CSS Pseudo-elementsA pseudo-class can be defined as a keyword which is combined to a selector that defines the special state of the selected elements. Unlike the pseudo-classes, the pseudo-elements are used to style the specific part of an element, whereas the pseudo-classes are used to style the element. As an example, a pseudo-element can be used to style the first letter or the first line of an element. The pseudo-elements can also be used to insert the content after or before an element. SyntaxPseudo-element has a simple syntax which is given as follows: We have used the double colon notation (::pseudo-element) in the syntax. In CSS3, the double colon replaced the single colon notation for pseudo-elements. It was an attempt from W3C to differentiate between the pseudo-elements and pseudo-classes. So, it is recommended to use double colon notation (::pseudo-element) instead of using single-colon notation (:). In CSS1 and CSS2, there is the use of a single colon (:) syntax for both pseudo-elements and pseudo-classes. The single colon syntax is valid for pseudo-elements in CSS1 and CSS2 for backward compatibility. Although there are several CSS pseudo-elements, we are discussing some of the most commonly used. The widely used CSS pseudo-elements are tabulated as follows:
Let's discuss the above pseudo-elements, along with an example. The ::first-letter pseudo-elementAs its name implies, it affects the first letter of the text. It can be applied only to block-level elements. Instead of supporting all CSS properties, it supports some of the CSS properties that are given below.
ExampleTest it NowOutput 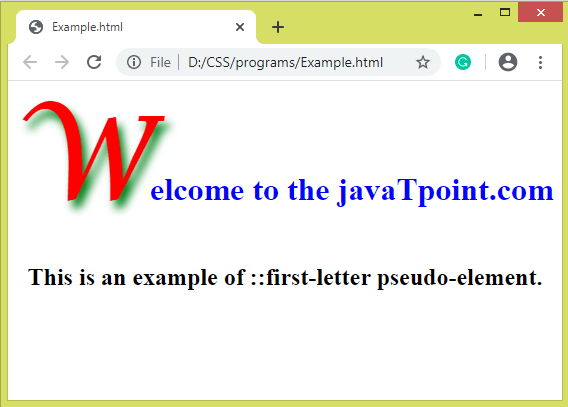
The ::first-line pseudo-elementIt is similar to the ::first-letter pseudo-element, but it affects the entire line. It adds the special effects to the first line of the text. It supports the following CSS properties:
ExampleIn this example we will see the use of ::first-line element to add special effects to the element's first line. Test it NowOutput 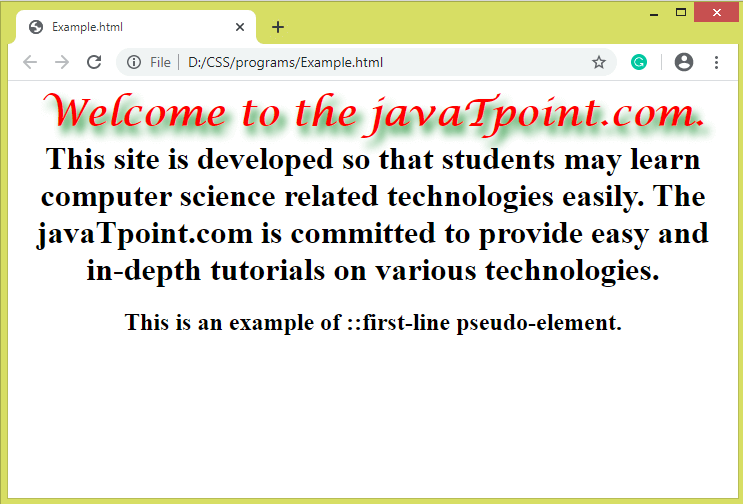
The ::before pseudo-elementIt allows us to add something before the element's content. It is used to add something before the specific part of an element. Generally, it is used with the content property. We can also add the regular strings or images before the content using this pseudo-element. ExampleTest it NowOutput 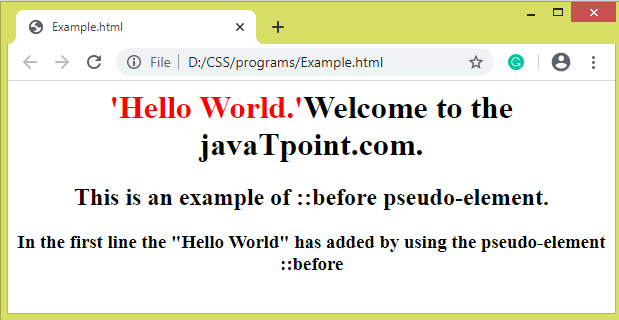
The ::after pseudo-elementIt works similar to ::before pseudo-element, but it inserts the content after the content of the element. It is used to add something after the specific part of an element. Generally, it is used with the content property. It also allows us to add regular strings or images after the content. ExampleTest it NowOutput 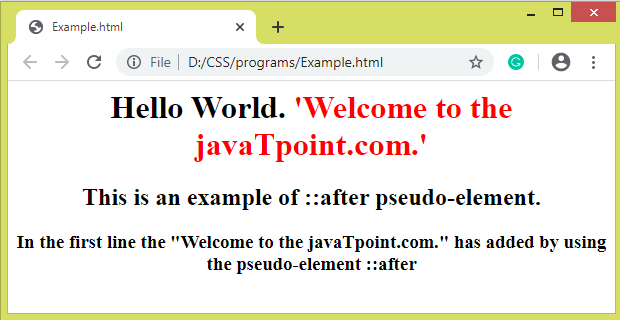
The ::selection pseudo-elementIt is used to style the part of an element that is selected by the user. We can use the following CSS properties with it:
ExampleTest it NowOutput 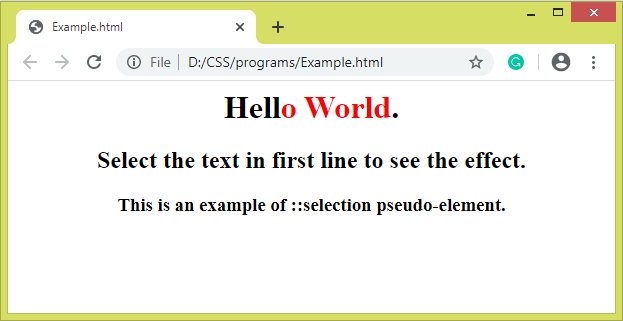
CSS classes and pseudo-elementThe pseudo-elements can be combined with CSS classes to style the specific element having that class. The syntax of combining the CSS classes with the pseudo-elements is given below. SyntaxIt can be written as: ExampleThis example will affect the first letter of those <h1> elements that have class="example" rather than affecting the all <h1> elements. Test it NowOutput 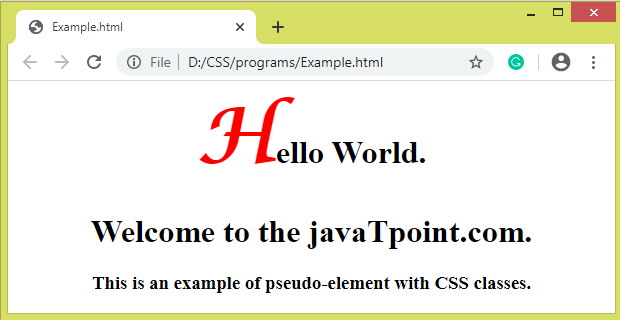
Next TopicCSS radial-gradient
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










