Genetic Algorithm in Machine Learning
A genetic algorithm is an adaptive heuristic search algorithm inspired by "Darwin's theory of evolution in Nature." It is used to solve optimization problems in machine learning. It is one of the important algorithms as it helps solve complex problems that would take a long time to solve.
Genetic Algorithms are being widely used in different real-world applications, for example, Designing electronic circuits, code-breaking, image processing, and artificial creativity.
In this topic, we will explain Genetic algorithm in detail, including basic terminologies used in Genetic algorithm, how it works, advantages and limitations of genetic algorithm, etc.
What is a Genetic Algorithm?
Before understanding the Genetic algorithm, let's first understand basic terminologies to better understand this algorithm:
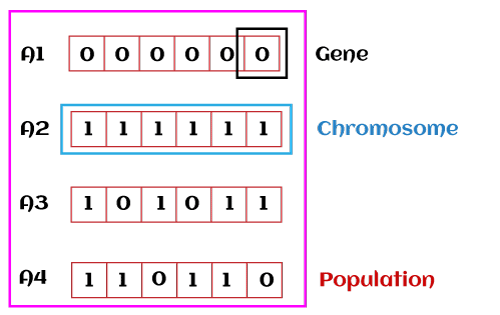
- Population: Population is the subset of all possible or probable solutions, which can solve the given problem.
- Chromosomes: A chromosome is one of the solutions in the population for the given problem, and the collection of gene generate a chromosome.
- Gene: A chromosome is divided into a different gene, or it is an element of the chromosome.
- Allele: Allele is the value provided to the gene within a particular chromosome.
- Fitness Function: The fitness function is used to determine the individual's fitness level in the population. It means the ability of an individual to compete with other individuals. In every iteration, individuals are evaluated based on their fitness function.
- Genetic Operators: In a genetic algorithm, the best individual mate to regenerate offspring better than parents. Here genetic operators play a role in changing the genetic composition of the next generation.
- Selection
After calculating the fitness of every existent in the population, a selection process is used to determine which of the individualities in the population will get to reproduce and produce the seed that will form the coming generation.
Types of selection styles available
- Roulette wheel selection
- Event selection
- Rank- grounded selection
So, now we can define a genetic algorithm as a heuristic search algorithm to solve optimization problems. It is a subset of evolutionary algorithms, which is used in computing. A genetic algorithm uses genetic and natural selection concepts to solve optimization problems.
How Genetic Algorithm Work?
The genetic algorithm works on the evolutionary generational cycle to generate high-quality solutions. These algorithms use different operations that either enhance or replace the population to give an improved fit solution.
It basically involves five phases to solve the complex optimization problems, which are given as below:
- Initialization
- Fitness Assignment
- Selection
- Reproduction
- Termination
1. Initialization
The process of a genetic algorithm starts by generating the set of individuals, which is called population. Here each individual is the solution for the given problem. An individual contains or is characterized by a set of parameters called Genes. Genes are combined into a string and generate chromosomes, which is the solution to the problem. One of the most popular techniques for initialization is the use of random binary strings.
2. Fitness Assignment
Fitness function is used to determine how fit an individual is? It means the ability of an individual to compete with other individuals. In every iteration, individuals are evaluated based on their fitness function. The fitness function provides a fitness score to each individual. This score further determines the probability of being selected for reproduction. The high the fitness score, the more chances of getting selected for reproduction.
3. Selection
The selection phase involves the selection of individuals for the reproduction of offspring. All the selected individuals are then arranged in a pair of two to increase reproduction. Then these individuals transfer their genes to the next generation.
There are three types of Selection methods available, which are:
- Roulette wheel selection
- Tournament selection
- Rank-based selection
4. Reproduction
After the selection process, the creation of a child occurs in the reproduction step. In this step, the genetic algorithm uses two variation operators that are applied to the parent population. The two operators involved in the reproduction phase are given below:
- Crossover: The crossover plays a most significant role in the reproduction phase of the genetic algorithm. In this process, a crossover point is selected at random within the genes. Then the crossover operator swaps genetic information of two parents from the current generation to produce a new individual representing the offspring.
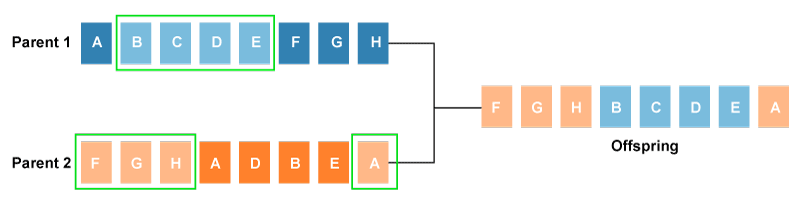
The genes of parents are exchanged among themselves until the crossover point is met. These newly generated offspring are added to the population. This process is also called or crossover. Types of crossover styles available:
- One point crossover
- Two-point crossover
- Livery crossover
- Inheritable Algorithms crossover
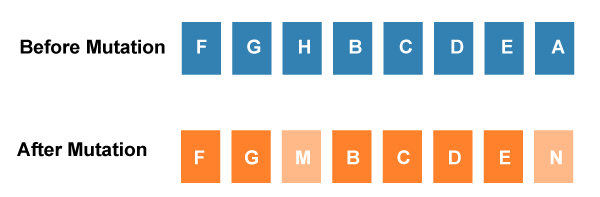
- Mutation
The mutation operator inserts random genes in the offspring (new child) to maintain the diversity in the population. It can be done by flipping some bits in the chromosomes.
Mutation helps in solving the issue of premature convergence and enhances diversification. The below image shows the mutation process:
Types of mutation styles available,
- Flip bit mutation
- Gaussian mutation
- Exchange/Swap mutation
5. Termination
After the reproduction phase, a stopping criterion is applied as a base for termination. The algorithm terminates after the threshold fitness solution is reached. It will identify the final solution as the best solution in the population.
General Workflow of a Simple Genetic Algorithm
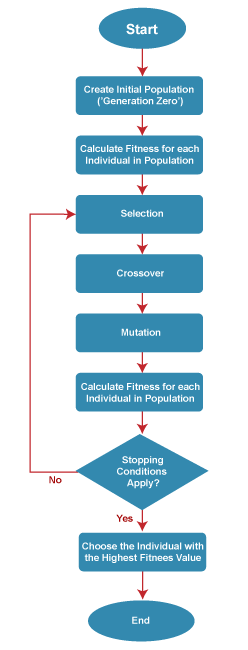
Advantages of Genetic Algorithm
- The parallel capabilities of genetic algorithms are best.
- It helps in optimizing various problems such as discrete functions, multi-objective problems, and continuous functions.
- It provides a solution for a problem that improves over time.
- A genetic algorithm does not need derivative information.
Limitations of Genetic Algorithms
- Genetic algorithms are not efficient algorithms for solving simple problems.
- It does not guarantee the quality of the final solution to a problem.
- Repetitive calculation of fitness values may generate some computational challenges.
Difference between Genetic Algorithms and Traditional Algorithms
- A search space is the set of all possible solutions to the problem. In the traditional algorithm, only one set of solutions is maintained, whereas, in a genetic algorithm, several sets of solutions in search space can be used.
- Traditional algorithms need more information in order to perform a search, whereas genetic algorithms need only one objective function to calculate the fitness of an individual.
- Traditional Algorithms cannot work parallelly, whereas genetic Algorithms can work parallelly (calculating the fitness of the individualities are independent).
- One big difference in genetic Algorithms is that rather of operating directly on seeker results, inheritable algorithms operate on their representations (or rendering), frequently appertained to as chromosomes.
- One of the big differences between traditional algorithm and genetic algorithm is that it does not directly operate on candidate solutions.
- Traditional Algorithms can only generate one result in the end, whereas Genetic Algorithms can generate multiple optimal results from different generations.
- The traditional algorithm is not more likely to generate optimal results, whereas Genetic algorithms do not guarantee to generate optimal global results, but also there is a great possibility of getting the optimal result for a problem as it uses genetic operators such as Crossover and Mutation.
- Traditional algorithms are deterministic in nature, whereas Genetic algorithms are probabilistic and stochastic in nature.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now











