Lot: What It Means in Stock and Bond Trading, Types, and ExamplesWhat is a Lot in the Trading of Securities?Lots in trading and securities refer to the number of financial instruments purchased in one transaction on an exchange. The lot name usually indicates the number of units. A round lot, for instance, in the stock market is 100 shares. Investors are not required to purchase round lots, though. Any amount of shares can be considered a lot. When fewer than 100 shares are purchased, for instance, the phrase "odd lot" is used. Key Lessons
The Operation of a Lot in Securities TradingIn the capital markets, traders and investors buy and sell financial instruments in large quantities. A lot is a predetermined number of units that varies depending on the transacted financial security. Before the introduction of online trading, round lot of 100 shares were the usual lot size for equities. Another definition of a round lot is a group of shares that may be evenly split by 100, such as 300, 1,200, and 15,500. 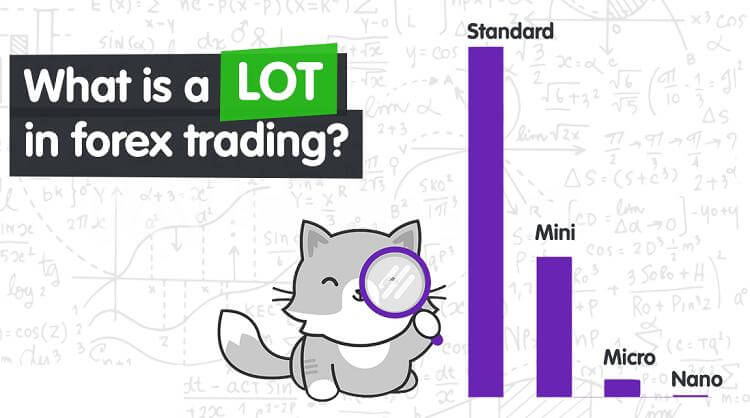
Now, however, orders for shares that are fewer than 100 are known as odd lots, and orders for shares that are greater than 100 but not divisible by 100 are known as mixed lots. The round lot for exchange-traded securities, like an exchange-traded fund (ETF), is 100 shares, the same as for stocks. Types of Lots (Securities Trading)1. BondsInstitutional investors control the bond market by making large-scale purchases of debt from bond issuers. In some areas, a round lot for U.S. corporate and government bonds equals $1 million. However, it is also possible for it to be $100,000, as with municipal bonds. That does not imply that a trader or investor must purchase that many bonds. Typically, bonds have a face value between $1,000 and $10,000. (Some are even lower). Even if a shareholder purchases a large number of bonds, the collection may still be unorthodox. 2. OptionsA lot in the context of options is the total number of contracts that make up a single derivative security. One hundred shares of stock are represented by one equity option contract. In other words, 100 shares constitute the lot for a single options contract. For instance, a trader in options bought a single call option on Bank of America (BAC) last month. The option expires this month with a strike price of $24.50. The option holder can buy 100 shares of BAC at the strike price of $24.50 if they exercise their call option today when the underlying stock, BAC, is trading at $26.15. They have the opportunity to buy a single option contract worth 100 shares at the specified strike price. Investors always know precisely how many units they are purchasing with each contract because of this uniformity, which also makes it simple to calculate the cost per unit. The valuation and trading of options would be unnecessarily difficult and time-consuming without such uniformity. The smallest options trade that may typically be made by an investor is for one contract, which equals 100 shares. Mini-stock options, which have an underlying share amount of 10, allow for the trading of options at a lower price. 3. FuturesLots in the futures market are also referred to as contract sizes. One futures contract's underlying asset may be a stock, a bond, interest rates, a commodity, an index, a currency, etc. As a result, depending on the type of contract traded, different contract sizes apply. One futures contract, for instance, can include 5,000 bushels of corn, soybeans, wheat, or oats. One contract for a Canadian dollar future is worth 100,000 CAD, one for a British pound, 62,500 GBP, one for a Japanese yen, 12,500,000 JPY, and one for a euro, 125,000 EUR. The typical contract sizes for options and futures are set and cannot be changed, unlike those for stocks, bonds, and ETFs, where odd lots can be bought. However, as forwards are non-standardized contracts that are made by the parties involved, derivatives traders buying and selling forward contracts can alter the contract or lot size of these contracts. 
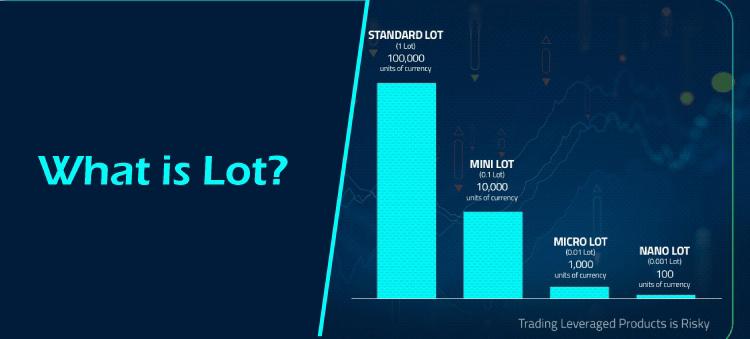
Standardized lots enable more liquidity in the financial markets and are determined by the exchange. Reduced spreads are a result of higher liquidity, which makes the process efficient for all parties involved. 4. Forex lotThere are micro, mini, and normal lots when trading currencies. A regular lot is 100,000, a mini lot is 10,000, and a micro lot is 1,000 of the basic currency. When trading through a foreign exchange broker, the smallest trade size is normally 1,000 unless otherwise stated, even though it is feasible to swap currencies through a bank or currency exchange in amounts smaller than 1,000. Example of LotsTrading in lots is less of an issue in the options and futures markets because you can trade any amount of contracts you like. The contract size of the underlying asset is determined by each futures contract, and each stock option will equal 100 shares. One can deal in forex with a minimum of 1,000 of the base currency in any 1,000-unit increment. They could exchange 1,451,000 wherein fourteen normal lots, five mini lots, and one micro lot make up this order. One can deal in odd lots of fewer than 100 shares while trading stocks. ConclusionLot, as written above, refers to the number of securities that are bought by traders. Even though any number of securities can be bought, a round lot usually points towards 100 shares. Odd and mixed lots have been introduced after the practice of online trading has taken a step into the market and has taken the process of trading to greater heights. There are a number of types of lots that are present in the market and have different meanings in different contexts but every kind is important and comes in handy when we talk about trading.
Next TopicStandard Lot
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









