Logistic Regression in Machine Learning
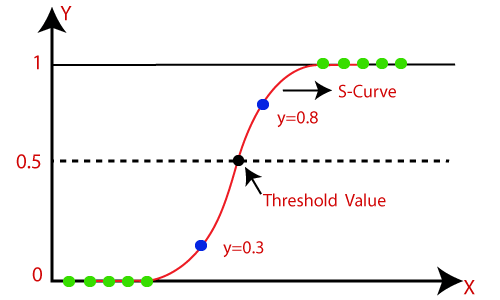
Note: Logistic regression uses the concept of predictive modeling as regression; therefore, it is called logistic regression, but is used to classify samples; Therefore, it falls under the classification algorithm.Logistic Function (Sigmoid Function):
Assumptions for Logistic Regression:
Logistic Regression Equation:The Logistic regression equation can be obtained from the Linear Regression equation. The mathematical steps to get Logistic Regression equations are given below:
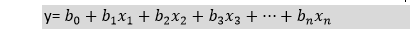
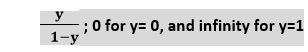
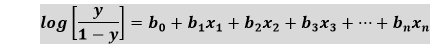
The above equation is the final equation for Logistic Regression. Type of Logistic Regression:On the basis of the categories, Logistic Regression can be classified into three types:
Python Implementation of Logistic Regression (Binomial)To understand the implementation of Logistic Regression in Python, we will use the below example: Example: There is a dataset given which contains the information of various users obtained from the social networking sites. There is a car making company that has recently launched a new SUV car. So the company wanted to check how many users from the dataset, wants to purchase the car. For this problem, we will build a Machine Learning model using the Logistic regression algorithm. The dataset is shown in the below image. In this problem, we will predict the purchased variable (Dependent Variable) by using age and salary (Independent variables). 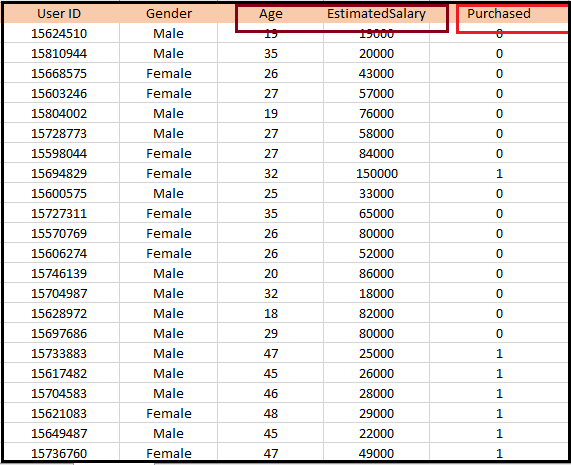
Steps in Logistic Regression: To implement the Logistic Regression using Python, we will use the same steps as we have done in previous topics of Regression. Below are the steps:
1. Data Pre-processing step: In this step, we will pre-process/prepare the data so that we can use it in our code efficiently. It will be the same as we have done in Data pre-processing topic. The code for this is given below: By executing the above lines of code, we will get the dataset as the output. Consider the given image: 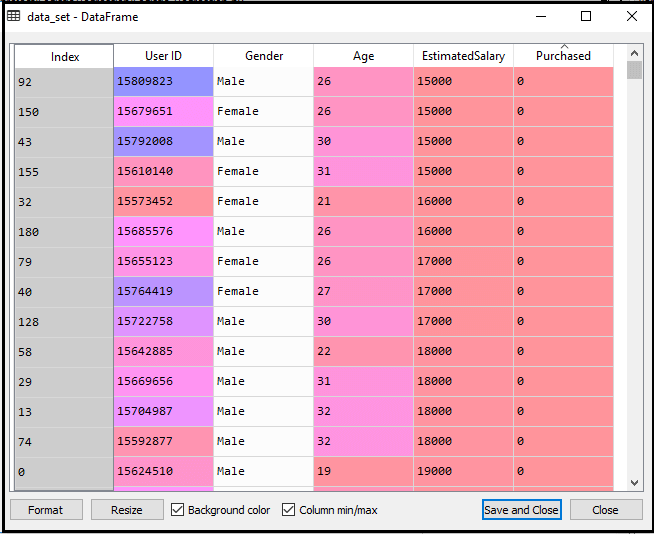
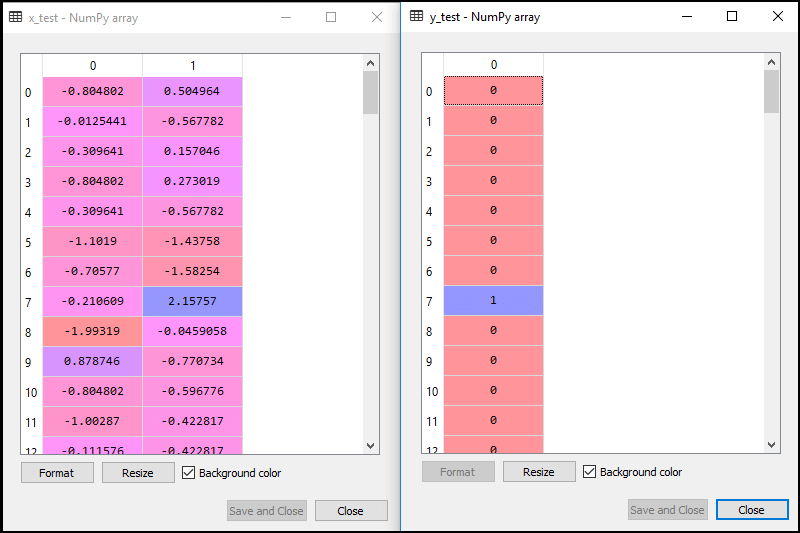
Now, we will extract the dependent and independent variables from the given dataset. Below is the code for it: In the above code, we have taken [2, 3] for x because our independent variables are age and salary, which are at index 2, 3. And we have taken 4 for y variable because our dependent variable is at index 4. The output will be: 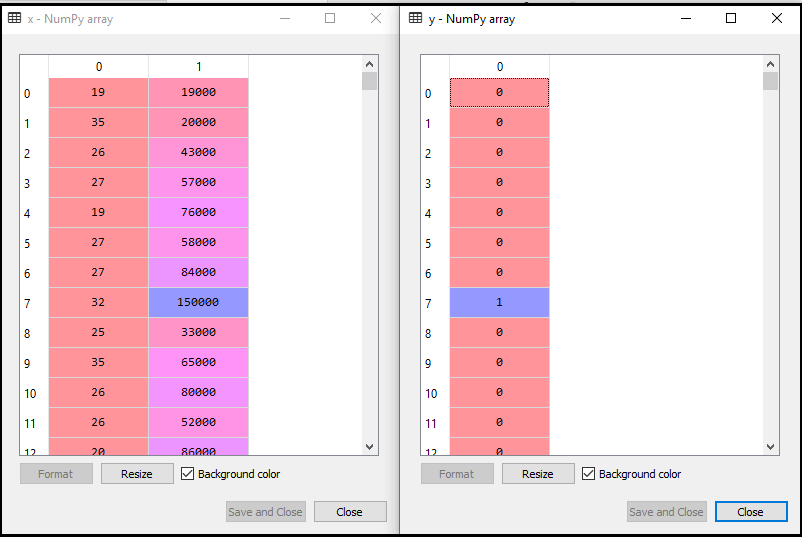
Now we will split the dataset into a training set and test set. Below is the code for it: The output for this is given below: For test set:
For training set: 
In logistic regression, we will do feature scaling because we want accurate result of predictions. Here we will only scale the independent variable because dependent variable have only 0 and 1 values. Below is the code for it: The scaled output is given below: 
2. Fitting Logistic Regression to the Training set: We have well prepared our dataset, and now we will train the dataset using the training set. For providing training or fitting the model to the training set, we will import the LogisticRegression class of the sklearn library. After importing the class, we will create a classifier object and use it to fit the model to the logistic regression. Below is the code for it: Output: By executing the above code, we will get the below output: Out[5]: Hence our model is well fitted to the training set. 3. Predicting the Test Result Our model is well trained on the training set, so we will now predict the result by using test set data. Below is the code for it: In the above code, we have created a y_pred vector to predict the test set result. Output: By executing the above code, a new vector (y_pred) will be created under the variable explorer option. It can be seen as: 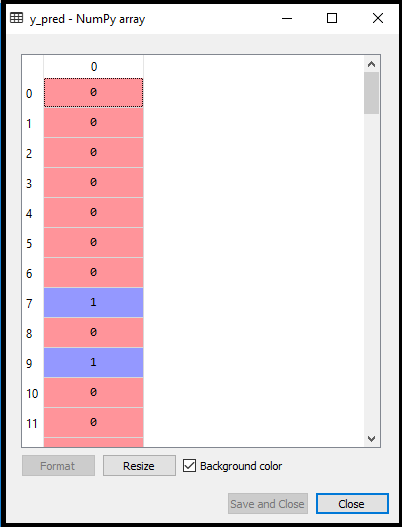
The above output image shows the corresponding predicted users who want to purchase or not purchase the car. 4. Test Accuracy of the result Now we will create the confusion matrix here to check the accuracy of the classification. To create it, we need to import the confusion_matrix function of the sklearn library. After importing the function, we will call it using a new variable cm. The function takes two parameters, mainly y_true( the actual values) and y_pred (the targeted value return by the classifier). Below is the code for it: Output: By executing the above code, a new confusion matrix will be created. Consider the below image: 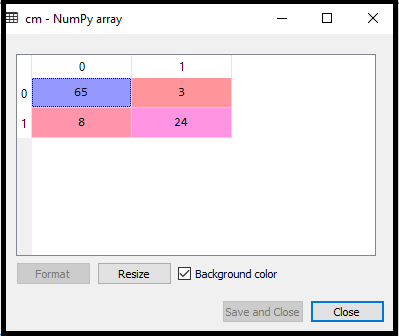
We can find the accuracy of the predicted result by interpreting the confusion matrix. By above output, we can interpret that 65+24= 89 (Correct Output) and 8+3= 11(Incorrect Output). 5. Visualizing the training set result Finally, we will visualize the training set result. To visualize the result, we will use ListedColormap class of matplotlib library. Below is the code for it: In the above code, we have imported the ListedColormap class of Matplotlib library to create the colormap for visualizing the result. We have created two new variables x_set and y_set to replace x_train and y_train. After that, we have used the nm.meshgrid command to create a rectangular grid, which has a range of -1(minimum) to 1 (maximum). The pixel points we have taken are of 0.01 resolution. To create a filled contour, we have used mtp.contourf command, it will create regions of provided colors (purple and green). In this function, we have passed the classifier.predict to show the predicted data points predicted by the classifier. Output: By executing the above code, we will get the below output: 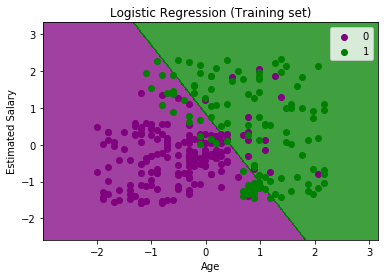
The graph can be explained in the below points:
The goal of the classifier: We have successfully visualized the training set result for the logistic regression, and our goal for this classification is to divide the users who purchased the SUV car and who did not purchase the car. So from the output graph, we can clearly see the two regions (Purple and Green) with the observation points. The Purple region is for those users who didn't buy the car, and Green Region is for those users who purchased the car. Linear Classifier: As we can see from the graph, the classifier is a Straight line or linear in nature as we have used the Linear model for Logistic Regression. In further topics, we will learn for non-linear Classifiers. Visualizing the test set result: Our model is well trained using the training dataset. Now, we will visualize the result for new observations (Test set). The code for the test set will remain same as above except that here we will use x_test and y_test instead of x_train and y_train. Below is the code for it: Output: 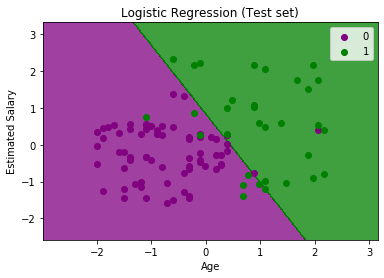
The above graph shows the test set result. As we can see, the graph is divided into two regions (Purple and Green). And Green observations are in the green region, and Purple observations are in the purple region. So we can say it is a good prediction and model. Some of the green and purple data points are in different regions, which can be ignored as we have already calculated this error using the confusion matrix (11 Incorrect output). Hence our model is pretty good and ready to make new predictions for this classification problem.
Next TopicK-Nearest Neighbor(KNN) Algorithm
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share