Tax AccountingUnderstanding Tax AccountingTax accounting is a group of accounting practices that prioritize paying taxes before disclosing financial information to the public. Tax accounting is governed by the Internal Revenue Code, which sets forth certain rules that organizations and individuals must follow while preparing their tax returns. 
Tax accounting is used as a means for tax-related calculations. People, businesses, corporations, and other organizations are all impacted. Even those who are exempt from paying taxes must practice tax accounting. Tax accounting aims to track money (both money coming in and money going out) connected to both persons and corporations. Importance of Tax AccountingFor both people and corporations, tax accounting is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, tax accounting ensures that tax regulations are followed, which is essential to prevent fines, penalties, and legal actions. Failing to abide by tax regulations may have serious financial and legal repercussions. Secondly, tax accounting helps to minimize tax liabilities by identifying tax deductions and credits and determining other strategies to reduce taxable income. This can lead to significant savings on tax bills and improve the financial position of individuals and businesses. Thirdly, tax accounting can help individuals and businesses plan for future tax obligations, which can be especially important for those with significant income or complex financial situations. Proper tax planning can help to avoid uncertain surprises and ensure that tax obligations are met in a timely and efficient manner. Overall, tax accounting plays a critical role in the financial well-being of individuals and businesses. By ensuring compliance with tax laws, minimizing tax liabilities, and planning for future tax obligations, tax accounting can help to improve financial stability and support long-term success. Key Terms in Tax AccountingIndividuals and businesses should be familiar with several key concepts in tax accounting to ensure compliance with tax laws, minimize tax liabilities, and effectively plan for future tax obligations. The following are some of the most important key terms in tax accounting:
Making educated decisions regarding tax planning, compliance, and reporting may benefit both people and organizations when they have a solid understanding of these fundamental tax accounting principles. It is important to work with a qualified tax professional or accountant to minimize tax liabilities and ensure that all tax obligations are met. Different Tax Accounting MethodsTax accounting methods refer to how businesses report their income and expenses for tax purposes. The tax accounting method a business uses can significantly impact its tax liability, so it's important for businesses to choose the method that's most appropriate for their needs. The following are some of the most common tax accounting methods:
It's important for businesses to choose the tax accounting method that's best suited to their needs and to consult with a tax professional to ensure they are following all applicable tax laws and regulations. Tax Accounting ServicesTax accounting services refer to the professional services provided by accountants, tax preparers, and tax advisors to assist individuals, businesses, and other entities with their tax-related matters. These services range from simple tax preparation and filing to more complex tax planning and advice. Some common tax accounting services include:
Tax accounting services are important for individuals and businesses because they help ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations and can help minimize tax liability. Additionally, tax accounting services can provide valuable advice and guidance on complex tax matters, which can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their financial and tax-related affairs. Difference between Tax Accounting and Financial Accounting
Tax accounting and financial accounting are two distinct branches of accounting, each with its own set of objectives and principles. Financial accounting is concerned with preparing financial statements that are used to communicate information about a company's financial performance to external stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and regulatory agencies. Financial accounting generates financial statements that detail a company's financial situation, performance, and cash flows in line with the approved standards of GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). In contrast, the application of tax rules and regulations to determine how much tax a corporation owes to the government is the focus of tax accounting. Tax accounting's major goal is to reduce a company's tax obligation while maintaining compliance with tax laws and regulations. Tax accountants use tax laws to prepare tax returns, estimate tax liabilities, and plan for future tax obligations. While both financial accounting and tax accounting involve the use of accounting principles and methods, they have different objectives and focus on different aspects of a company's financial activities. It is important for companies to understand the differences between these two branches of accounting to ensure that they are compliant with tax laws and regulations while also providing accurate financial information to stakeholders. Career Opportunities in Tax AccountingThere are many career opportunities in tax accounting, and it can be a rewarding field for individuals who are detail-oriented, analytical, and have an interest in tax laws and regulations. Some career opportunities in tax accounting include:
Overall, there are many career opportunities in tax accounting, and the demand for tax professionals is expected to continue to grow as tax laws and regulations become more complex. Tax Accounting Software & Benefits of Using ThemTax accounting software refers to a group of programs designed to automate and streamline tax-related tasks for individuals, businesses, and accounting professionals. Tax preparation, tax planning, and tax compliance are common functions of tax accounting software. Some of the benefits of using tax accounting software include the following: 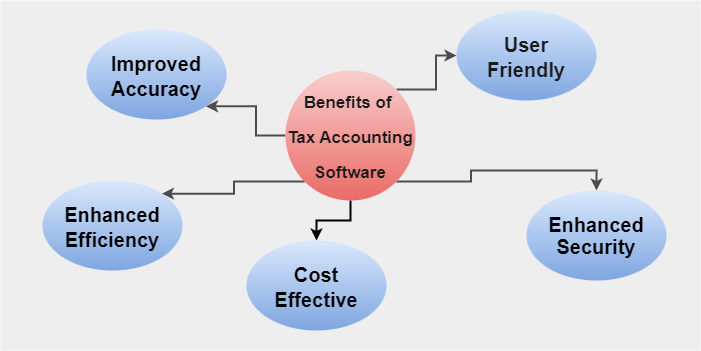
There is a wide range of different tax accounting software on the market, each with a different set of features and price points. Some examples of popular tax accounting software include QuickBooks, TurboTax, H&R Block, and TaxAct. When selecting tax accounting software, it's important to consider factors such as ease of use, features, pricing, and customer support. The Bottom LineAccounting for taxes is a crucial component of financial management for both people and companies. While financial accounting provides information to external stakeholders about a company's financial performance, tax accounting is primarily focused on calculating and minimizing tax liabilities while remaining compliant with tax laws and regulations. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









