Two-Sided Market DefinedA two-sided market is formed when the buyer and seller interact to interchange various goods or services, assembling combined bids and offers to buy and sell. It is possible when two different user groups or trade agents communicate with each other through a mediating platform for the profit of both involved parties. Hence, it is also known as a "two-sided market", "two-sided network", or "two-way market". There are many companies and industries which display real-life examples of two-sided markets. One such example is seen in the market-makers relationship, where the firms (or specialists) typically provide the bid and ask prices for the transactions made in the market while being intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring security. In contrast, the one-sided market just has either bids or offers. 
"A two-sided market refers to a meeting place for two sets of agents who interact through an intermediary or platform." This is what The Financial Times Lexicon defined as the Two-sided market. In this fast-growing world, the world's economy is disturbed by the sharing economy. The whole responsibility goes to the two-sided market areas. Let us understand the two-sided markets deeply. In easy words, we can say that the two-sided market hosts both buyers and sellers. That is to say that the participants perform both buying and selling actions against those corresponding platforms or market-makers. Market makers are sometimes appointed to deliver prices in both directions (seller and buyer) of the market at the same time. A two-sided market is able to form values by simplifying and accelerating the payment procedures and reducing the cost for the connecting parties. As the growth of the two-sided network happens, the scale also happens in successive stages. The user who is observing market areas with enormous potential will give a higher amount to get to the platform. The two-sided marketplaces give out an advantage over traditional one-sided markets. These markets have reduced returns on the growth of the market at some point in time. Let us know in detail about a two-sided market: About a Two-sided MarketA two-sided market is a place of connection through an intermediary or platform of two different agents willing to communicate or collaborate. Hence, it is a model of business where direct contact between supplier and consumer is facilitated, and profit is earned by doing so through an intermediary platform. 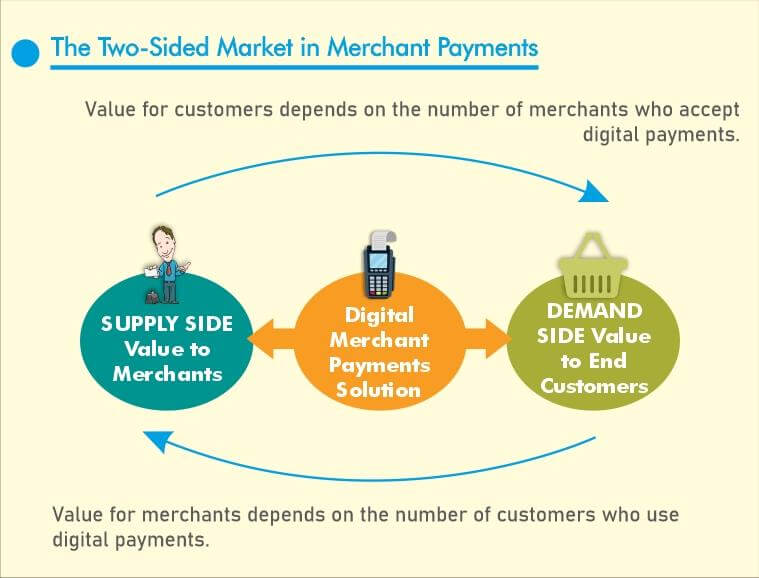
Some Examples of the Two-sided MarketThe following are the essential examples of the two-sided market:
When considering the example of a two-way market, Google's main ad-network service comes into play. If Google had only a few users, advertisers would not be involved in paying to use the service. However, Google has a broad user base. Likewise, if Google lacked advertisers, then it would not have been possible for it to give such free search results to millions of users worldwide. It is because Google earns a significant amount through advertisers. It was in December 2007, after eight years of Google's inception, it owned around 58.4% share of 9.6 billion US searches. Another example of a two-sided marketplace is Waze, which uses value propositions to get into its network effect. This company sells the space for the advertisement to the businesses locally, which wish to target an audience of any specific geographic region. In order to get the views for these ads, the company users gain access to live traffic information and about turn-by-turn navigation. History of Two-sided MarketFor a few centuries, this business model has been in existence. The Penny Press (est. - the 1830s, in America) is one of the oldest examples of the two-sided market. A reader would typically pay money to buy and read the newspaper, whereas an advertiser would pay money to get his products and services featured in the newspaper. Hence, the newspaper's production cost was reduced and made affordable for all. Why is a two-sided market famous?The two-sided market is well-known just because of its simplicity. A two-sided market is a very convenient way to bring the consumer and service provider in contact. Let us have a look at an example of UBER. While using UBER, the consumer demands safe and affordable transport. The driver providing you with the services is, however, the service provider but he is not directly connected with the customer; it is done through the UBER platform. The network effects on the Uber platform are there to let the customer choose between numerous drivers and let the service providers select the customer he wants to provide service. Here, Uber is just an intermediary and earns from both parties. However, it aims to provide the desired services to the parties while maintaining the security of the transaction and optimizing the service qualities. Understanding Two-sided Network EffectAs James Currier has rightly said, "A network effect is when another user makes the service more valuable for every other user. Once your company gets ahead, users won't find as much value in your competitors' smaller networks." The two-way network brings with it the characteristic of customer dependability, an irreplaceable establishment in the sharing economy. 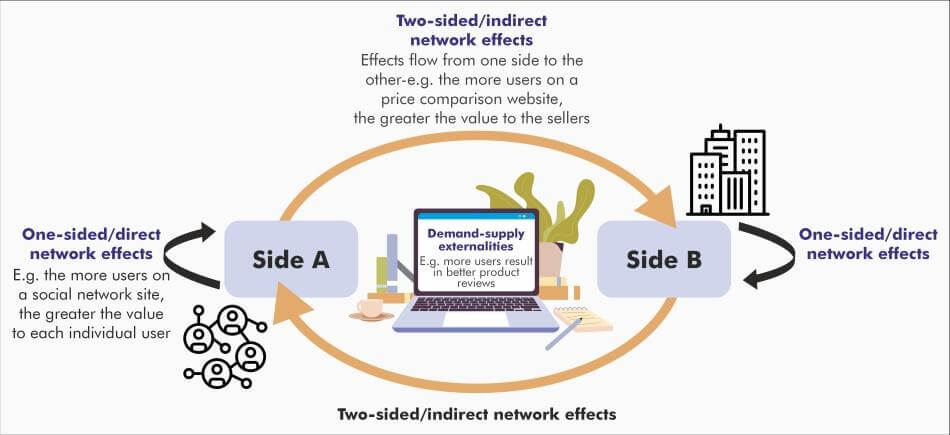
James Currier, an expert on Silicon Valley's most famous entrepreneurs, also says that the effect of the network might be positive or negative, and the impact of a positive same-sided network will be more focused towards user-to-user contact on social media. This might lead to building better relationships and greater sales. What is the difference between traditional value chains and two-sided marketplaces?In a value chain, the value passes on from left to right or from cost to revenue. This is a typical traditional value chain. However, in the two-sided market, the payment and fee move toward the left as well as the right as the users are on both sides. One of the sides is typically subsidized. Structural characteristics of Two-sided MarketThere usually are just two distinct user groups in a two-sided network. The members of either group have the option to show their choices regarding the number of services on the platform. Since this is the cross-side network effect, any specific group can also choose the number of users for the interaction and serving. The results of cross-sided networks are generally positive. However, depending on the reaction of the customer to the advertisement, it can be harmful too. In the case of the same-sided network, the effects may be positive as well as destructive. The network effects represent the relationship between the buyer and seller and the intermediary platform. For example, in a market such as eBay or Taobao, there are two groups: buyer and seller. The buyer is in want of a large number of sellers, and the seller also needs a large number of buyers, such that each person in each of the groups of buyers and sellers gets a trading partner for themselves. Hence, the effect of a cross-sided network is positive. However, a large number of sellers lead to the huge competition among themselves. Some sellers may not compete well in the market. Therefore, same-sided networks can sometimes have negative effects. But the effects of a Cross-side network or the effects of the same-sided network are not sufficient for a multi-sided platform. After looking at and examining traditional supermarkets, it is clear that the customers give preference to a higher number of suppliers and an increase in customers. A conventional supermarket is not eligible as a multi-sided platform as it does not permit direct communication between shoppers and suppliers. On the other side, the network effects are optional for any firm to be eligible as a multi-sided platform. An example can be a condition where the event organizers of a niche use a ticketing service, which is looked after by a small online ticket provider on their websites. The consumers get connected to the ticket provider online at the time when they reach the website to get the ticket. But then, multi-sided platforms are common in the cross-sided network effects and the same-sided network effects. Security Trading and the Two-Sided MarketsIn the economic world, the FINRA, i.e. Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, majorly uses the content of a "two-sided market" for the necessity that the firm bid and firm ask receives from the market makers for every security where they form a market. The same term of FINRA also works same for the bond market. Some of the broker-dealers, on a larger scale and active trade bonds, form dynamic trade bonds and improved liquidity and increase the efficiency of the market. This relationship of the two-sided market is shown with the external groups or agents on the intermediary platform. It is in particular pricing that this relationship is being observed. The one who oversees the intermediates should keep track of the equilibrium of both the direction of the network, sometimes while subsidizing the price-sensitive side and greater changes. The overseas platforms should also maintain stability in the two-sided network order. Hence, subsidizing is done to a side which is more price-demanding. Also, there is a waterbed effect which will hang the price of goods or services on the other side. What is multihoming in the two-sided market?When there is more than one intermediary platform competing in the two-sided market, users being connected to more than one such intermediary platform is called multihoming. For instance, when the customer takes a credit card from more than one network of banking or from two different systems, this leads to an increase in the cost of homing, which includes all the network expenses spent by the users to set up and manage the connection with the platform. However, there is a difference in the ongoing costs of affilIation of outlets and the changing prices, which is suggested as a single-time cost for stopping one network connection and getting into another. The importance of the industry and antitrust laws comes from the fact that if the multihoming costs are higher, then the higher is the tendency to the concentration in the market. However, the higher the cost of multihoming, there is reducing the willingness of the user to manage the relationship with competing networks providing the same services. 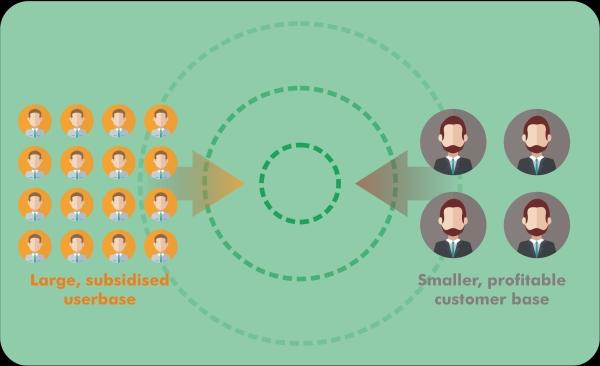
Competition in the Two-sided MarketDue to the network's effect, successful platforms benefit from increasing the number of returns to the scale. The users will be ready to pay more for access to a more extensive network, so margins will enhance as the number of users increases. This puts the platform asides from the other production and service businesses. However, in traditional companies, the development, to some extent, results in negative results. Hence, getting newer customers is difficult as significantly lesser people need to get the appealing proposition of the firm value. Charged with the will to increase returns, the competition in the two-sided market network can sometimes be very aggressive. The head of the intermediary platforms can strengthen their higher margins to spend more on research and development or decrease the products'' cost by moving aside the rivals who are weaker. Thus, the two-sided network industries are generally dominated by a handful of the major platforms, similar to the credit card industries. In extreme conditions, such as in the PC operating systems, almost all of the market is taken over by a single company, which emerges as a winner. Why are two-sided markets digitally important for strategy?The two-sided markets provide assistance to the customers to tap the crowd's network. With their higher delivery speed, they have a supplier-to-customer ratio of more than one. The customer has the right to decide the correct balance in the delivery rate, quality of service, and cost. The service provider who can provide the most economical, speediest and best service is the winner. It can be challenging to run and develop a two-sided marketplace. A balance must be maintained between managing and assuming supply and demand, creating customer experiences, technologies facilitating faster and more effective service, and responsiveness to the peaks and troughs of seasons. These all are very necessary to run and develop a two-sided marketplace. It is difficult, but possible, to disturb the two-sided market economy, as it is digitalization that brings efficiency and profits to it. Thus, digital technology continuously assists the economy's growth, along with employment opportunities and innovation drive. All these factors, to some extent, make it necessary for any nation to have a two-party market, treating buyers as well as sellers equally. Essential Key Takeaways
Next Topic4 Ways To Trade Options
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










