Bagging Machine LearningIntroductionIn this tutorial, we discuss bagging in machine learning. Bagging, or bootstrap aggregation, is the ensemble getting-to-know method generally used to lessen variance within a loud dataset. In Bagging, a random pattern of statistics in this study set is selected with replacement, meaning that the character statistics factors may be chosen more soon as possible. After numerous facts samples are generated, those susceptible fashions are trained independently. For example, the common or Majority of these predictions yield a correct estimate depending on the sort of task- regression or type. As a note, the random woodland set of rules is considered an extension of the bagging approach, using both bagging and function randomness to create an uncorrelated wooded area of selection trees. The Bagging is an assembling approach that tries to resolve overfitting for class or the regression problems. Bagging pursuits to improve the accuracy and overall performance of gadget mastering algorithms. It does this by taking random subsets of an original dataset, with substitute, and fits either a classifier (for classification) or regressor (for regression) to each subset. Bagging is also known as Bootstrap aggregating. It is an ensemble learning approach that enhances the overall performance and accuracy of the gadget for learning algorithms. It is miles used to address bias-variance alternate-off increases and decreases the variance of a prediction version. The Bagging avoids overfitting of data and is used for each regression and classification of the class, in particular for the decision tree algorithms. What is Ensemble Learning?Ensemble learning gives us credence to the idea of the "wisdom of crowds," it suggests that the choice-making for a more extensive organization of humans is usually higher than that of an individual professional. Another side, ensemble learning refers to a collection (or ensemble) of base newbies or fashions, which are paintings collectively to attain a better very last of the prediction. A single model, also called a base or susceptible learner, may not perform well due to high variance or bias. But, while vulnerable learners are aggregated, they could shape a sturdy learner, as their combination reduces bias or variance, yielding higher model performance. Ensemble learning is a widely used and desired tool learning technique in which more than one person models, often referred to as base models, are blended to produce a powerful ideal of the prediction version. An example of ensemble learning is the Random Forest algorithm. Ensemble learning is frequently illustrated using selection timber as this algorithm may be liable to overfitting (excessive variance and low bias) when it has not been pruned. It could additionally lend itself to underfitting (low variance and extreme bias) when it is very small, like a decision stump, a decision tree with one stage. While an algorithm overfits or fits its education set, it cannot generalize nicely to new datasets, so ensemble strategies are used to counteract this conduct to allow for the generalization of the model to new datasets. While selection timber can showcase excessive variance or high bias, it is worth noting that it is not the best modelling approach that leverages ensemble learning to find the "sweet spot" in the bias-variance trade-off. What is the difference between Bagging and Boosting?There are some differences between Bagging and boosting. These are two principal forms of ensemble studying strategies. The main difference between these two learning strategies is the way they are skilled. In the bagging technique, it is vulnerable newcomers trained in parallel. But in the boosting, they are trained sequentially. This means that a sequence of fashions is constructed, and with each new version generation, the weights of the misclassified information in the preceding version are improved. This redistribution of weights enables the algorithm to perceive the parameters it wishes to the consciousness of to enhance its performance. AdaBoost, which stands for "adaptative boosting set of rules," is onemost maximum famous boosting algorithmbecamened into one of the first of its kind. Different varieties of boosting algorithms consist of XGBoost, GradientBoost, and BrownBoost. Another difference between Bagging and boosting is the scenarios wherein they may be used. For example, bagging strategies or techniques are usually used on susceptible novices, mainly showcasing excessive variance and occasional bias. But the boosting plans are leveraged while low friction and high tendency are located. Difference between bagging and boosting are:
What are the similarities between Bagging and Boosting?The similarities between Bagging and boosting are the commonly used strategies with a general similarity of being labelled as ensemble strategies. Now here we will briefly explain the similarities between Bagging and boosting.
Describe the Bagging Technique:Assume the set D of d tuples, at each iteration I, a schooling set Di of d tuples is selected thru row sampling with a substitute approach (i.e., there may be repetitive factors from distinct d tuples) from D (i.e., bootstrap). Then a classifier version Mi is discovered for each training set D < i. every classifier Mi returns its class prediction. The bagged classifier M* counts the votes and assigns the class with the most votes to X (unknown pattern). What are the Implementation Steps of Bagging?
Application of the Bagging:There are various applications of Bagging, which are given below - 1. IT: Bagging can also improve the precision and accuracy of IT structures, together with network intrusion detection structures. In the meantime, this study seems at how Bagging can enhance the accuracy of network intrusion detection and reduce the rates of fake positives. 2. Environment: Ensemble techniques, together with Bagging, were carried out inside the area of far-flung sensing. This study indicates how it has been used to map the styles of wetlands inside a coastal landscape. 3. Finance: Bagging has also been leveraged with deep gaining knowledge of models within the finance enterprise, automating essential tasks, along with fraud detection, credit risk reviews, and option pricing issues. This research demonstrates how Bagging amongst different device studying techniques was leveraged to assess mortgage default hazard. This highlights how Bagging limits threats by saving you from credit score card fraud within the banking and economic institutions. 4. Healthcare: The Bagging has been used to shape scientific data predictions. These studies (PDF, 2.8 MB) show that ensemble techniques had been used for various bioinformatics issues, including gene and protein selection, to perceive a selected trait of interest. More significantly, this study mainly delves into its use to expect the onset of diabetes based on various threat predictors. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Bagging?Advantages of Bagging are -There are many advantages of Bagging. The benefit of Bagging is given below - 1. Easier for implementation: Python libraries, including scikit-examine (sklearn), make it easy to mix the predictions of base beginners or estimators to enhance model performance. Their documentation outlines the available modules you can leverage for your model optimization. 2. Variance reduction: The Bagging can reduce the variance inside a getting to know set of rules which is especially helpful with excessive-dimensional facts, where missing values can result in better conflict, making it more liable to overfitting and stopping correct generalization to new datasets. Disadvantages of Bagging are -There are many disadvantages of Bagging. The disadvantages of Bagging are given below - 1. Flexible less: As a method, Bagging works particularly correctly with algorithms that are much less solid. One which can be more stable or a problem with high amounts of bias does now not provide an awful lot of gain as there is less variation in the dataset of the version. As noted within the hands-On guide for machine learning, "the bagging is a linear regression version will efficaciously just return the original predictions for huge enough b." 2. Loss of interpretability: The Bagging slows down and grows extra in depth because of the quantity of iterations growth. accordingly, it is no longer adequately suitable for actual-time applications. Clustered structures or large processing cores are perfect for quickly growing bagged ensembles on massive look-at units. 3. Expensive for computation: The Bagging is tough to draw unique business insights via Bagging because of the averaging concerned throughout predictions. While the output is more precise than any person's information point, a more accurate or whole dataset may yield greater precision within a single classification or regression model. Bagging classifier example:Example: Here we give an example of a bagging classifier using python. The example is given below - Output: By utilizing iterating thru exceptional values for the range of estimators, we will see an increase in version overall performance from 82.2% to 95.5%. After 14 estimators, the accuracy begins to drop, and once more, if you set an exceptional random_state, the values you see will range. This is why cross-validation is an adequate exercise to ensure solid consequences. In this case, we see a 13.3% boom in accuracy concerning identifying the type of wine. Now we compile the above program and then run it. After that, the output is screened below - 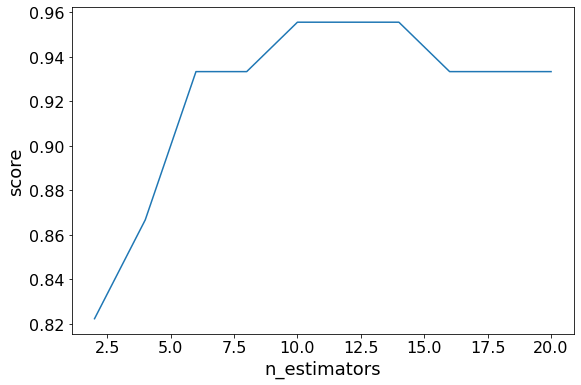
Another form for the Evaluation:As bootstrapping chooses random subsets of observations to create classifiers, some observations might need to be addressed in the selection process. Those "out-of-bag" observations can then be used to assess the model in addition to that of a test set. Remember that out-of-bag estimation can overestimate mistakes in binary class troubles and should be used as praise to different metrics. We saw in the remaining exercise that 12 estimators yielded the very best accuracy, so we can use that to create our model-this time setting the parameter oob_score to proper to evaluate the model without-of-bag rating. Example: Here we give an example of "out of the bag" using python. The example is given below - Output: Now we compile the above program and then run it. After that, the output is screened below - 0.8951612903225806
Next TopicBERT Applications
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









