 5G networks early in some cities nationwide, providing faster speeds and better connectivity. The American government has also helped to promote the adoption of 5G. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has taken actions to simplify rules, distribute spectrum assets, and encourage competition among service providers. Additionally, programs like the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund are aimed at providing underserved rural communities with high-speed internet connectivity, including 5G. The U.S. has acknowledged the strategic significance of 5G for national security, technical advancement, and economic prosperity. To advance 5G development and applications, the government has promoted collaboration between industry players, research institutes, and academia. To investigate the potential of 5G across a range of industries, including healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and smart cities, continuous efforts are being made to set up testbeds, innovation centers, and partnerships. Sprint Corp., T-Mobile US Inc. (TMUS), Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ), and ATT Inc. (T) are among the U.S. carriers actively developing, testing, and implementing 5G components. As of January 2020, 5G has been properly introduced and incorporated in approximately 50 US cities. Atlanta, Chicago, Dallas-Fort Worth, Houston, Kansas City, Phoenix, Los Angeles, New York City, and Washington, D.C. all have mobile 5G service from Sprint. ATT has made its mobile 5G+ network available to customers in approximately 35 cities and parts of 190 markets. JapanJapan, which is famous for its technological innovation, has always been working hard to implement 5G technology. Japan wanted to use 5G to promote economic growth, improve connectivity, and investigate new applications. Soon, it rolled out 5G in its popular cities and made its way into 5G-using countries. It is always working on research and development projects, collaborating with businesses, and receiving government funding. NTT Docomo, KDDI, and SoftBank are just a few Japanese telecom firms leading the way in the 5G implementation. For broad coverage and quick connectivity, they have invested in creating strong 5G infrastructure, which includes base stations and tiny cells. These businesses have also collaborated with suppliers of technology and content to create cutting-edge services and programs that use 5G technology's potential. Through legislative efforts and regulatory frameworks, the Japanese government has been aggressively promoting the development of 5G. To speed up the rollout of 5G, they have allotted spectrum resources for those networks, shortened the approval procedure, and offered financial incentives. To promote innovation and examine the potential of 5G in various industries, the government has also fostered collaborations between business players, research institutions, and local governments. Japan places a lot of emphasis on using 5G for relevant applications to the sector. Manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and agriculture are among the sectors examining how 5G can boost productivity, automation, and efficiency. Examples include telemedicine, precision agriculture, intelligent transportation systems, and remote monitoring and repair of industrial equipment. By 2020, Japan's plan to introduce 5G mobile service was realized. NTT DOCOMO, the largest wireless provider in Japan, initially started testing for 5G in 2010. However, the business could launch pre-commercial 5G services in September 2019. After a successful test phase, NTT DOCOMO launched its consumer 5G services on March 25, 2020. ChinaChina has made remarkable progress in the adoption and application of 5G technology and has established itself as a major player in the global 5G race. China has become a leader in the implementation and use of 5G because of its lofty objectives and significant investments. Chinese telecom firms, including Huawei, ZTE, and China Mobile, have led the way in the development of 5G. To further 5G innovation, these businesses have made significant investments in infrastructure deployment, research and development, and partnerships with foreign partners. China's sizable market and strong manufacturing capabilities have enabled it to roll out infrastructure quickly, including building 5G base stations and conducting nationwide network testing. Currently, China has the second-highest number of cities with 5G service, behind South Korea. China had installed 5G technology in over 57 cities as of January 2020. China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom debuted their 5G networks in October 2019. Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen now have the best coverage, although it could be better in some places. The Chinese government has been instrumental in promoting the uptake of 5G. Through legislative measures, spectrum allotment, and regulatory frameworks, the Chinese government has strongly supported the development of 5G. They have created supportive regulations to promote adoption in many businesses and established ambitious goals for 5G coverage. Impressive 5G network rollout in China has allowed coverage to reach even rural areas and big cities. With this technology's widespread acceptance, China can now investigate many significant applications of 5G, such as smart cities, driverless vehicles, industrial automation, and remote healthcare. The leading telecom firms in China have carried out an incredible amount of testing and infrastructure development for the 5G network, appearing intent to avoid repeating earlier 4G blunders. By 2025, China is expected to have 460 million 5G connections, according to the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSMA). Countries Making Efforts towards 5GDue to the key significant benefits, even smaller countries such as Sweden, Turkey, and Estonia have taken crucial steps to make 5G networks commercially available for their citizens. Sweden and EstoniaSweden and Estonia have made notable progress in adopting 5G technology, demonstrating their commitment to being at the forefront of digital innovation. Major telecom firms like Ericsson and Telia have their headquarters in Sweden and have made significant investments in 5G infrastructure. In order to provide extensive coverage and high-speed connectivity, the nation carried out successful testing and commercial deployments in a number of localities. The Swedish government has encouraged business collaboration and allocated spectrum allocations to encourage the adoption of 5G. Sweden believed that 5G will drive advancements in healthcare, transportation, and economic growth. The digitally savvy nation of Estonia has embraced 5G technology. The nation has initiated to build an environment that encourages innovation and experimentation. Early 5G deployments and testing of novel use cases have been made possible by Estonia's robust digital infrastructure and tech-savvy population. The Estonian government has fostered collaboration between telecommunications corporations, academic institutions, and startups to promote 5G adoption and investigate applications in smart cities, e-governance, and e-health. On December 20, 2018, Stockholm, Sweden, and Tallinn, Estonia, went online with their 5G test networks, according to Swedish-Finnish operator Telia Company AB and Swedish supplier Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson. Although access to all is likely to take some time, it is believed that both Estonia and Sweden will have 5G networks commercially available to everyone in the coming years. TurkeyThe 5GTR Forum in Turkey, comprised of mobile network providers, Turkish government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and domestic manufacturers, is accelerating the adoption of 5G technology. While working together, the organizations share knowledge and concepts to assist Turkey in implementing the technology and updating the public on its progress. When used, 5G technology will connect people, vehicles, objects, and cities at faster speeds and with fewer lags while still utilizing the same infrastructure. Turkey always wanted to increase local manufacturing through research and development (RD) and offer its citizens access to technology at reasonable prices. To utilize the technology, Turkish firms actively participated in RD research and assist with infrastructure development. The Ministry of Science, Industry, and Technology also looked at possible home uses for mobile communication items, hardware, and software. Turkish operators have not yet launched 5G services in the country. However, the nation has been using 4.5G since 2016. Although there have been several trials and successful implementations of 5G for several projects in partnership with mobile phone operators, it is still unclear when 5G will be made publicly available. When 5G access will be offered commercially is unknown as Turkey is still developing the necessary infrastructure and testing the technology to make it completely faultless. Nevertheless, 5G is expected in Turkey soon, with the first expected to debut in Istanbul. The Bottom LineCountries worldwide enthusiastically embrace the possibilities of 5G technology, making it an international phenomenon. Nations are investing in infrastructure, promoting innovation, and benefiting from improved connections, from forerunners like South Korea to technology powerhouses like the United States and China. Many businesses, including healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing, will benefit significantly from the rollout of 5G networks. Countries promote economic growth, technological development, and societal changes as they compete to become 5G leaders. The competition to adopt and use 5G technology heralds a new era of connection, paving the way for a more advanced, connected, and digital future. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










