Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)Overview of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)Establishing and interpreting financial accounting and reporting standards is one of the primary responsibilities of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), a private, autonomous entity with headquarters in the United States. It is the main source of forming generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) that are used in the creation of financial records of public, private, and municipal organizations across the nation. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has named the FASB, a private sector organization, as the designated accounting standard-setting authority for U.S. public businesses. 
The goals of FASB are to develop and enhance financial accounting and reporting guidelines, offer advice to both the public and private sectors, and encourage the uniform and consistent implementation of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). In order to give investors, creditors, and other consumers of financial reports valuable information, the FASB works to ensure that financial reporting is founded on sound principles. The Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF) is responsible for appointing the seven core members of the board of the FASB, who typically come from a variety of origins and experiences. The FASB and the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) both operate under the supervision of the FAF, which is an autonomous, private-sector, non-profit entity. Research, conversation, debate, and considerable feedback from the public are all part of the rigorous process by which the FASB develops financial accounting rules. Additionally, it examines and analyzes current financial accounting standards and publishes technical memos, interpretations, and statements that offer additional advice on GAAP. Through its Codification of Accounting Standards, the FASB often provides advice on accounting-related matters. In the U.S., public corporations, numerous private businesses, as well as a number of federal and non-profit groups usually adopt FASB standards. More than 120 nations use the FASB's standards as the foundation for their accounting systems, which makes it one of the main organizations in the world that sets accounting standards. History of the Financial Accounting Standards BoardThe Accounting Principles Board, which fulfilled the same function as the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) from 1959 to 1973, was replaced by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), established in 1973. It is essential to note that the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF), the Governmental Accounting Standards Advisory Council (GASAC), the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) and the Financial Accounting Standards Advisory Council (FASAC) are all separate organizations. Together, they improve financial reporting in the U.S. while empowering and instructing stakeholders on how to read and comprehend accounting standards. This is crucial for the market as well as helpful for potential buyers. Functions of the Financial Accounting Standards BoardThe FASB carries out a wide variety of tasks, from formulating new rules to informing the public. The following are some of the primary functions of the FASB: Establishes Reporting StandardsThe primary responsibility of the FASB is to make sure that all middlemen who handle financial information, such as CPAs (certified public accountants), produce thorough reports that are distributed to stakeholders. A market and businesses can operate more effectively when a collection of standards is followed consistently. Improves Accounting StandardsThe FASB's website prominently promotes major goals through notifications, which is done to constantly update and make it possible for CPAs to use better accounting principles. The FASB is researching how technology affects bookkeeping in the twenty-first century so it can take advantage of some of the tools and instruments to improve accounting standards. Ensures that Information is Transparent and Useful for InvestorsInvestors must be given details about a company's earnings and liabilities in the capital markets. Companies are now bound to disclose the information necessary for the clients, even if it isn't always the most pertinent information, thanks to a recent FASB shift. However, the companies may limit the information, following the rules and guidelines. The regulation primarily affects biotech and pharmaceutical firms that carry out testing and trial stages, which may not be as important to investors besides the effects of the final product. Creates New Accounting PrinciplesThe FASB is in charge of formulating new rules that strengthen the system. The disclosure principle, which gives a business the right to publicize its specifics and structure of expenses accrued in the year, is an example of a recently formed accounting principle. Enables the General Public to be Educated on Accounting StandardsProfessionals go through years of education to truly grasp the bookkeeping standards and principles that are already in place. To uphold its goal and purpose while also promoting transparency, FASB makes sure to regularly teach accountants of its standards and respective pros. The FASB's Principles-Based Approach to Accounting StandardsIn recent years, the FASB has adopted an accounting standards strategy that is founded on several distinct principles. This strategy is predicated on the notion that accounting standards ought to be founded on overarching principles as opposed to detailed regulations. With this strategy, the FASB has created a collection of general guidelines that businesses must adhere to when presenting their financial results. Objectivity, accurate depiction, materiality, comparability, and consistency are some of these guiding concepts. Financial accounting standards must be founded on credible data rather than the preparer's subjective judgment in order to be objective. The financial statements must correctly depict the underlying transactions and occurrences in order to be a faithful depiction. Financial accounts or records must only include information that is material enough to influence the user's choice of action. Financial statements must be displayed consistently across all businesses in order for the comparison to be made possible. Last but not least, consistency calls for reporting comparable activities and occurrences in the same way. Therefore, reports must be created by adhering to similar structures and guidelines. It is the goal of the principles-based strategy to accounting standards to give businesses more freedom in how they present their financial outcomes. This strategy aims to simplify accounting principles and make financial records simpler to read and comprehend. Additionally, it pushes businesses to depend less on prescriptive guidelines and more on their own judgment when preparing their financial statements. FASB's Conceptual FrameworkIn order to handle and resolve newly emerging problems, the FASB Conceptual Framework was developed in 1973 as a clear collection of standards and guidelines. The rationale used by the board in making choices regarding standards-setting was the conceptual structure that supported financial accounting. The conceptual framework serves two purposes: defining financial statement components and stating the goals of financial reporting. The conceptual framework provides a basis for financial accounting and uniform standards that emphasize the purpose, limitations, and character of financial reporting. The FASB's Process of Standards-SettingAs already said above, accounting standards are created, modified, and published under the supervision of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). For this, FASB often utilizes its standards-setting process. The FASB's standards-setting procedure is an intricate and multi-step process. The following are the important steps of this process: 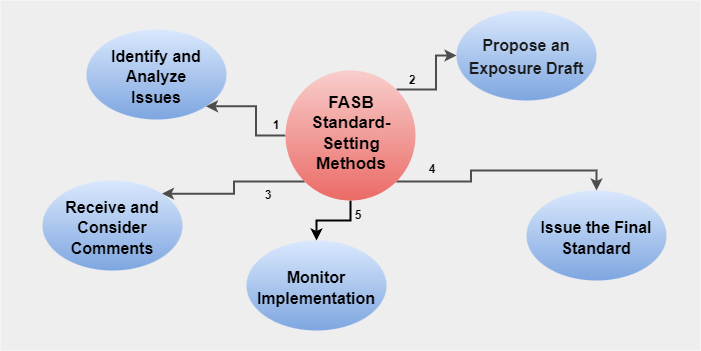
The standard-setting method used by the FASB is intended to guarantee that all accounting standards that are published are of the greatest caliber, accurately represent the state of the economy and accounting principles, and serve the interests of creditors, investors, and other users of financial information. The FASB's Role in Enhancing Financial ReportingThe FASB is dedicated to improving financial reporting's caliber, value, and openness. The FASB sets guidelines that are based on the best available proof in an effort to guarantee the relevance and accuracy of financial information. The FASB also conducts outreach to parties and conducts a study to track the application/ uses of its standards. The FASB has made a number of improvements to financial reporting over time. The FASB published an Accounting Standards Update (ASU) in 2017 that mandates businesses to disclose more specific information regarding their contract responsibilities. The FASB published an ASU in 2018 requiring businesses to disclose more details regarding their stock assets. Furthermore, the FASB released an ASU in 2018 that mandates businesses to offer improved information regarding their financial tools. The FASB employs cutting-edge technology to enhance the caliber of financial data. Blockchain technology may be used by the FASB to increase the precision and dependability of financial data. The FASB is also trying to create a standard global financial reporting vernacular that will make it simpler for stakeholders to compare financial data internationally. The U.S. financial system depends on the FASB's attempts to improve financial reporting. The FASB contributes to ensuring that investors and other stakeholders have access to accurate and open financial information by establishing Accounting Standards, delivering more thorough disclosures, and bringing new technologies. The FASB's Relationship with Other Accounting OrganizationsTo establish, sustain, and enhance accounting standards, the FASB collaborates closely with other accounting groups. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) is one of the FASB's many connections to other accounting groups. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) is in charge of establishing the industry's expert standards. The combined Accounting Standards Executive Committee (AcSEC) of the FASB and AICPA is in charge of creating and upholding accounting standards for nonpublic organizations. Representatives from the FASB and the AICPA equally head the AcSEC, which was established in 1973. Additionally, the FASB belongs to the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The IASB is the body in charge of establishing international accounting standards, and it collaborates closely with the FASB to guarantee uniformity in those standards across various nations. Additionally, to make sure that municipal organizations adhere to the proper accounting standards, the FASB collaborates with the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB). The GASB is in charge of establishing accounting guidelines for municipal and state administrations in the U.S. The American Accounting Association (AAA) and Financial Executives International (FEI) are two additional groups that collaborate with the FASB. Setting standards for accounting instruction and study is the responsibility of the AAA, an academic group. The FASB and the FEI collaborate closely to make sure that the accounting standards are current and applicable to the business climate. The FEI is a professional association for financial leaders. In general, the FASB collaborates closely with other accounting bodies to make sure that accounting rules are current, uniform, and applicable to the current business climate. Together, the FASB and other organizations make sure that debtors, investors, and other interested parties have access to trustworthy financial data. Recent Changes to the FASBThe Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2020-05, which addresses the reporting of specific debt extinguishment expenses, was just released by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). According to the new standard, businesses must now show debt extinguishment expenses as a straight decrease from the debt liability's carrying amount rather than in the income statement. For fiscal years starting after December 15, 2020, as well as interim times within those fiscal years, the new norms were applied to public and corporate entities. ASU 2020-04, a new FASB standard on reporting reference rate reform (RFR) changes, was also released. According to this new standard, businesses must report the effect of reference rate reform as a distinct line item on their revenue statements. The standard is applicable to public business organizations for interim times falling within fiscal years starting after December 15, 2020. ASU 2020-03, which offers additional advice on the accounting for specific lease kinds and lease changes, was also released by the FASB. This new standard mandates that businesses identify lease changes as distinct lease components and reevaluate whether to classify a lease as an operating lease or a financial lease. For fiscal years starting after December 15, 2020, as well as interim times within those fiscal years, the new norms have been applied to public, corporate entities. The Future of the FASBThe autonomous, private organization in charge of setting accounting rules in the U.S. is known as the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). The goal of the FASB is to create and enhance financial accounting and reporting guidelines that will give investors and other users of financial records valuable information. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is presently reviewing the standards-setting procedure, so the FASB's future is unclear. The SEC is debating whether to install a brand-new, autonomous regulator in lieu of the FASB. The SEC has not yet made any decisions regarding the FASB's future, so it is possible that it will continue to exist in the near future. The FASB is presently trying to increase the effectiveness of the standards-setting process as well as the transparency and relevance of financial reporting. The FASB is also looking into methods to match its standards with global accounting standards more closely. The FASB is likely to keep working to raise the standard of financial reporting and simplify decision-making for investors and other consumers through financial reports in the future. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










