Roman Numerals 1 to 100IntroductionRoman numerals are a system of numbers widely used across the Roman Empire and developed in ancient Rome. They use a combination of Latin alphabetic letters to represent numerals. Counting, keeping track of dates, and numbering book chapters were just a few applications of this numeral system. 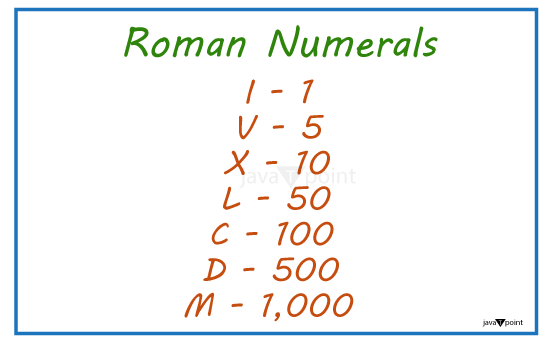
Seven fundamental symbols together make up the Roman number system: I: stands for the number one, V: for the number five, X: for the number ten, L: for the number fifty, C: for the number one hundred, D: for the number five hundred, And M: for the number one thousand. These symbols can be combined to represent more significant numbers. The Romans' numeral system does not contain zero since they did not have a sign for it. Roman numerals are composed according to the following rules:
Roman numerals were widely employed in historical times and are still used in various circumstances today, including on clocks, kings' or popes' names, and the numbering of movie sequels. Roman numerals still play a significant role in history and culture, although having less practical use today. The History of Roman NumeralsAround 500 B.C., the Roman numeral system was created for expressing numbers. Roman numerals became the accepted method for portraying numbers in Europe for centuries after the Romans conquered a significant chunk of the world at the time that was then known to them. Roman numerals began to die out in most of Europe around 1300 in favor of the more precise Hindu-Arabic system, which is still used today. In the numeral system used by Hindus and Arabs, the number three is symbolized by the number 3. When the number 3, as in 30, 300, 3000, etc., stays in place by one or more zeros, the value increases by an order of magnitude. A variety of letters represents Roman numerals. The basic Roman numerals are I = 1, V = 5, X = 10, L = 50, C = 100, D = 500, and M = 1000. These numbers can be connected, which would be added to represent greater numbers. For instance, LXXII (or 50 + 10 + 10 + 1 + 1 in Arabic numbers) might represent 72. 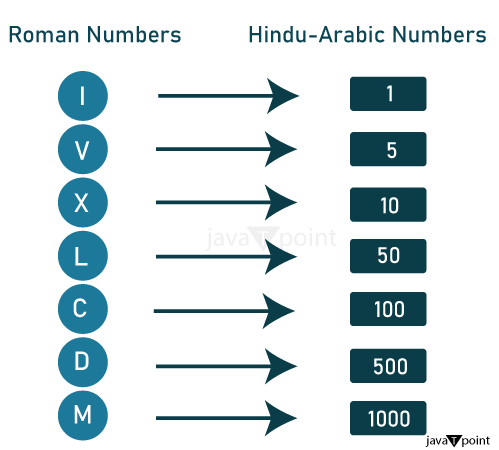
The symbols the Romans used for their numerals were adapted from various sources, including Greek alternates. Simple counting on one's hand, where one finger, which resembles I, equals one of whatever was being counted, is where the origin of I as a representation of one comes from. The V became a symbol for five because, depending on five things on the hand, the space between the thumb and first finger forms a V. At first, the Romans used the Greek letter X, sometimes known as chi, to denote 50. Historians have figured out through the analysis of monument transcriptions that X became 10 and L became 50. It's unclear how X came to signify 10. According to one idea, X was created by stacking one V, or five, on top of another V that was turned upside down, and this is how the number 10 came into existence. According to another concept, the Romans counted to ten by creating ten vertical marks, which they then crossed out with an X to make it easier to count groups of ten. It is similar to how Americans keep tabs on groups of five, crossing through four vertical markings with a fifth diagonal mark. The Romans eventually settled on the single letter X as the symbol for 10. Since C is the first letter of the Latin word for 100, centum, it came to stand for 100. Similarly, M was chosen for 1000 since mille is the Latin word for 1000. Compared to the Greeks, the Romans were not interested in pure mathematics, including number theory, geometric proofs, and other abstract concepts. The Romans valued practical mathematics instead. Romans utilized mathematics primarily to maintain military records, calculate personal and governmental accounts, and assist in building reservoirs and other structures. The operations of adding and subtracting were made simple by the Roman numeral system. The Romans sped up addition by lining up all the numerals from the added numbers. For instance, the digits were initially put in ascending order, or XXVIIII, to answer the equation 7 + 22, or VII + XXII. It was altered to IX, the accepted way of writing 9, because VIIII, or 9, is not in proper form. The correct response is still XXIX, or 29. Compared to addition, subtraction can be performed by removing similar digits from the two separate numbers. The Romans used counting boards to help teach division and multiplication because they found these operations quite challenging. The counting boards could be used for addition and subtraction, resembling the famous abacus. Up to the Middle Ages, counting commissions with Roman-inspired designs was used throughout Europe. Even with these counting boards, multiplying and dividing huge quantities was still challenging. Therefore, the Romans created and frequently read multiplication and division tables to tackle difficulties involving huge numbers. The lack of a way to express fractions numerically was another drawback of the Roman numeral system. Romans were aware of particles, but because they were expressed in writing, it was challenging to put them to use. Three-eighths would have been written as tres octave in Roman script. Romans often used the uncia to represent fractions. The English word "ounce" is derived from the Latin "uncia," which initially denoted one-twelfth of the Roman weight unit. The Romans could express one-sixth, one-fourth, one-third, and half despite using fractions based on 1/12s. While the Romans would have written one-fourth as three unciae, the modern numerical representation of one-fourth is 1/4. Due to this technique, the Romans could measure approximately, but they found it difficult to provide exact measurements. Another flaw in Roman math was that the idea of zero didn't exist. In contrast to earlier numbers used by the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Egyptians, the Romans did not have a place-value system using zero as a placeholder for numerals. As a result, the Romans were forced to establish a complex system using numbers that stood for 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, and 1000. Unlike the ancient Greeks, Romans were unaware of or interested in irrational numbers. Because most geometry depends on knowing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, the Romans were severely hampered in their ability to understand geometry. How are Large Numbers Represented in Roman Numerals?This issue was resolved in several ways during the early Roman Empire. For such situations, they had unique numbers. Back then, the most typical symbol for huge numbers was the mirror image of the C. As the empire expanded, a modified form of the three signs (I, V, and X) began to be used more frequently for numerals above a thousand. The Romans added a line over the symbols. There were extra lines on the sides of Roman numerals in the hundreds of thousands. Roman numerals are rarely used today to indicate numbers more significant than 3,999. And given the century we are in, it won't be for a very long time until we run into problems with Romanizing the years. The Roman numeral system represents a typical year in the twenty-first century. For instance, MMXIII can be used to write the year 2018. The number for the year 2299 can be slightly longer: MMCCXCIX. In contrast to quantities more significant than 3999, years or numbers are still doable. Representations of Roman Numerals from 1 to 100
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










