Activity-Based Costing (ABC): Method and Advantages Defined with ExampleActivity- Based Costing is a costing system that focuses on the activities conducted in producing the products. It is the system in which the cost of various production activities is identified, and the final cost is added to the product. The idea behind this costing system is that activities incur costs at every stage for the production of any product, so it is logical to do an accounting of incurred costs based on activities. 
In the traditional absorption costing system, costs are traced to the organizational units, like any department, and then the cost incurred is traced to the final product. While in the ABC system of costing, the cost is first assigned to the activities and then passed on to the product. The important and common fact about both costing systems is that the cost is assigned to the product at the second or final stage. Activity-Based Costing: MeaningActivity-Based costing is allocating costs to the activities involved in the production. It can be defined as a system of costing that recognizes activities involved in producing a product and then traces the cost incurred in performing each activity. As per the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA), the ABC has been defined as: "ABC is the cost attribution to cost units based on benefits received from indirect activities, e.g., ordering, setting up, assuring quality, etc." From the above definition, ABC is the costing system in which cost is attributed to each activity, and then it is summed up to the product. Features of ABC
Objectives of the ABC System of Costing
Difference between the Traditional Absorption Costing Method and the Activity-Based Costing Method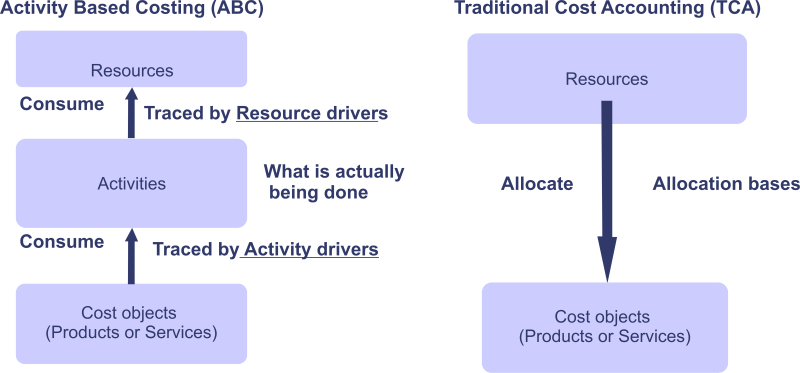
What are the steps involved in setting up the Activity- Based costing?In developing the ABC method of cost, several steps are needed to be followed: 1) Identifying Resources Identifying resources means finding out the possible expenditure of the organization, which is to be assigned to the cost of the product. So, resources mean expenses that are to be incurred at each activity, which will be allocated first to the activity, and then to the product. 2) Identification of Activities The method of ABC costing is based on the activities performed during the production of the product or delivery of the services. Therefore, it is very necessary to point out the activities associated with the production of the product to allocate the incurred expenses. In this step, activities are identified for the allocation of cost. 3) Identification of Cost Drivers The identification of cost components is the cost drivers involved in different activities. Cost drivers or cost objects are the factors that impact the cost of a particular activity. It is very important to find out the things that determine the cost of an activity. 4) Assigning Cost to the Product The final step is assigning the cost to the product after tracing all the incurred costs to the product. What is the importance of the ABC method of cost?
Uses of Activity-Based Costing MethodThe information gained from the ABC method of costing is useful in different areas of decision-making, which are discussed below: 1) Activity Cost The motive of the ABC method of costing is to allocate the overheads involved in the activity. This helps us track whether the cost of the activities is in line with the industry's standards. Therefore, it acts as a tool for measuring the cost of activities and thus helps in decision-making. 2) Customer Profitability The company has to bear various customer costs apart from the cost of product production, like consumer services, return product handling, cooperative marketing, etc. The ABC costing system can help sort this additional cost and help the management identify profitable customers. 3) Distribution Cost Efficient distribution of products to consumers is a major task for any entity. Organizations use distribution channels like retail, e-commerce, wholesalers and distributors, etc. In the distribution of products through any of these channels, an overhead is involved in maintaining the channel. So, with the help of ABC, the company can determine which form of distribution channel and how much it costs, and on that, decisions can be made to determine which type of channel is profitable and which is not. 4) Domestic or Outsource The ABC provides information about the cost incurred on each production activity; with that help, the management can decide which activity is profitable to perform domestically and which is required to be outsourced. Management can outsource any activity if that incurs a higher cost domestically than outsourcing. 5) Determination of Margins For any business, the margin is a very important component as it is the profit earned after selling the product. By properly allocating overheads under the ABC costing method, management can determine the maximum desired margin of the product. It also helps position the company's resources to earn the highest margins. 6) Minimum Price Fixation Product pricing is the price the market can bear, and the manager's motive should be to avoid selling the product below the minimum profitable price. Therefore, the ABC costing method helps the management to determine which activity cost to be included in the minimum cost of the product so that the product can be delivered profitably.
Next TopicAsset-Based Lending
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









