Private vs. Public Company: What's the Difference?A company is an association of people assembled to carry out a business to achieve a common objective. It is a corporate legal body having separate status and personality to accomplish a common goal. An incorporated company exists either under a Special Act of Parliament or under the country's company law. Broadly, companies have been categorised as private or public, like in India, LIC, SBI, IOCL, BPCL, ONGC, etc., are public companies. In contrast, Reliance Industries Ltd., Tata Steel Ltd., etc., are Private companies. The majority of shareholdings of public companies are held with the government or the general public. In contrast, in private companies, most shareholdings are borne by the promoters or the members of the companies, who are usually ordinary individuals, not the government. 
Private CompaniesAs per the Companies Act, a private company is a company that has a prescribed minimum share capital and adheres to the following criteria:
Different private companies, like Sole proprietorships, Partnerships and Corporations, have been differentiated based on the number of members or owners. Private companies are not bound to release their financial reports and balance sheets to the public; it only shares their financial statements internally with its member. Examples of famous private companies in India are Reliance Industries Ltd., Wipro Ltd., ITC Ltd., Infosys Technologies Ltd., ICICI Bank Ltd., etc. Public CompaniesAs per the Companies Act, a public company is a company that is:
As per the Act, a public company is formed for any legal purpose by a minimum number of seven or more people by subscribing their names to the memorandum. 
In a public company, the company's securities can be quoted on Stock Exchange, and the number of maximum members is unlimited. There are no restrictions on the transferability of shares. The public company must disseminate its financial information, like issuing financial reports and balance sheets, to the public because it raises capital from the people, and the general public is its stakeholders. Some examples of public companies are IOCL, BPCL, HPCL, SBI, BSNL, AAI, SAIL, BEL, BHEL, etc. The Difference between Public and Private CompaniesThe key differences between a Public and Private Company have been discussed below based on different attributes: 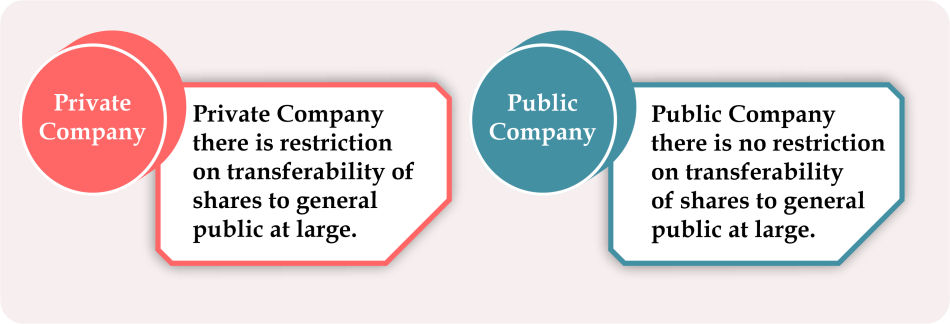
Next TopicQQQ ETF Risks and Rewards
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










