Precision and Recall in Machine LearningWhile building any machine learning model, the first thing that comes to our mind is how we can build an accurate & 'good fit' model and what the challenges are that will come during the entire procedure. Precision and Recall are the two most important but confusing concepts in Machine Learning. Precision and recall are performance metrics used for pattern recognition and classification in machine learning. These concepts are essential to build a perfect machine learning model which gives more precise and accurate results. Some of the models in machine learning require more precision and some model requires more recall. So, it is important to know the balance between Precision and recall or, simply, precision-recall trade-off. 
In this article, we will understand Precision and recall, the most confusing but important concepts in machine learning that lots of professionals face during their entire data science & machine learning career. But before starting, first, we need to understand the confusion matrix concept. So, let's start with the quick introduction of Confusion Matrix in Machine Learning. Confusion Matrix in Machine LearningConfusion Matrix helps us to display the performance of a model or how a model has made its prediction in Machine Learning. Confusion Matrix helps us to visualize the point where our model gets confused in discriminating two classes. It can be understood well through a 2×2 matrix where the row represents the actual truth labels, and the column represents the predicted labels. 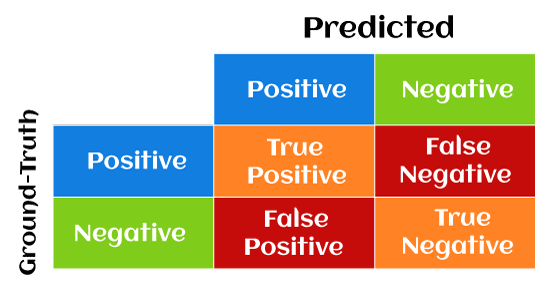
This matrix consists of 4 main elements that show different metrics to count a number of correct and incorrect predictions. Each element has two words either as follows:
If the predicted and truth labels match, then the prediction is said to be correct, but when the predicted and truth labels are mismatched, then the prediction is said to be incorrect. Further, positive and negative represents the predicted labels in the matrix. There are four metrics combinations in the confusion matrix, which are as follows:
Hence, we can calculate the total of 7 predictions in binary classification problems using a confusion matrix. Now we can understand the concepts of Precision and Recall. What is Precision?Precision is defined as the ratio of correctly classified positive samples (True Positive) to a total number of classified positive samples (either correctly or incorrectly).
Hence, precision helps us to visualize the reliability of the machine learning model in classifying the model as positive. Examples to calculate the Precision in the machine learning modelBelow are some examples for calculating Precision in Machine Learning: Case 1- In the below-mentioned scenario, the model correctly classified two positive samples while incorrectly classified one negative sample as positive. Hence, according to precision formula; 
Precision = TP/TP+FP Precision = 2/2+1 = 2/3 = 0.667 Case 2- In this scenario, we have three Positive samples that are correctly classified, and one Negative sample is incorrectly classified. Put TP =3 and FP =1 in the precision formula, we get; 
Precision = TP/TP+FP Precision = 3/3+1 = 3/4 = 0.75 Case 3- In this scenario, we have three Positive samples that are correctly classified but no Negative sample which is incorrectly classified. Put TP =3 and FP =0 in precision formula, we get; Precision = TP/TP+FP Precision = 3/3+0 = 3/3 = 1 Hence, in the last scenario, we have a precision value of 1 or 100% when all positive samples are classified as positive, and there is no any Negative sample that is incorrectly classified. What is Recall?The recall is calculated as the ratio between the numbers of Positive samples correctly classified as Positive to the total number of Positive samples. The recall measures the model's ability to detect positive samples. The higher the recall, the more positive samples detected.
Unlike Precision, Recall is independent of the number of negative sample classifications. Further, if the model classifies all positive samples as positive, then Recall will be 1. Examples to calculate the Recall in the machine learning modelBelow are some examples for calculating Recall in machine learning as follows Example 1- Let's understand the calculation of Recall with four different cases where each case has the same Recall as 0.667 but differs in the classification of negative samples. See how: 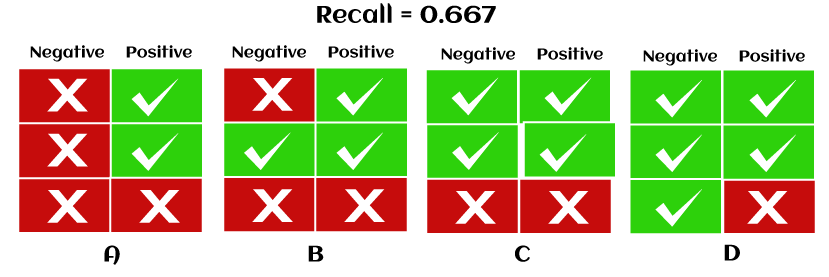
In this scenario, the classification of the negative sample is different in each case. Case A has two negative samples classified as negative, and case B have two negative samples classified as negative; case c has only one negative sample classified as negative, while case d does not classify any negative sample as negative. However, recall is independent of how the negative samples are classified in the model; hence, we can neglect negative samples and only calculate all samples that are classified as positive. 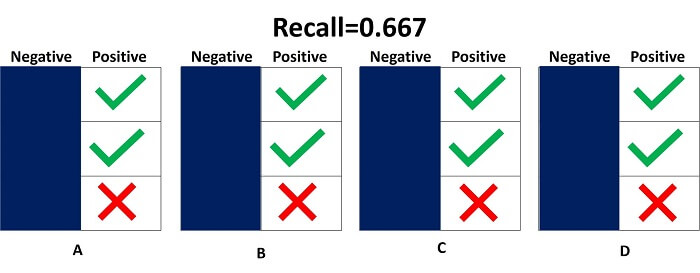
In the above image, we have only two positive samples that are correctly classified as positive while only 1 negative sample that is correctly classified as negative. Hence, true positivity rate is 2 and while false negativity rate is 1. Then recall will be: Recall = TP/TP+FN =2/(2+1) =2/3 =0.667 Note: This means the model has correctly classified only 0.667% of Positive SamplesExample-2 Now, we have another scenario where all positive samples are classified correctly as positive. Hence, the True Positive rate is 3 while the False Negative rate is 0. 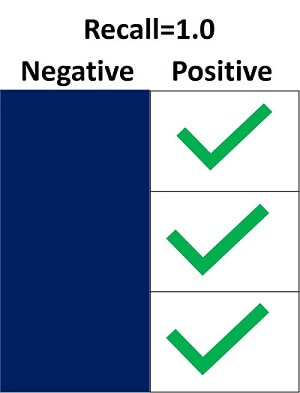
Recall = TP/TP+FN = 3/(3+0) =3/3 =1 If the recall is 100%, then it tells us the model has detected all positive samples as positive and neglects how all negative samples are classified in the model. However, the model could still have so many samples that are classified as negative but recall just neglect those samples, which results in a high False Positive rate in the model. Note: This means the model has correctly classified 100% of Positive Samples.Example-3 In this scenario, the model does not identify any positive sample that is classified as positive. All positive samples are incorrectly classified as Negative. Hence, the true positive rate is 0, and the False Negative rate is 3. Then Recall will be: Recall = TP/TP+FN = 0/(0+3) =0/3 =0 This means the model has not correctly classified any Positive Samples. Difference between Precision and Recall in Machine Learning
Why use Precision and Recall in Machine Learning models?This question is very common among all machine learning engineers and data researchers. The use of Precision and Recall varies according to the type of problem being solved.
Conclusion:In this tutorial, we have discussed various performance metrics such as confusion matrix, Precision, and Recall for binary classification problems of a machine learning model. Also, we have seen various examples to calculate Precision and Recall of a machine learning model and when we should use precision, and when to use Recall.
Next TopicGenetic Algorithm in Machine Learning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









