Overfitting in Machine LearningIn the real world, the dataset present will never be clean and perfect. It means each dataset contains impurities, noisy data, outliers, missing data, or imbalanced data. Due to these impurities, different problems occur that affect the accuracy and the performance of the model. One of such problems is Overfitting in Machine Learning. Overfitting is a problem that a model can exhibit. A statistical model is said to be overfitted if it can’t generalize well with unseen data. Before understanding overfitting, we need to know some basic terms, which are: Noise: Noise is meaningless or irrelevant data present in the dataset. It affects the performance of the model if it is not removed. Bias: Bias is a prediction error that is introduced in the model due to oversimplifying the machine learning algorithms. Or it is the difference between the predicted values and the actual values. Variance: If the machine learning model performs well with the training dataset, but does not perform well with the test dataset, then variance occurs. Generalization: It shows how well a model is trained to predict unseen data. What is Overfitting?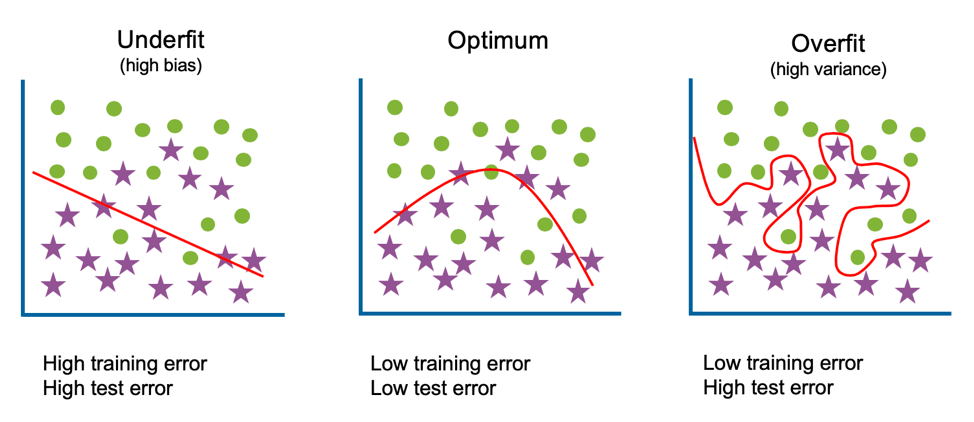
Example to Understand OverfittingWe can understand overfitting with a general example. Suppose there are three students, X, Y, and Z, and all three are preparing for an exam. X has studied only three sections of the book and left all other sections. Y has a good memory, hence memorized the whole book. And the third student, Z, has studied and practiced all the questions. So, in the exam, X will only be able to solve the questions if the exam has questions related to section 3. Student Y will only be able to solve questions if they appear exactly the same as given in the book. Student Z will be able to solve all the exam questions in a proper way. The same happens with machine learning; if the algorithm learns from a small part of the data, it is unable to capture the required data points and hence under fitted. Suppose the model learns the training dataset, like the Y student. They perform very well on the seen dataset but perform badly on unseen data or unknown instances. In such cases, the model is said to be Overfitting. And if the model performs well with the training dataset and also with the test/unseen dataset, similar to student Z, it is said to be a good fit. How to detect Overfitting?Overfitting in the model can only be detected once you test the data. To detect the issue, we can perform Train/test split. In the train-test split of the dataset, we can divide our dataset into random test and training datasets. We train the model with a training dataset which is about 80% of the total dataset. After training the model, we test it with the test dataset, which is 20 % of the total dataset. 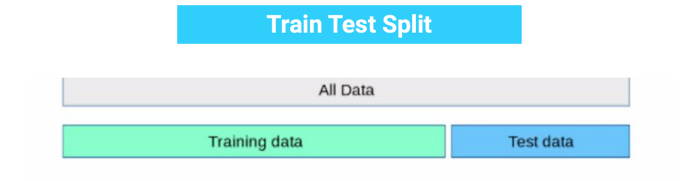
Now, if the model performs well with the training dataset but not with the test dataset, then it is likely to have an overfitting issue. For example, if the model shows 85% accuracy with training data and 50% accuracy with the test dataset, it means the model is not performing well. 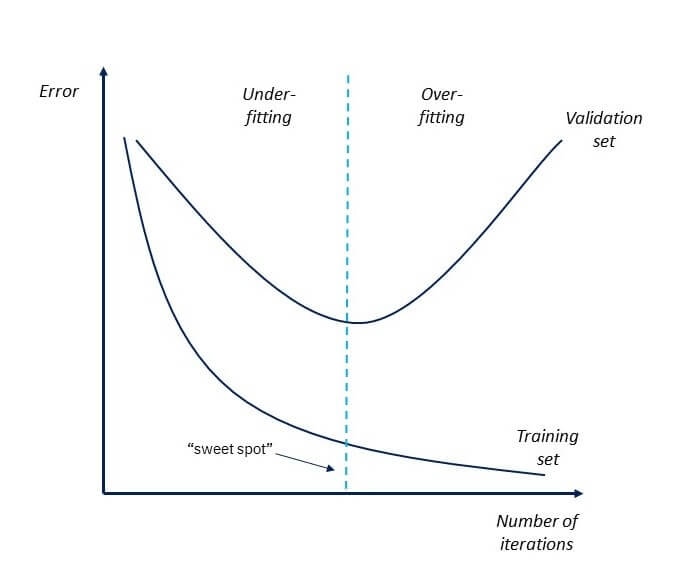
Ways to prevent the OverfittingAlthough overfitting is an error in Machine learning which reduces the performance of the model, however, we can prevent it in several ways. With the use of the linear model, we can avoid overfitting; however, many real-world problems are non-linear ones. It is important to prevent overfitting from the models. Below are several ways that can be used to prevent overfitting:
Early StoppingIn this technique, the training is paused before the model starts learning the noise within the model. In this process, while training the model iteratively, measure the performance of the model after each iteration. Continue up to a certain number of iterations until a new iteration improves the performance of the model. After that point, the model begins to overfit the training data; hence we need to stop the process before the learner passes that point. Stopping the training process before the model starts capturing noise from the data is known as early stopping. 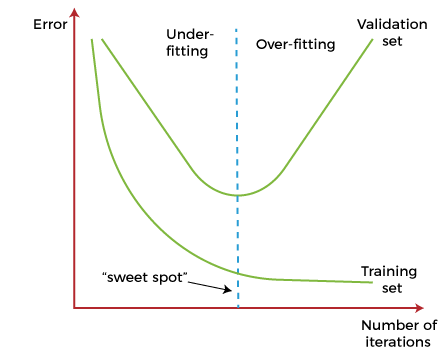
However, this technique may lead to the underfitting problem if training is paused too early. So, it is very important to find that "sweet spot" between underfitting and overfitting. Train with More dataIncreasing the training set by including more data can enhance the accuracy of the model, as it provides more chances to discover the relationship between input and output variables. It may not always work to prevent overfitting, but this way helps the algorithm to detect the signal better to minimize the errors. When a model is fed with more training data, it will be unable to overfit all the samples of data and forced to generalize well. But in some cases, the additional data may add more noise to the model; hence we need to be sure that data is clean and free from in-consistencies before feeding it to the model. Feature SelectionWhile building the ML model, we have a number of parameters or features that are used to predict the outcome. However, sometimes some of these features are redundant or less important for the prediction, and for this feature selection process is applied. In the feature selection process, we identify the most important features within training data, and other features are removed. Further, this process helps to simplify the model and reduces noise from the data. Some algorithms have the auto-feature selection, and if not, then we can manually perform this process. Cross-ValidationCross-validation is one of the powerful techniques to prevent overfitting. In the general k-fold cross-validation technique, we divided the dataset into k-equal-sized subsets of data; these subsets are known as folds. Data AugmentationData Augmentation is a data analysis technique, which is an alternative to adding more data to prevent overfitting. In this technique, instead of adding more training data, slightly modified copies of already existing data are added to the dataset. The data augmentation technique makes it possible to appear data sample slightly different every time it is processed by the model. Hence each data set appears unique to the model and prevents overfitting. RegularizationIf overfitting occurs when a model is complex, we can reduce the number of features. However, overfitting may also occur with a simpler model, more specifically the Linear model, and for such cases, regularization techniques are much helpful. Regularization is the most popular technique to prevent overfitting. It is a group of methods that forces the learning algorithms to make a model simpler. Applying the regularization technique may slightly increase the bias but slightly reduces the variance. In this technique, we modify the objective function by adding the penalizing term, which has a higher value with a more complex model. The two commonly used regularization techniques are L1 Regularization and L2 Regularization. Ensemble MethodsIn ensemble methods, prediction from different machine learning models is combined to identify the most popular result. The most commonly used ensemble methods are Bagging and Boosting. In bagging, individual data points can be selected more than once. After the collection of several sample datasets, these models are trained independently, and depending on the type of task-i.e., regression or classification-the average of those predictions is used to predict a more accurate result. Moreover, bagging reduces the chances of overfitting in complex models. In boosting, a large number of weak learners arranged in a sequence are trained in such a way that each learner in the sequence learns from the mistakes of the learner before it. It combines all the weak learners to come out with one strong learner. In addition, it improves the predictive flexibility of simple models.
Next TopicTypes of Encoding Techniques
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










