Adversarial Machine LearningThe term "adversary" is used in the field of computer security to make a fool or misguide a machine learning model with malicious input. Cyber security is one of the most important concepts for all data scientists and programmers as well. As hackers always try to hack data using different techniques. Similarly, Adversarial machine learning is also a technique that misguides any machine learning model with deceptive data and reduces the accuracy and performance of the model. In this article, we will discuss a very important concept of Machine Learning and Artificial intelligence that helps you to protect machine learning models from digital attacks and make them secure from unauthorized attacks. So, let's start with a quick introduction to Adversarial Machine Learning. 
What is Adversarial Machine Learning?Adversarial Machine Learning is referred to as a cyber-attack that aims to make a fool or misguide a model with malicious input. It is used to execute an attack to corrupt or disrupt a machine learning model by providing deceptive input. Adversarial Machine Learning can be widely used in image classification and spam detection, where some changes are made on the set of images that cause a classifier to produce incorrect predictions. Examples of Adversarial Machine LearningAdversarial Machine learning examples are referred to deceptive inputs that aim to misguide or disrupt a machine learning model or computer program. There are some images examples crafted by an attacker that our model cannot predict correctly. Let's understand with the popular example of Panda vs. Gibbon. Although both these images are different but are indistinguishable to the human's eye. 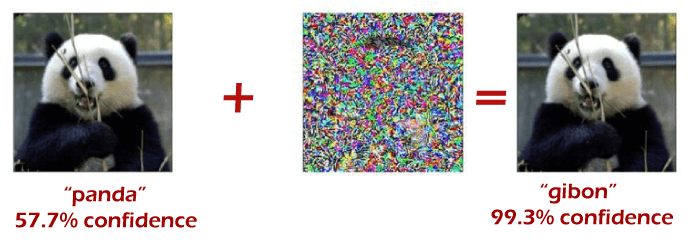
The image on the left is one of the clean images in the ImageNet dataset, used to train the GoogLeNet model. However, the first image is slightly different from than third image or even a modified version of the first. The right-side image is created with the help of introducing a small perturbation in the central image. The first image is predicted by the model to be a panda, as expected, while the right side image is recognized as a gibbon with high confidence. Hence, while introducing a typical image with adversarial input, it can cause a classifier to misguide a panda as a gibbon. Now, take another example that shows different views of a 3D turtle the authors printed and the misclassifications by the Google Inception v3 model. Adversarial machine learning has yielded results that range from the funny, benign, and embarrassing-such as to following turtle being mistaken for a rifle-to potentially harmful examples, such as a self-driving car mistaking a stop sign for a speed limit. What do you mean by adversarial Whitebox and Blackbox attacks?There are two ways in which attacks are categorized in machine learning. These are as follows:
Black Box Attack: Black Box attacks are the scenario where attackers do not have model information about the targeted model and also have no access to its architecture, parameters, and gradients. White Box Attack: These attacks are just opposite to black-box attacks, where attackers have all access to the targeted model and information of its architecture, parameters, and gradients as well. Black box attacks and white box attacks are further categorized into two types as follows:
How to protect against Adversarial Examples?Although adversarial machine learning is always harmful to a model from the security perspective, we can protect our model by giving adversarial training. As a general machine learning model is trained with some old data or experience for predicting the outcome; similarly, an adversarial machine learning model is also provided with the training. In which a model is trained on various adversarial examples to make them robust against malfunction in the data. 
Although, it is not easy to give Adversarial training to model as it is a very slow and costly process. Every single training example must be probed for adversarial weaknesses, and then the model must be retrained on all those examples. Scientists are developing methods to optimize the process of discovering and patching adversarial weaknesses in machine learning models. Further, some AI researchers are also working on preventing such attacks with the help of deep learning concepts through combining parallel neural networks and generalized neural networks. Types of Adversarial AttacksThere are so many types of adversarial attacks that can harm your machine learning system. The aim of these adversarial attacks is to decrease the accuracy as well as the performance of classifiers on specific tasks and misguide the model also. Adversarial Machine Learning is a department of machine learning that studies these attacks and reduces their effect on the model. There are some important types of Adversarial Attacks as follows: Poisoning Attack:Poisoning attacks take place whenever the machine learning model is under training or during deployment. It is also referred to as contaminating attacks. In poisoning attacks, attackers influence the data or its labels when a model is in the training phase, which causes system skewed or generates inaccurate decisions in the future. It reduces the accuracy and performance of the machine learning system. Further, when a machine learning model is re-trained during deployment, attackers introduce malicious input and disrupt the model. This is very difficult for data researchers to identify when data gets poisonous and behaves wrongly on specific types of input samples. Also, it is hard to detect what types of sample data will trigger a machine learning model to behave wrongly. Let's understand with an example of poisoning a Chatbot. Microsoft has launched a chatbot for Twitter to learn to engage in conversation through repeated interactions with other users. Initially, it engaged in casual and playful conversation between users but later, they examined that chatbot does not contain appropriate filters. Due to this, the system gets started abusive tweets into its algorithm. As soon as the number of users gets increased, abusive tweets also increase. Hence, as a result, Microsoft has to close down this chatbot on the same day. Evasion Attacks:These attacks are just opposite to the poisoning attacks, where attacks take place after a machine learning system has already been trained. These attacks are commonly used attacks type in machine learning. It occurs when the ML model calculates the probability around a new sample and is often developed by trial-and-error methods. The attackers manipulate the data during deployment, but they are unknown when a machine learning model breaks. Let's understand with an example. Suppose the attacker wants to investigate the algorithm of the machine learning model that is designed to filter the spam email content. Then attackers may do various experiments on different emails to bypass the spam filter by introducing a new email that includes enough extraneous words to "tip" the algorithm and classify it as not spam from spam. These attacks may affect the righteousness and confidentiality of a machine learning model, which leads it to provide malicious output that is intended by an attacker. These attacks can also be used to reveal private or sensitive information. One of the most prevalent examples of evasion attacks is spoofing attacks against biometric verification systems. Model Extraction:Model Extraction is referred to as a black box machine learning system. It is used to reconstruct the model by extracting data on which it got trained. It helps to steal the stock marketing prediction model, and later attackers reconstruct a new model similar to the previous model for their own financial benefit. Model Extraction attacks are important when either the training data or the model itself is sensitive and confidential. Techniques/Methods used in generating Adversarial Attack
ConclusionWell, in this way, we have understood how adversarial machine learning examples are so important for security perspectives in machine learning and Artificial Intelligence. Hopefully, you will get complete basic information about adversarial machine learning after reading this tutorial.
Next TopicBasic Concepts in Machine Learning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









