Compatible Array Sizes for Basic Operations in MATLABCompatible array sizes mean the dimension sizes of the input arrays are either the same, or one of them is scalar, for every dimension. Binary operators and functions operate well with the arrays that have compatible sizes. MATLAB implicitly expands array with compatible sizes to make them the same size during the execution of the element-wise operation or function. Array Inputs with Compatible Sizes2-D Array inputs Let's understand with some combinations of scalars, vectors, and matrices that have compatible sizes:
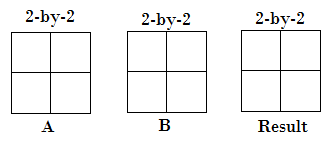
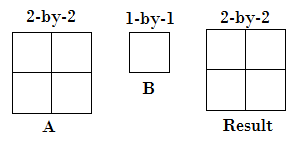
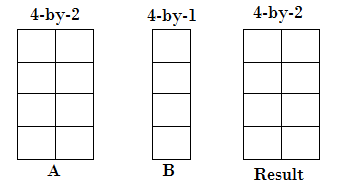
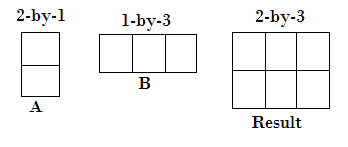
Multi-dimensional Array Input
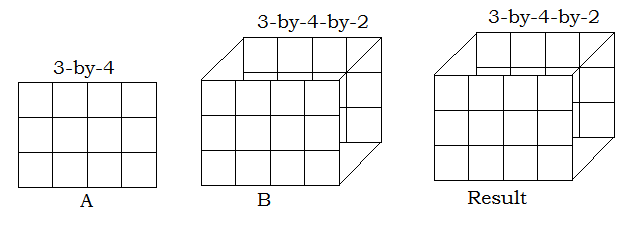
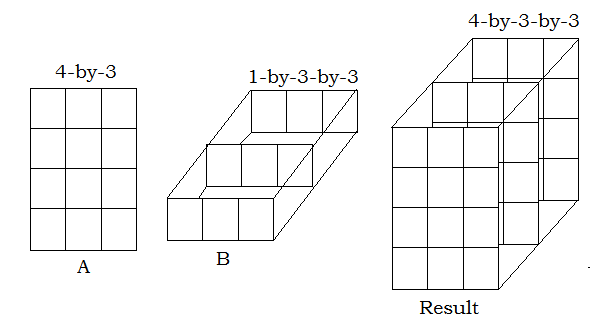
Empty Array inputEmpty arrays are the arrays with no elements and dimension size of zero. The rules for empty arrays and non-empty arrays are the same, and the size of the dimension that is not equal to 1 determines the size of the output. Example: Output: >> a.*b ans = 3x3x0 empty double array MATLAB implicitly expands arrays with compatible sizes, but incompatible sizes cannot be implicitly expanded to be the same size.
Example: Output: >> a+b Matrix dimensions must agree. >> a-b Matrix dimensions must agree. >> a.*b Matrix dimensions must agree.
Example: Output: >> a+b Matrix dimensions must agree. >> a-b Matrix dimensions must agree. >> a.*b Matrix dimensions must agree Row and Column Vector CompatibilityRow and column vectors always have compatible sizes, even with different sizes and lengths. And performing arithmetic operations on these vectors creates a matrix. Example: Output:
>>% adding two row and column vectors
>> a + b
ans =
1.9058 1.9058 1.9058
1.1270 1.1270 1.1270
1.9134 1.9134 1.9134
1.6324 1.6324 1.6324
>>% subtraction of two row and column vectors
>> a - b
ans =
0.0942 0.0942 0.0942
0.8730 0.8730 0.8730
0.0866 0.0866 0.0866
0.3676 0.3676 0.3676
>>% array multiplication of two row and column vectors
>> a.*b
ans =
0.9058 0.9058 0.9058
0.1270 0.1270 0.1270
0.9134 0.9134 0.9134
0.6324 0.6324 0.6324
Next TopicSparse Arrays in MATLAB
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









