Workspace, Variables, and Functions in MATLAB
Workspace
- The workspace contains all variables we create while working in MATLAB.
- Whenever we assign a value to a variable, it automatically gets space in the workspace.
- Workspace variables lose their existence after the closing of the environment, so save these variables in a file to use later on.
- We can import variables into MATLAB from data files.
- We can import variables into MATLAB from other programs also.
- The assignment operator (=) facilitates the creation of variables.
- To access the variable from the workspace, we need to enter its name at the command line.
- To view all available variables in the workspace, enter the command- 'whos' at the command line.

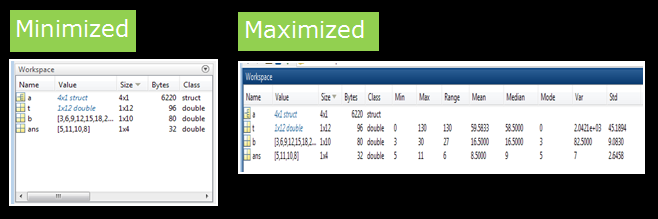
Workspace Pane in MATLAB
- It is an area in the MATLAB environment with the name Workspace written on its top bar.
- All variables currently being used or in the workspace, are displayed here.
- Workspace pane can be maximized or minimized as per requirement.
- We can add or remove the fields of the contents, which describe variables.
MAT-file in MATLAB
- The file saved with .mat extension is called a MAT-file in MATLAB.
- As variables in the workspace no longer exist after the closing of the environment, so these variables are saved in MAT-file for later use.
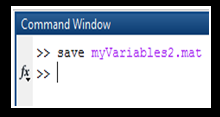
- Use save command to save workspace contents in a file.
- Ensure the file name is different from the previous file. Otherwise, it will overwrite the last existing file with the new one.
- It saves the current workspace in the current working folder and a compressed file.
Current Folder Pane
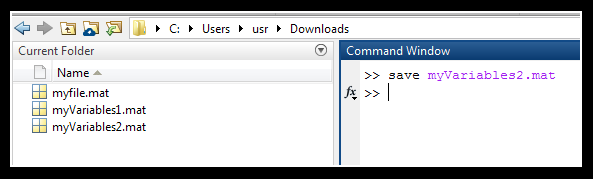
- We can change the current working folder by using the Browse For Folder button located above the current folder pane.
- After running the save command, the file saved with .mat extension becomes visible in the Current Folder Pane.
- After saving the workspace, we can clear all the contents of the workspace by using the clear command at the command line.
- Syntax of the save command:
Using .mat files
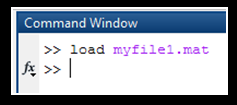
- Any .mat file can be included in the current workspace.
- Use command load followed by filename with extension.
- Syntax:
- Before loading the file, ensure the parent folder is selected as the current folder; otherwise, it will show error:
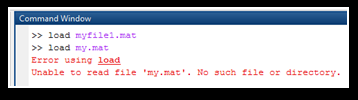
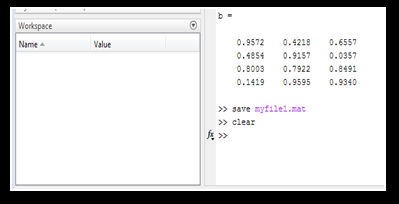
Workspace after saving the file, clearing the content of the workspace, and before loading of the file:
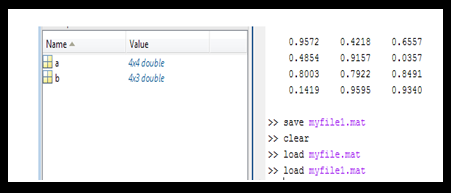
Workspace after loading of the file, now we can use variables inside that file:
Text and Characters in MATLAB
Text in String Arrays
- When text is enclosed in double quotes (" "), its data type or class is declared as String.
- Strings are also arrays, like all other MATLAB variables.
- Syntax:
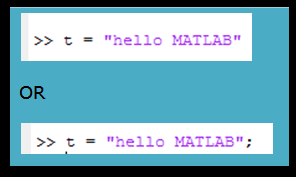
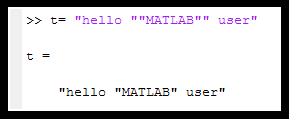
Double quotes inside double quotes
- When the text of the String itself includes double quotes, then use double quotes within the text, as:
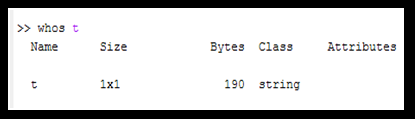
Using whos command to View a single variable
- As 'whos' command shows all variables within the workspace, we can use 'whos variable_name' command to view only the particular variable.
Concatenation of String using plus (+) operator
- We can combine the value of other variables into a String.

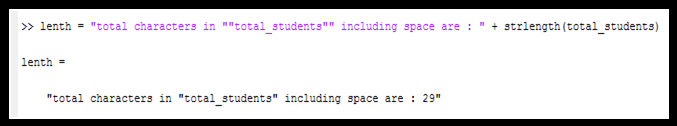
Find the length of the String array in MATLAB
- We can find the length of a string by using the strlength function.
String array with multiple elements
- String array can also have multiple elements like number arrays.

Find the length of String array with multiple elements
- The same strlength function is used to find the length.
- It will display length in an array format with length calculated as an individual element.

Character Arrays in MATLAB
- We use character array to store data that is not meaningful, or we can say that it doesn't resemble a text, such as a key or a password sequence, a DNA sequence.
- Character array has a char data type.
- Character array is declared in single quotes (' ').

Find a single character in character array
- In character array, each character is stored as a separate element.
- To find the character of an element, use the index number of that element in parenthesis with the variable.
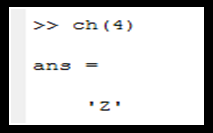
Concatenation of Character Array in MATLAB
- As we concatenate numeric arrays, here also use square brackets to concatenate character arrays.
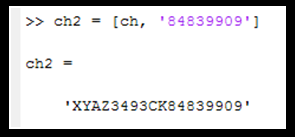
Calling Functions in MATLAB
- In MATLAB, a large number of functions are available that perform computational tasks.
- These functions are the same as subroutines or methods in other programming languages.
- Functions are called providing input arguments in its parenthesis.
- Example:
- function-name....max()
- use.....finds the largest value in the array.
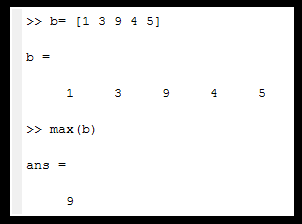
- If it is a matrix, it will find the maximum value column-wise.

- Use a comma to separate multiple input arguments.
- Passing multiple arguments requires to agree on the matrix dimensions, as per calculation.

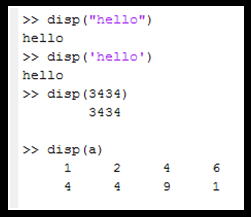
disp function in MATLAB
- Used to display the input data as it is.
- It doesn't store the output to the default ans variable.
- Inputs for the function are provided in parenthesis.
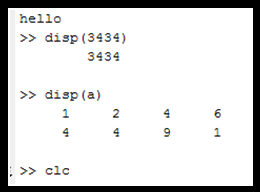
clc function in MATLAB
- It clears the command window by erasing all commands and outputs.
- But previously entered commands can be accessed by using keyboard array keys on the command line.
- It doesn't take any input, so it doesn't output anything.
|
















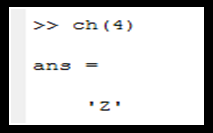

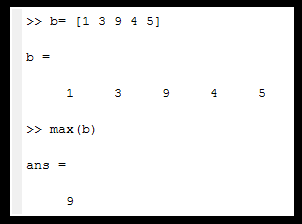




 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









