Majority Voting Algorithm in Machine Learning
In the realm of machine learning, an exciting technique called the Majority Voting Algorithm is making waves. This ingenious approach allows multiple models to collaborate and make decisions as a team, resulting in more accurate predictions. By harnessing the wisdom of the crowd, the Majority Voting Algorithm has become a valuable tool for enhancing prediction accuracy across various applications. In this article, we will explore the concept of Majority Voting, how it works, and its applications in the world of machine learning.
Understanding Majority Voting
At its core, the Majority Voting Algorithm is a simple yet effective ensemble learning method. Ensemble learning involves combining the predictions of multiple models to create a more robust and reliable final prediction. In Majority Voting, a group of diverse machine learning models is trained on the same dataset, each employing unique algorithms or techniques. When it's time to make a prediction, each model casts its vote for the outcome, and the final prediction is determined by the majority's decision.
How Majority Voting Works
Let's break down the Majority Voting process into easy-to-understand steps:
- Training Phase: Gather a diverse set of machine learning models, such as Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests, or Logistic Regression. Train each model on the same dataset using a specific subset of features and instances.
- Prediction Phase: When a new data point needs to be predicted, each trained model receives the data as input. All models independently make their predictions based on their unique knowledge and understanding of the data.
Each model's prediction is treated as a "vote" for a particular class label.
- Majority Decision: The final prediction is determined by the class label that receives the most votes from the individual models. In case of a tie, the algorithm can employ various tie-breaking strategies, such as selecting the first or last prediction.
Applications of Majority Voting Algorithm in Machine Learning
The Majority Voting Algorithm finds applications in various real-world scenarios, including:
- In the field of healthcare, accurate diagnosis plays a vital role in providing timely and effective treatments. The Majority Voting Algorithm can be applied to medical datasets to combine predictions from different diagnostic models. By aggregating the expertise of various models, it enhances the accuracy of disease detection and helps medical professionals make more informed decisions.
- Detecting fraudulent activities is a critical task in many industries, such as finance and e-commerce. By employing the Majority Voting Algorithm, multiple fraud detection models can work together to identify suspicious transactions or behaviors. The combined predictions improve the accuracy of fraud detection systems, reducing false positives and minimizing financial losses.
- Image classification tasks, such as object recognition and scene understanding, can benefit from the Majority Voting Algorithm. By leveraging multiple image classification models, the algorithm can make more accurate predictions, even in challenging scenarios. It enhances the robustness of image recognition systems, enabling applications like autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and medical imaging.
- In the field of natural language processing, the Majority Voting Algorithm can be utilized for tasks such as sentiment analysis, text classification, and spam filtering. Combining predictions from different language models enhances the accuracy of text-based applications. This approach helps improve customer sentiment analysis, content moderation, and personalized recommendation systems.
- Credit scoring models are used to assess the creditworthiness of individuals or businesses. The Majority Voting Algorithm can combine the predictions from various credit scoring models to make more reliable credit decisions. By considering multiple perspectives, it reduces the risk of incorrect credit assessments and improves lending practices.
Advantages of Majority Voting Algorithm in Machine Learning
The Majority Voting Algorithm offers several benefits and finds applications in various domains:
- The primary advantage of the Majority Voting Algorithm is its ability to improve prediction accuracy. Combining the predictions from multiple models leverages the strengths and compensates for the weaknesses of individual models. The aggregated prediction tends to be more reliable and robust, resulting in enhanced overall accuracy.
- Different machine learning models may have inherent biases due to their design or training data. By utilizing the Majority Voting Algorithm, these biases can be mitigated or even eliminated to a certain extent. The algorithm ensures that predictions are based on a diverse set of models, reducing the influence of individual biases and promoting fair and unbiased decision-making.
- The Majority Voting Algorithm enhances the robustness of machine learning systems. It reduces the risk of making incorrect predictions caused by the instability or limitations of individual models. By combining predictions, the algorithm creates a more stable and reliable decision-making framework that can handle diverse data patterns and adapt to different scenarios.
- In situations where individual models produce conflicting predictions or have uncertainties, the Majority Voting Algorithm provides a mechanism to handle such uncertainties effectively. It considers the collective opinion of multiple models, which helps in making more informed decisions and reducing the impact of individual model variations or outliers.
- The Majority Voting Algorithm is flexible and compatible with various machine learning models and algorithms. It can be applied to both classification and regression problems, accommodating a wide range of applications. This versatility makes it suitable for diverse domains and allows integration with existing machine-learning pipelines.
Implementation of Majority Voting Algorithm in Machine Learning
Output:
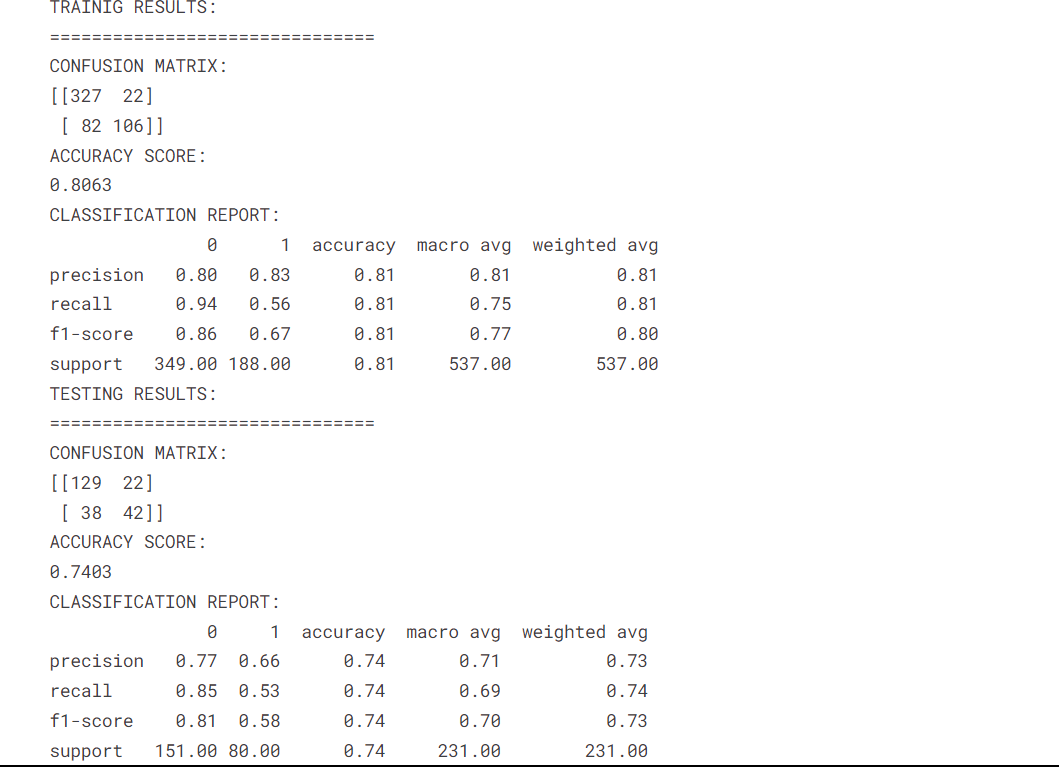
This Voting classifier combines the predictions of multiple individual classifiers, in this case, Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, and Support Vector Machine (SVM). The aim is to leverage the collective decision-making of these classifiers to improve overall prediction performance.
Conclusion
The Majority Voting Algorithm is a straightforward yet powerful technique in machine learning. By aggregating predictions from multiple models, it harnesses the collective wisdom to arrive at consensus-based decisions. Its simplicity, robustness, and improved accuracy make it a valuable tool in various domains. As machine learning continues to advance, the Majority Voting Algorithm will continue to play a significant role in ensemble learning and decision-making.
|


 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










