Bias and Variance in Machine LearningMachine learning is a branch of Artificial Intelligence, which allows machines to perform data analysis and make predictions. However, if the machine learning model is not accurate, it can make predictions errors, and these prediction errors are usually known as Bias and Variance. In machine learning, these errors will always be present as there is always a slight difference between the model predictions and actual predictions. The main aim of ML/data science analysts is to reduce these errors in order to get more accurate results. In this topic, we are going to discuss bias and variance, Bias-variance trade-off, Underfitting and Overfitting. But before starting, let's first understand what errors in Machine learning are? 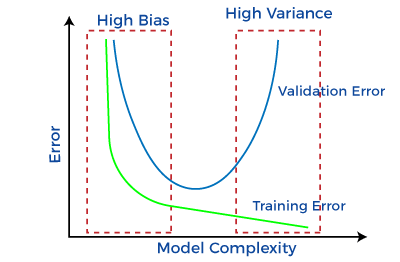
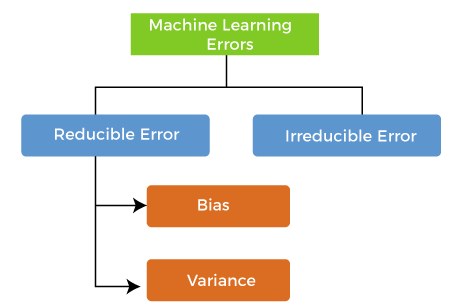
Errors in Machine Learning?In machine learning, an error is a measure of how accurately an algorithm can make predictions for the previously unknown dataset. On the basis of these errors, the machine learning model is selected that can perform best on the particular dataset. There are mainly two types of errors in machine learning, which are:
regardless of which algorithm has been used. The cause of these errors is unknown variables whose value can't be reduced. What is Bias?In general, a machine learning model analyses the data, find patterns in it and make predictions. While training, the model learns these patterns in the dataset and applies them to test data for prediction. While making predictions, a difference occurs between prediction values made by the model and actual values/expected values, and this difference is known as bias errors or Errors due to bias. It can be defined as an inability of machine learning algorithms such as Linear Regression to capture the true relationship between the data points. Each algorithm begins with some amount of bias because bias occurs from assumptions in the model, which makes the target function simple to learn. A model has either:
Generally, a linear algorithm has a high bias, as it makes them learn fast. The simpler the algorithm, the higher the bias it has likely to be introduced. Whereas a nonlinear algorithm often has low bias. Some examples of machine learning algorithms with low bias are Decision Trees, k-Nearest Neighbours and Support Vector Machines. At the same time, an algorithm with high bias is Linear Regression, Linear Discriminant Analysis and Logistic Regression. Ways to reduce High Bias:High bias mainly occurs due to a much simple model. Below are some ways to reduce the high bias:
What is a Variance Error?The variance would specify the amount of variation in the prediction if the different training data was used. In simple words, variance tells that how much a random variable is different from its expected value. Ideally, a model should not vary too much from one training dataset to another, which means the algorithm should be good in understanding the hidden mapping between inputs and output variables. Variance errors are either of low variance or high variance. Low variance means there is a small variation in the prediction of the target function with changes in the training data set. At the same time, High variance shows a large variation in the prediction of the target function with changes in the training dataset. A model that shows high variance learns a lot and perform well with the training dataset, and does not generalize well with the unseen dataset. As a result, such a model gives good results with the training dataset but shows high error rates on the test dataset. Since, with high variance, the model learns too much from the dataset, it leads to overfitting of the model. A model with high variance has the below problems:
Usually, nonlinear algorithms have a lot of flexibility to fit the model, have high variance. 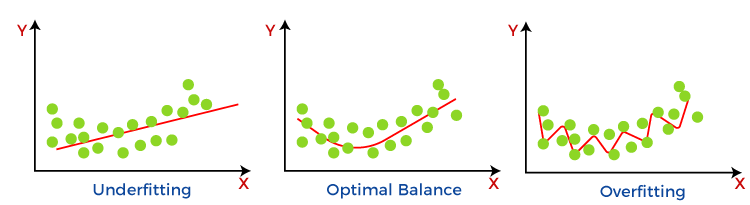
Some examples of machine learning algorithms with low variance are, Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, and Linear discriminant analysis. At the same time, algorithms with high variance are decision tree, Support Vector Machine, and K-nearest neighbours. Ways to Reduce High Variance:
Different Combinations of Bias-VarianceThere are four possible combinations of bias and variances, which are represented by the below diagram: 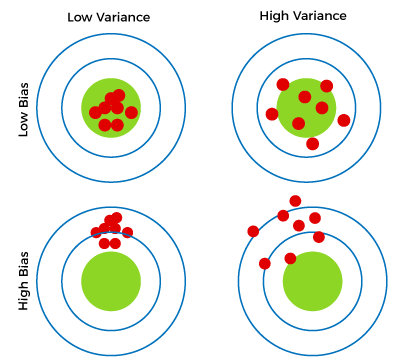
How to identify High variance or High Bias?High variance can be identified if the model has: 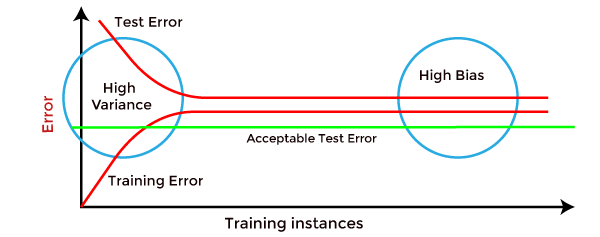
High Bias can be identified if the model has:
Bias-Variance Trade-OffWhile building the machine learning model, it is really important to take care of bias and variance in order to avoid overfitting and underfitting in the model. If the model is very simple with fewer parameters, it may have low variance and high bias. Whereas, if the model has a large number of parameters, it will have high variance and low bias. So, it is required to make a balance between bias and variance errors, and this balance between the bias error and variance error is known as the Bias-Variance trade-off. 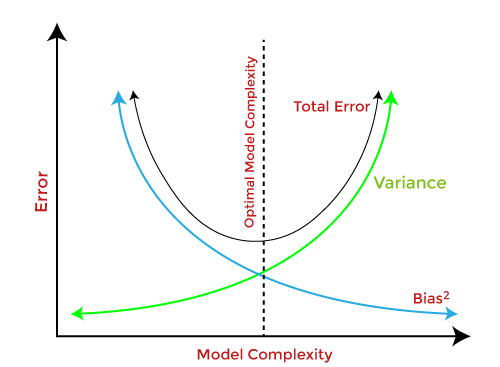
For an accurate prediction of the model, algorithms need a low variance and low bias. But this is not possible because bias and variance are related to each other:
Bias-Variance trade-off is a central issue in supervised learning. Ideally, we need a model that accurately captures the regularities in training data and simultaneously generalizes well with the unseen dataset. Unfortunately, doing this is not possible simultaneously. Because a high variance algorithm may perform well with training data, but it may lead to overfitting to noisy data. Whereas, high bias algorithm generates a much simple model that may not even capture important regularities in the data. So, we need to find a sweet spot between bias and variance to make an optimal model. Hence, the Bias-Variance trade-off is about finding the sweet spot to make a balance between bias and variance errors.
Next TopicMachine Learning Tools
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share