Financial Institutions: The Different Types and How They WorkFinancial Institutions are entities engaged in providing financial services directly or indirectly, like commercial banks, insurance companies, investment banks, etc. It is the umbrella name under which different forms of entities function. 
What is meant by financial institutions?Financial institutions are those who are solely engaged in dealing with financial matters. They are considered the brain of an economy that guides any economy on the path of development. Every country has plenty of financial institutions that facilitate financial work. The country's central bank also comes under the category of a financial institution. The financial institution helps businesses and individuals in fulfilling their financial necessities. The financial institution offers services like withdrawal and deposit of money, investment advisory, broking services, etc. Financial institution ushers the way for saving, investing, and wise usage of funds. It is composed of multiple activities. These institutions channel the funds of the individuals and utilize the funds to fuel the financial system and the economy. Apart from performing financial transactional activities, financial institutions also offer financial consulting and advisory services. Functioning of Financial InstitutionsThe functioning of different types of financial institutions varies in their operation, but the overall objective of all such institutions is somehow similar to channelize the savings of individuals, offering interest, granting loans and advances, earning through interest, etc. Handling huge amounts of money comes with great responsibilities, so they also offer risk management operations. They also offer consultation and financial advisory services to cater to individuals in managing their funds in the right place with the highest possible returns. Main Functions of Financial Institutions
Types of Financial InstitutionsThere are multiple types of financial institutions which have been categorized based on their core functions, which are explained below: Central BankCentral banks are financial institutions whose core function includes managing currency-related issues and foreign exchange, formulating the country's monetary policy, and supervising commercial banking operations. Every country has a central bank like the Federal Reserve in the USA, Reserve Bank of India in India, etc. Central Bank is the apex financial institution of any country. Central banks' main functions are managing monetary policy, reserve management, financial stability, deciding interest rates, banks supervision, coins, and notes issuance, granting loans to banks, etc. It only offers loans and advances to the government and banks, not individuals. Commercial BanksCommercial banks are such types of financial institutions that are engaged in accepting time and demand deposits, granting loans to individuals, etc. It is the bank whose customers are common people. It is the main element in the functioning of the financial system in the country; by accepting deposits from those who have more and granting those funds in need in lieu of some interest, thus the financial cycle continues. The primary function of commercial banks' primary functions is accepting deposits through savings, recurring, or current accounts, granting loans and advances, offering overdraft facilities, and implementing credit creation. Some famous commercial banks are the State Bank of India, Canara Bank, DBS Bank, HDFC bank, etc. Investment BanksInvestment Banks are the type of financial institution that offers only investment-related services. The functioning of such banks is different from commercial banks. These banks mainly deliver financial consultation services and assist in structuring investment plans for big MNCs, governments, high-net-worth individuals, etc. Another function of an investment bank is to provide underwriting services for new securities and facilitate the formation of big companies' merger, acquisition, and reorganization plans. Primarily, the main function of an investment is to provide financial advisory and investment services to large corporates, governments, and multinational organizations. The investment banks function as an intermediary between the investors and the company at the time of issuance of shares in the market. The investment banks buy the company's shares at the time of IPO; later on, these investment banks sell those shares in the secondary market to retail investors. This results in maximizing the revenue for the company under due compliance framed by the regulators. Some famous investment banks are JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, etc. Non-Banking Financial Corporations (NBFC)NBFC is a type of financial institution registered as a company under the Companies Act 2018 to offer some of the prominent banking and financial services. It provides loans and advances, acquires government securities, leasing, hire-purchasing, etc. As per RBI, if the financial assets of a company engaged in the business of financial activity are more than 50% of the total asset and the share of income through financial assets is above 50%, that company is eligible to be registered as NBFC. Difference between Banks and NBFC
Credit UnionsCredit Union, a cooperative form of a financial institution, works in a non-profit mode specifically for its members. The services provided by credit unions are almost similar to commercial banks, like accepting demand deposits, providing loan facilities, and other essential financial services. The difference between commercial banks and credit unions is that credit unions offer their financial services only to their members, whereas commercial banks are open to everyone. The other difference is that credit unions do not function with the motive of profit earning, whereas the motive of most commercial banks is earning profit. Some of the most famous credit unions are Alliant Credit Union (ACU), Pentagon Federal Credit Union (PenFed), Navy Federal Credit Union (NFCU), Consumers Credit Union (CCU), etc. Insurance CompaniesAn insurance company is a registered financial entity engaged in creating and distributing insurance products to cover its customers' risks. Insurance companies charge periodical premiums in return for covering the risk. Insurance companies are very important for a healthy financial system; they provide stability to the financial system because these companies are the major investors in the financial market and bridge the gap between banks and insurers. Insurance companies protect the insurers through a contract that guarantees that the insured person will be paid the specified amount on the occurrence of certain contingent events in the future, for which periodic premiums are paid. Insurance is the tool of risk management provided by insurance companies. Brokerage FirmsBrokerage firms are financial institutions that bridge the gap between clients and the exchange. These firms buy and sell financial products on behalf of clients. It provides broking services in exchange for some brokerage fees. The main function of brokerage firms:
Mortgage Companies/ Mortgage BankA mortgage company is a type of financial institution that could be a bank, credit union, trust, or any other financial institution engaged in mortgaging. A mortgage lending company provides underwriting services for home loans. The key aspects of any mortgage loan are fixed by these mortgage companies, like terms & conditions, interest rates, repayment period, etc. These companies offer home loans under various schemes and specialize in them. Features of mortgage companies:
Savings and Loan AssociationSavings and Loan Association is a financial institution that operates from public funds. It comes under the thrift association. In such types of financial institutions, the depositors and the borrowers of loans are the association's members and work similarly with Credit unions. S & L could be anything; it could be a joint stock company or insurance company, but it functions specifically for its members with voting rights to select its board. 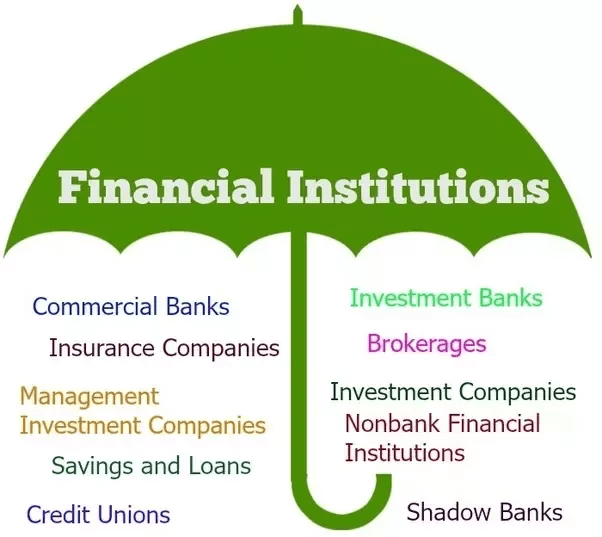
Bottom LineFinancial Institutions are the drivers of growth in any economy. They channel the funds and make the circulation of money operational. The proper circulation of funds requires a smooth functioning mechanism by financial institutions. These institutions help achieve financial inclusion for the most vulnerable section of society. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









