What are natural numbers?Natural numbers are part of the number system, including all the positive numbers from 1 to infinity. Natural numbers are called as counting numbers because they do not include zero or negative numbers. We can also say natural numbers are subset of real numbers, because it contains every number that real numbers have except the zero, fractions, decimals, and negative numbers. These are used significantly in our day-to-day activities and speech. We see numbers everywhere around us, for exchanging money, counting objects, to measure time, for measuring temperature, etc. The numbers that are used to do these tasks are known as natural numbers. For example, while counting objects we say, 10 litre of water, 15 cups, 13 books, 3 bottle and so on. Definition of natural numbersNatural numbers are the numbers that are used for counting and are a part of real numbers. The set of natural numbers includes only the positive integers, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ……….∞. Examples of natural numbersA few examples of natural numbers are 35, 65, 79, 2000000, 50000 and so on. Set of natural numbersSet is defined as collection of elements (numbers in this context). The set of natural numbers in Mathematics is written as {1, 2, 3,}. The set of natural numbers is denoted by the symbol, N. N= {1, 2,3,4,5,… infinity}.
Smallest natural number
The smallest natural number is 1. We know that the smallest element in N is 1 and that for every element in N, we can talk about the next element in terms of 1 and N (which is 1 more than that element). For example, two is one more than one, three is one more than two, and so on. Natural Numbers from 1 to 100The natural numbers from 1 to 100 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99 and 100. Is 0 a natural number?As we studied earlier, natural numbers are counting numbers, this proves 0 is NOT a natural number. For counting any number of objects, we start counting from 1 and not from 0. Odd Natural numbersThe odd natural numbers are the numbers that are odd and belong to the set N. So, the set of odd natural numbers is {1,3,5, 7, ….}. Even Natural NumbersThe even natural numbers are the numbers that are even, exactly divisible by 2, and belong to the set N. So, the set of even natural numbers is {2,4,6, 8...}. Natural Numbers and Whole Numbers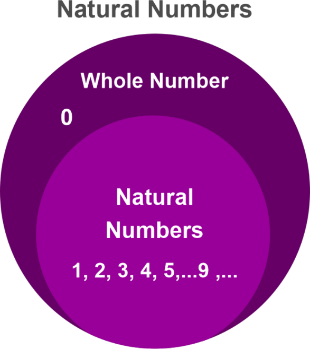
The set of whole numbers is the same as the set of natural numbers, except that it includes an additional number which is 0. The set of whole numbers in Mathematics is written as {0,1,2, 3,}. It is denoted by the letter, W. W = {0,1,2,3,4…} From the above definitions, we can understand that every natural number is a whole number. Also, every whole number other than 0 is a natural number. We can say that the set of natural numbers is a subset of the set of whole numbers. Difference Between Natural Numbers and Whole NumbersNatural numbers are all positive numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. They are the numbers you usually count and they continue till infinity. Whereas, whole numbers are all natural numbers including 0, for example, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Integers include all whole numbers and their negative counterpart. e.g., -4, -3, -2, -1, 0,1, 2, 3, 4 and so on. The following table shows the difference between a natural number and a whole number.
Natural Numbers on Number Line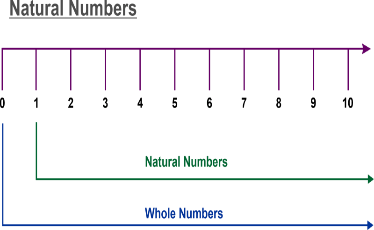
As we already know the set of natural numbers or whole numbers can be represented on the number line. All the positive numbers are located to the right of the number 0. Every number right to zero except the number 0 are natural number, however, if we include the number 0 we will get whole numbers. Different properties of natural numbersThere are four operations addition, multiplication, subtraction, and division, that can take place on natural numbers, and lead to four main properties of natural numbers:
Closure Property:The sum and product of two natural numbers is always a natural number. This property is applicable to addition and multiplication but is not applicable to subtraction and division. Closure property of addition: a + b = c. 12 + 3 = 15. 50 + 90 = 140. This proves that the sum of natural numbers is always a natural number. Closure property of multiplication: a * b = c. 5 * 4 = 20, 20 * 20 = 400. Hence this proves that the multiplication of natural numbers is always a natural number. Associative Property:The sum or product of any three natural numbers remains the same even if the grouping of numbers is changed. This property applies to addition and multiplication but is not applicable to subtraction and division.
Commutative Property:The sum or product of two natural numbers remains the same even after interchanging the order of the numbers. This property applies to addition and multiplication but is not applicable to subtraction and division.
Distributive Property:The distributive property is known as the distributive law of multiplication over addition and subtraction. It states that an expression that is given in form of a (b + c) can be solved as a × (b + c) = ab + ac. This distributive law which is also applicable to subtraction is expressed as, a (b - c) = ab - ac. This means operand 'a' is distributed between the other two operands.
First 10 Natural NumbersNatural numbers are counting numbers that start from 1. So, the first 10 natural numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10. Important Points:
Next TopicRational Numbers
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










