What Is a Recession?No legal definition is written for recession, but it is the phenomenon's name. A recession refers to a situation of a continuous downturn in the economic activity of a nation. This economic downturn is not for a shorter period; the period of decline for recession is a bit longer that results in the loss of employment and jobs, food and energy crisis due to increases in prices, failure of businesses, etc. 
Globally, a recession is a steep fall in a nation's real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for a minimum period of two consecutive quarters in the financial year. This fall in the GDP can be more than two quarters. It is a broader concept, and the impact of the recession of one country is also felt in the other economies. When the downfall of the economic activity and the GDP is seen in multiple countries, that recession is termed a global recession because all the economies in the world are somehow coupled, which means interlinked to each other. So, the recession in any economy suffers the globe as a whole, though the proportion of damage can be different. History of RecessionPost World War II, the world experienced only four major global recessions that lasted hardly for a year. Those four were in 1975, 1982, 1991, and 2009, and all of them lasted for a year; the recession of 2009 is regarded as the most devastating economic shock for the world economy. The 2009 recession has been termed the Great Recession, which affected all the economies around the world. According to reports, many countries have gone through a recession since 1951, and the number of years of suffering is also high. Libya has experienced a recession for 27 years since 1951; Iraq and Argentina were in a recession for 24 years. Causes of RecessionRecession is the result of multiple wrong economic decisions and sudden economic catastrophes. It involves all those activities that contribute to the declining economy's growth rate. Like sudden surge in the prices of oil can lead to an overall increase in the price level of all the utilities in the country, which will subsequently result in a decrease in demand. This change in the price level of energy rates can lead to economic disruption and disturbance in the supply chain. There are some of the common causes of the recession that were directly or indirectly observed in all the recession periods, including:
Recession is not a sudden blow to the economy; however, the continuous slowdown in the initial growth results can predict it. The signs of recession can be observed while the reason for the recession is realized after thoroughly evaluating the economic decisions and their impacts. Types of RecessionCertain types of recession have been categorized based on their causes, patterns, and impacts, like: Boom and Bust RecessionThe boom and Bust form of recession is a type of recession in which the graph of the growth alternatively goes up and down. When an economy experiences a very high growth rate that is above its projected rate, and the chart of growth is high, it is termed a 'boom', which probably leads to an increase the inflation. To tackle the possibility of inflation, that country's central bank takes the step to stabilize the growth rate and cool the economy. They do it by increasing interest rates and taxes to control money flow. Consequently, these steps suddenly regulate the fast-moving upside graph of growth; thus, the chart shows a sudden drop in the growth rate. 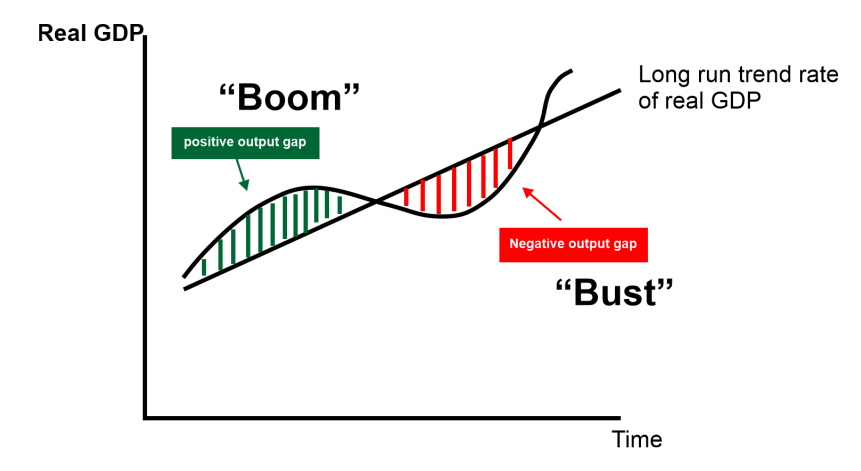
This sudden up-and-down change in the graph of the growth rate of an economy is called a Boom and Bust recession. Balance Sheet RecessionRichard Koo coined the word Balance sheet recession. This recession situation is seen in economies where consumers are primarily in debt. The debt usually changes its spending habits, so people choose to slow down their spending and focus on paying off the debt, to clear their balance sheets. So due to the reduction in the spending activity of the consumers, the scenario of recession comes out. When the government increases its spending or reduces taxes, it instigates the borrowers to pay off their debts, so the priority shifts from spending to paying debts. This leads to the initiation of a period of recession. DepressionWhen the recession extends for a longer period than a year, it takes the form of depression. Depression is an economic downturn that exists for more than a year in one or more countries. Generally, the phenomena of economic depression are marked when the following two rules are fulfilled-
When the economic condition of any country fulfils the above-stated requirements, it can be inferred that the economy is suffering through the phase of economic depression. The likely consequences of depression are an increasing unemployment level that often reaches two-digit numbers, a fall in production and closure of factories, a decrease in demand due to the reduction of purchasing power of the consumers, and a decrease in credit availability due to banking and financial failure. People suffer from personal bankruptcy due to the loss of their businesses and jobs and severe disruption in trade. Supply-Side ShockExtraordinary external contingent events like natural calamities, pandemics, wars, etc., can directly affect the economies around the world due to disturbances and disruptions in the supply chain, which can throw the economy into recession. Like during the 1970s crisis, the price of oil suddenly spiked to its highest level, which drove the spending of nations' income more on oil-based products, as a large share of their income was spent on oil products. This led to a recession due to the high concentration of spending on one sector, leaving the other sectors with significantly less share. 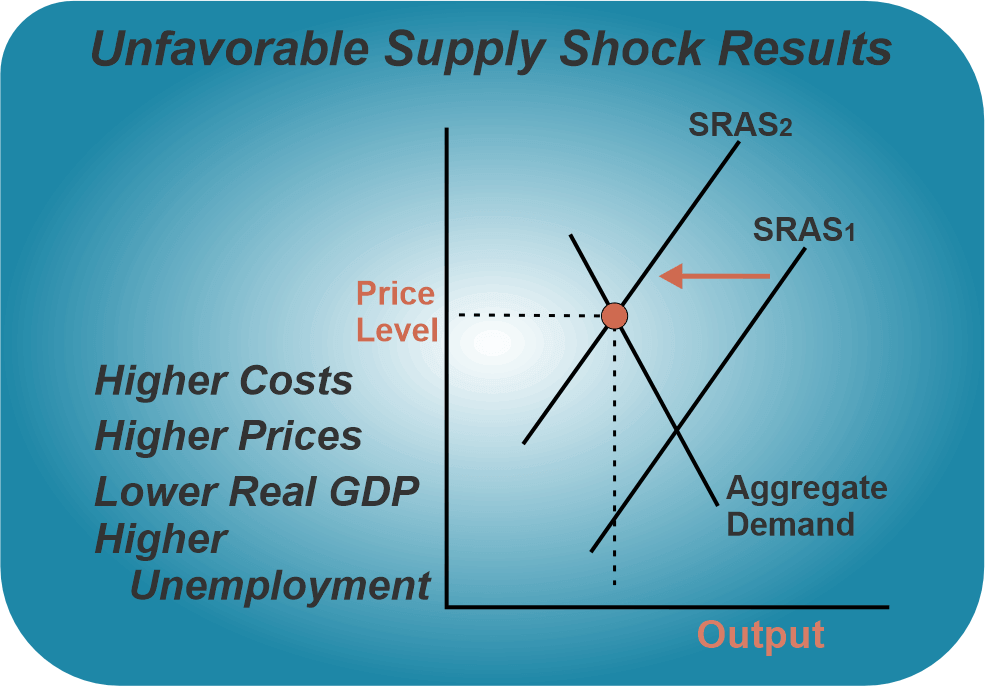
In the last two years, the world suffered the Covid-19 pandemic, due to which lockdowns were imposed, and international transits were restricted, severely impacting the supply chain in the world. The aftershocks of the pandemic on the economies can be seen in their GDP rates; most economies' GDPs declined drastically, and some even went negative. But this is not the end; it is believed that the world will see a recession in the coming months. In all above stated economic downturns, the reason for the recession was the supply side; thus, such a recession is termed a Supply-side shock. The Types of Recoveries in a RecessionIt is a truth that after every sunset, the sun rises again. Similarly, after every period of recession or downturn, every time there is scope for recovery. In all the past recession phases, the economies have recovered, and the pattern of their recovery is also different depending upon the type of economy and their economic recovery measures. Some of the types of recovery patterns have been discussed below: V-Shaped RecoveryA V-shape recovery is a form of graphical representation of the growth rate. When an economy is recovering from a recession, the best form of recovery is a V-shaped recovery. 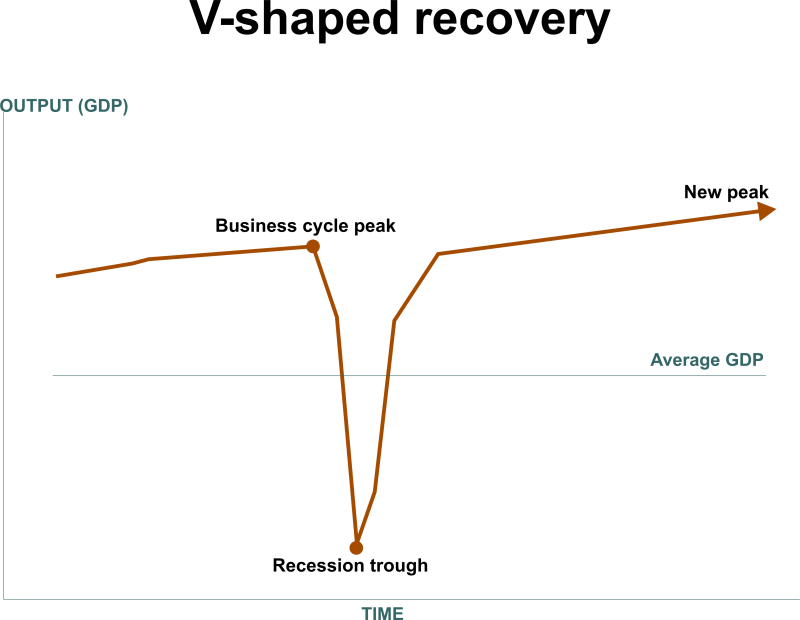
In this recovery type, the graph shows the pattern in the alphabetical letter 'V', where the first point depicts the usual scenario of the economy. The letter's bottom movement, or the depression, shows the recession or the economic downturn. After the downturn, the growth line shows resilience and moves upside. This is the whole graphical journey of the recovery in a V shape. The meaning of V shape recovery is very positive; it shows the fast and sharp recovery from the quick and sharp downturn in the growth rate. It shows that the recession affected the economy, but it successfully fought back and returned to the path of growth. U Shaped RecoveryThe U-shaped recovery is when the economy takes a bit longer than V-shaped to recover from the recession or the downturn period. In this type, the shape U shows the downfall in the economy first, and then the fall stretches and becomes stagnant for some time. It starts moving upward and shows some positive growth movements, making the alphabetical letter 'U' shape. 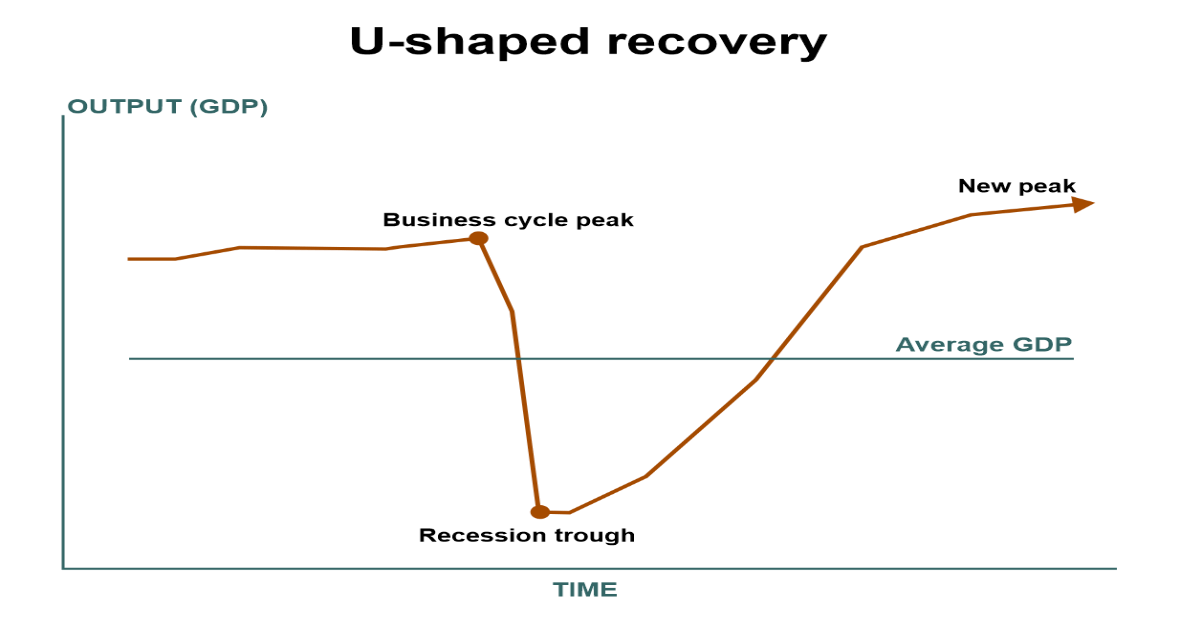
U-shaped recovery signifies that the economy fell drastically, and then the recession remained stagnant. After being the economy under recession for some period, then it again starts to come back on track, and the graph shows the rise. The U-shaped recovery was seen during the global recession of 1973-75 and 1981-82. K Shaped RecoveryA k-shaped recovery is a unique form of healing; it is positive as well as damaging at the same time. In K-shaped recovery, the economy is split into two categories: such as two sectors, two geographical locations, two classes, etc. After the downturn, when the economy starts to recover, sometimes one sector or industry gets back on track smoothly, and the graph moves upward. On the other hand, another industry or part of the economy continues to suffer from the downfall. The part of the declining economy shows downside movement on the graph. This dilemma of the economic structures the graph in such a shape that it looks like the alphabetical letter 'K'. After the recession, this part bounces back and moves with positive growth, whereas the other part downfalls pathetically. 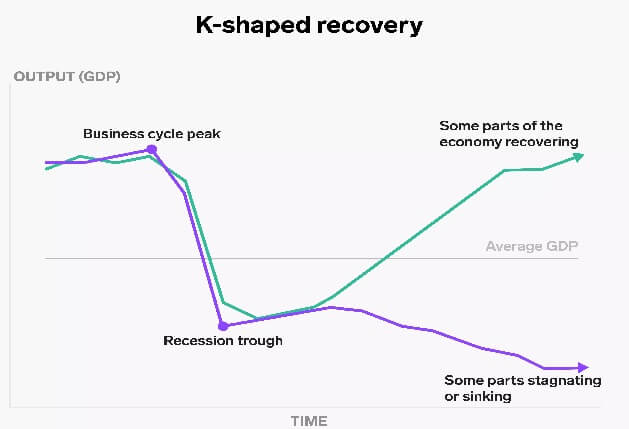
The K-shaped recovery depicts that a divide has been created in the economy, which continues to widen the gap in the economy. K-shaped recovery creates the problem of inequality, which is the worse thing for any economy, where one part is prospering while the situation of the other one is devastating. During the pandemic, this situation was created, where the food and healthcare sector was booming while the tourism and hospitality sector worsened. W Shaped RecoveryW-shaped recovery is the case of recovery in which, after the fall of the economy, it bounces back and starts recovering, then again it comes down into recession, and this ups and down continues for some time. It disturbs the economy's stability, where it has to encounter ongoing recessions. In this, firstly, the economy undergoes recession, and the graph of the growth fall, then it recovers itself and returns on track. Then immediately, for some reason, the economy falls again, and then it recovers and moves the graph upward vigorously. This subsequent up and down in the economic chart of the economy makes the shape of the alphabetical letter 'W'. It shows two recession and two recovery positions. 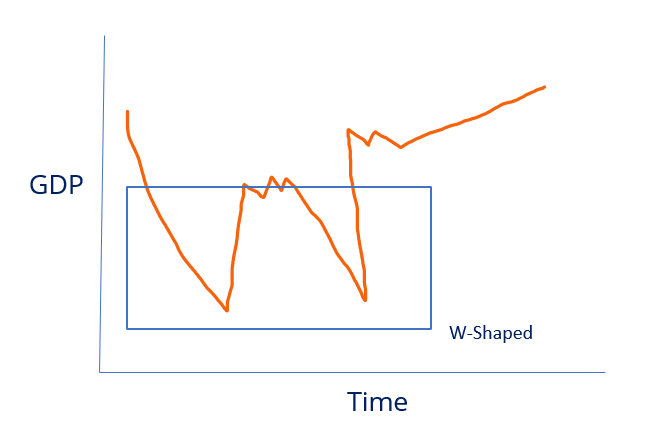
W shapes recovery is disturbing for any economy. Still, it is believed that the second dip in the economy makes it resilient and helps it come back more strongly with more chances of stability. The latter recovery lasts a long time and signals strength in the economy. L Shaped RecoveryL-shaped recovery is the worst among the types of recoveries for an economy. It shows a low growth rate and depicts that the economy will take a lot of time to return to its previous position. The economy moves very slowly after the recession, and the growth becomes stagnant for a long time. The graph moves upward very slowly and in an upward-inclined manner. This movement of the recovery makes the shape of the alphabetical letter 'L' on the chart of the economy. 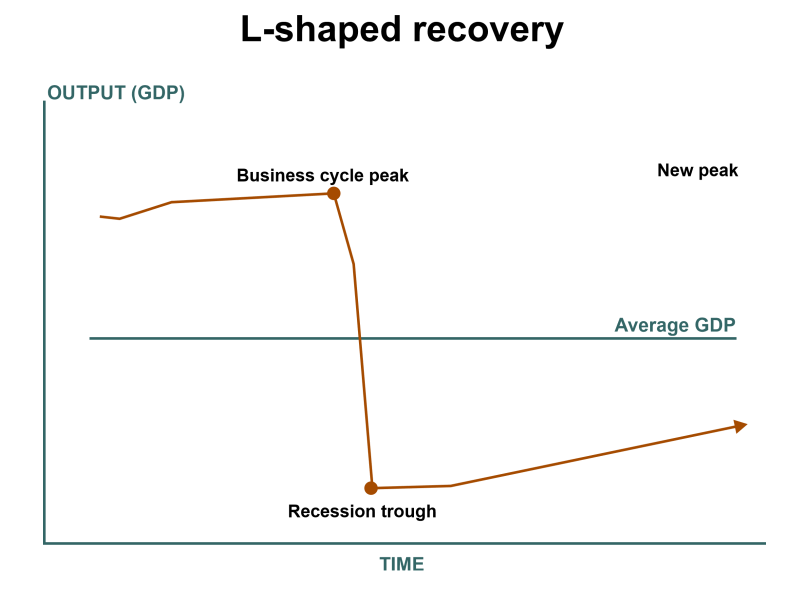
The L-shaped recovery is a worrying situation for any economy. During this time, the unemployment level and the recession continue to exist high, along with the slow pace of resilience of the economy. It takes many years to attain a positive growth rate. Therefore, it is a situation of destruction for an economy. Normal Square Root RecoveryAverage square root recovery is the form of recovery in which the graph of the recovery takes the shape of square root, where the chart of the economy falls due to the recession. Still, it makes a comeback very strongly and grows faster than last time. 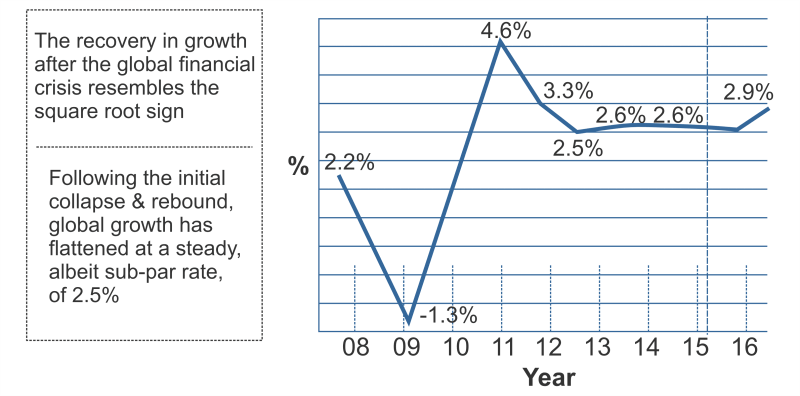
In this, firstly, the economic graph of the economy moves downside, then it immediately bounces back and recovers quickly. The exciting thing about this is that it heals with a better growth rate than before the recession. Sometimes, it is regarded the same as a V-shaped recovery, but it is different in the form that the growth of it flattens after a particular surge. The downfall, then recovery, and then stagnation make the shape of a square root on the economic graph of the economy. It shows that the economy recovered immensely after the fall, and its growth flattened. The Bottom LineA recession is an unfavourable economic situation that arises due to a disturbance in the financial status of the economy. The recession leads to unemployment, inflation, downfall in industrial production, cutting of jobs and increase in layoffs, disparity in demand and supply, etc. There has been a situation of inflation in the world a few times at a global level, like in 1975, 1982, 1991, and 2009. The recession of 2009 is regarded as the most devastating economic downturn and is named the 'Great Recession'.
Next TopicBusiness Day
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









