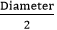Circle
In geometry, the circle is the most important shape to learn. The theoretical importance of a circle applied in many subjects such as physics, astronomy, mathematics, etc. In early education, we introduce with many geometrical shapes so that we can understand other subjects where the principles of circle apply.
In geometry, a round-shaped figure is called a circle. In this section, we will learn the circle definition, diameter of a circle, circumference of a circle, and other parts of circle. Along with this we will also learn the types of circle, properties, and formulas.
Circle Definition
A curved line that has the same distance from the center and connects at the point where it starts, called the circle. In other words, it is the locus of all points that have equidistant from the origin. The examples of the circle are wheel, coin, compact disc, etc. The following figure represents the shape of a circle.
Parts of Circle
There are following parts of a circle:
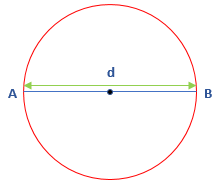
- Diameter: A line segment that passes through the center and touches the boundary of the circle at both sides, called the diameter. It is the longest chord of the circle. It is twice the length of the diameter. It is denoted by d. In the following figure, the line segment AB is the diameter.
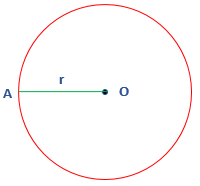
- Radius: A line segment that touches the center from one side and touches the boundary from another side, called the radius. In other words, the distance between the center and circumference is called the radius. It is half the length of the diameter. It is denoted by r. In the following figure, the line segment OA is the radius.
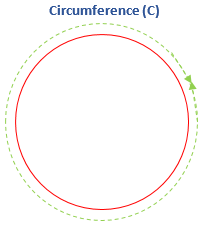
- Circumference: The distance around the circle is called the circumference. In other words, the arc length of the circle is called the circumference. It is the perimeter of the circle. It is denoted by The following figure, the green dotted line denotes the circumference.
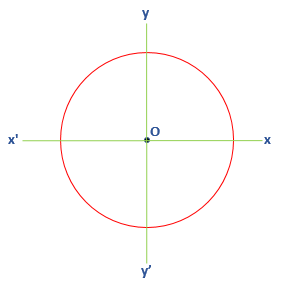
- Origin or Center: A point in the middle of the circle that has equidistant from all the points on the circle called the origin. It is also known as center. It is denoted by O. In the following figure, O denotes the origin or center of the circle.
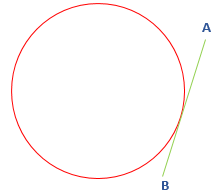
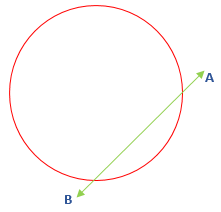
- Tangent: A line segment that touches the circle at a common point is called a tangent. It is always drawn out of the circle. In the following figure, the line segment AB is a tangent.
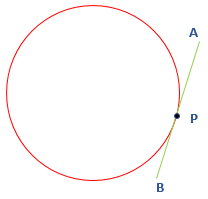
- Tangency Point: The point where the tangent line touches the circle is called tangency point. In the following figure, the line segment AB touches the circle at point P.
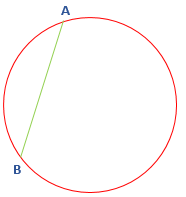
- Chord: A line segment whose endpoints lies on the circle is called chord. It also divides the circle into two parts. In the following figure, the line segment AB is a chord.
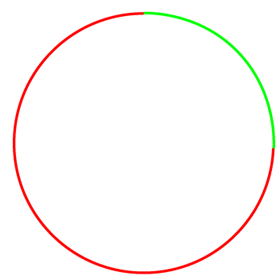
- Arc: A part of the circumference is called an arc. There are two parts of the arc:
- Minor Arc: The smaller part of the arc is called the minor arc. In the following figure, green arc shows the minor arc.
- Major Arc: The larger part of the arc is called the major arc. In the following figure, red arc shows the major arc.
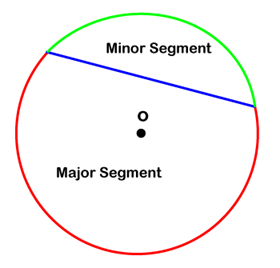
- Segment: The region enclosed between arc and chord is called the segment. There are two parts of segments:
- Minor Segment: The smaller part of the circle's segment is called the minor arc.
- Major Segment: The larger part of the circle's segment is called the major arc.
The following figure shows the minor and major segment of the circle.
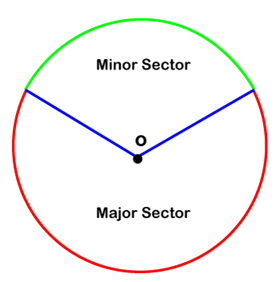
- Sector: The region enclosed between two radii of equal length is called the sector of the circle.
- Minor Sector: The smaller part of the circle's sector is called the minor sector.
- Major Sector: The larger part of the circle's sector is called the major sector.
The following figure shows the minor and major sector of the circle.
- Secant: A line segment that intersects the circle at two points is called secant. In the following figure, the line segment AB is a secant.
Types of Circle
There are three types of circle are as follows:
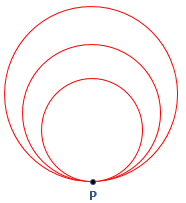
- Tangent Circle: It is a circle that intersects more than two circles at a common point is called tangent circles. It does not share the common center. The following figure shows tangent circle. All the three circles intersect each other at common point P.
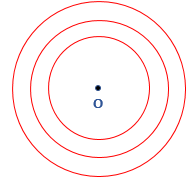
- Concentric Circle: Two or more than two circles that have the same center are called the concentric circle. These circles are of different radii. In the following figure, there are three circles of different radii having the same center O.
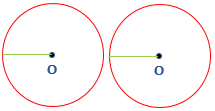
- Congruent Circle: Two or more than two circles with the same radii but different centers are called congruent circle. In the following figure, there are two circles with the same radii but having two different centers.
Circle Formulas
- Area of Circle (A)=πr2
- Diameter (d)= 2×radius (r)
- Radius (r)=
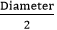
- Circumference (C)=2πr
We can also find the radius by using the following formula. It applies when circumference is given in the question.
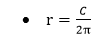
Circle Properties
Some of the important properties of the circle are as follows:
- The circles having equal radii are called congruent.
- The diameter of a circle is the longest chord of a circle.
- Perpendicular dropped from the center divides a chord into two equal parts.
- Radius is always perpendicular to the tangent at the point where it touches the circle.
- Angles formed by the same arc on the circumference of the circle is always equal.
- An angle formed by an arc at the center is twice the inscribed angle formed by the same arc.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now