How to Check the Accuracy of your Machine Learning ModelAccuracy is well-known for the models used in Machine Learning for the validation method that is used in evaluating the classification problems. The relative simplicity of the accuracy is the main reason for its popularity. We can understand the accuracy very easily, and it is simple to implement. Using the accuracy, we can easily assess the performance of the model. In Real-life situations, the problems that are in the modelling are rarely easy when compared to other problems. We can work with such datasets that are imbalanced or have multiclass or many classification problems. When we are doing any problem using any method of machine learning, then always a high accuracy is not our main goal. As you are able to solve more problems in ML, working out and utilizing precision ends up being more suitable and requires additional thought. To get a better understanding of the importance of accuracy, Actually, what accuracy is, and how to calculate accuracy all will be covered in this article. Accuracy:Accuracy is mainly used in classification problems to get the appropriate percentage of the models being executed to know how much of it is correctly predicted. In any model, there will be several classification problems will present when we execute them, then the accuracy plays the main role by talking about whether all the problems are correctly predicted or not with respect to the total number of predictions made by the model. We can calculate the accuracy of any model by dividing the correctly predicted problems by the total number of predictions made. 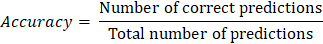
The above formula is very useful for calculating the accuracy of any model. It provides a simple understanding of a binary classification problem. Accuracy Paradox:When we execute the model, the default form will give the accuracy of the overall metric about the performance of the whole dataset. However, the overall accuracy of the classification models in machine learning can be misleading when the distribution of the problems to the specific class is imbalanced, and at that point in time, it is very difficult to predict the class of the model correctly. In this situation, the class with the most occurrence will be predicted correctly, and the accuracy of this predicted class will be a high accuracy score, whereas the class with the low occurrence will be misclassified. When this type of situation occurs in the model, then there is a high probability that the predicted accuracy will be wrong, and we cannot predict the performance of the model correctly. For example, in any health issue prediction model, we cannot miss any harmful disease cases by any changes in the files of the patients. If any of the files got changed due to any issues, then the predictor will directly predict the condition based on the files or classes. Then the person with any small health issue has to face serious treatment because of the changes or misclassified classes. Now let us take an example that uses the dataset of breast cancer, which is used to classify the breast tumor cases
Before executing the model, we change the data that is imbalanced by removing the data that is more harmful, so after removing all the harmful data from the dataset, the accuracy will be around 5.6%. Output: Good 0.854698 Bad 0.0548726 Name: labels, dtype: float64 Let us know how to predict the accuracy of the model Output: 0.9854126 Our model accomplished a general accuracy of ~0.9464 for the entire model. This outcome is, by all the data, strikingly great. However, on the off chance that we investigate the class-level forecasts utilizing a disarray framework, we get a totally different picture. 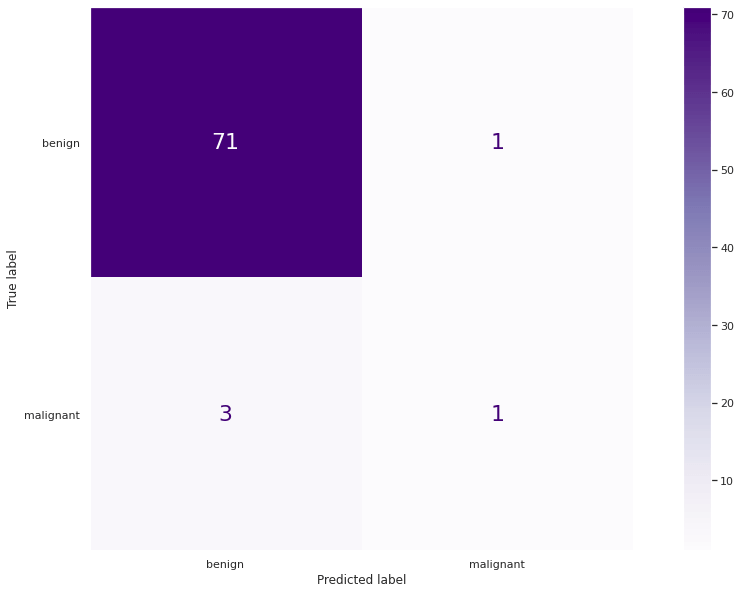
Our model misdiagnosed practically all difficult cases. The outcome is the very inverse of what we anticipated in view of the general precision metric. The circumstance is a commonplace illustration of the precision mystery. While you accomplish a high exactness esteem, it gives you a bogus reason as your dataset is exceptionally imbalanced, and misprediction of the minority class is exorbitant. In such circumstances, you attempt to anticipate uncommonly, however basic, dangers with systemic consequences. Models are serious clinical diseases, monetary emergencies, militant psychological assaults, meteors, and so forth. It does not make any difference in the event that your model accomplishes 99.99% precision, assuming missing a solitary case is sufficient to disrupt the entire framework. Depending on the exactness score as determined above is not sufficient and could misdirect. If the accuracy of the model is not a suitable metric for the evaluation of our machine learning model performance, we covered more suitable examples of accuracy.
Accuracy in Binary Classification:In the binary classification case, we can communicate precision in True/False Positive/Negative qualities. The accuracy recipe in Machine learning is given as follows: 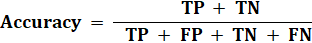
In the accuracy classes, there are only two classes present. They are positive/negative:
Accuracy in Multiclass Problems:In a multiclass classification problem, we can use the same definition as the binary classification problem. But in the multiclass, we cannot directly predict the outcome as true/false definitions. So, in multiclass problems, we can use other formulas to calculate the accuracy of the model. 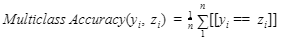
The terms used in the above formula are:
Example: Let us take a confusion matrix with some true values and predict the accuracy for any three classes of the dataset. 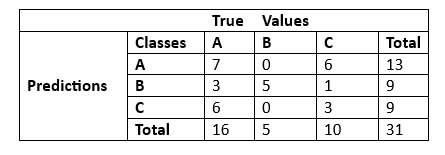
Now, we have to select the number of correct predictions in the table, and then we have to find the accuracy of the model using the formula given above. Multiclass Accuracy = 7+5+3/31 = 0.483 The above result of the formula says that our model achieved a 48% accuracy in this class (i.e., multiclass classification problem). Accuracy in Multilabel Problems:In Multilabel classification problems, the classes of the dataset are mutually exclusive to each other. Whereas multilabel classification is different from multiclass problems because, in multiclass classification, the classes are mutually non-exclusive to each other. In machine learning, we can represent multilabel classification as multiple binary classification problems. The multilabel accuracy is also known as Hamming score. In multilabel classification, the accuracy is calculated by the correctly predicted labels and the number of active labels. 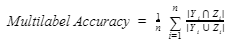
The terms used in the above formula are
Multilabel Accuracy gives a more adjusted metric since it does not depend on the 'exact match' rule (like Subset Accuracy). It neither one of them considers 'True Negative' values as 'right' (as in our guileless case). Example: Output: 0.45827400 If the hamming score we get after the calculation is closer to one, then the performance of the model will be good. Hamming Loss:Hamming loss is a method that is used to get the ratio of data that is predicted labels wrongly. It will take the values in the range of 0 and 1, where the 0 is used to represent no errors in the model. 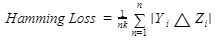
The terms used in the above formula are
Output: 0.03501485 If the hamming loss we get after the calculation is closer to one, then the performance of the model will be good. Other than these measurements, you can utilize the multilabel adaptation of similar arrangement measurements you have found in the paired and multiclass case (e.g., accuracy, review, F-score). You can likewise apply averaging methods (miniature, large-scale, and test-based) or ranking-based measurements. Subset Accuracy or Exact Match Ratio:Subset accuracy is also known as Exact match Ratio or Label set accuracy. It is a strict version for calculating the accuracy of the model, where in this type of prediction it will show the correct prediction if all the labels are matched for the given sample. 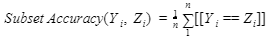
The terms used in the above formula are
In Machine learning, we always work with a large number of labels and datasets. Sometimes it takes more work to predict all of them correctly. But using the above accuracy technique, ques we can find the accuracy very easily when compared with others. The subset accuracy technique shows the low performance of the model compared with other techniques. This measurement does not give data about halfway accuracy due to the stringent standard it depends on. On the off chance that our model neglects to foresee just a solitary mark from the 103 but performs well on the rest, Subset Precision actually orders these expectations as disappointments. When to use Accuracy Score in Machine Learning:Accuracy score should be utilized when you need to know the expertise of a model to group data points of the classes accurately in the dataset, regardless of the performance prediction per class or label of the dataset. It gives you an instinct for whether the given data of the dataset is suitable for the classification purpose or not. Assuming you really want to use the precision metric in your project or work, there are exceptionally easy-to-utilize packages like deep checks that make sure that it is used to give you the top to bottom reports on important measurements to assess your model. This makes it simpler or easier for you to all the more likely understand your model's performance. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










