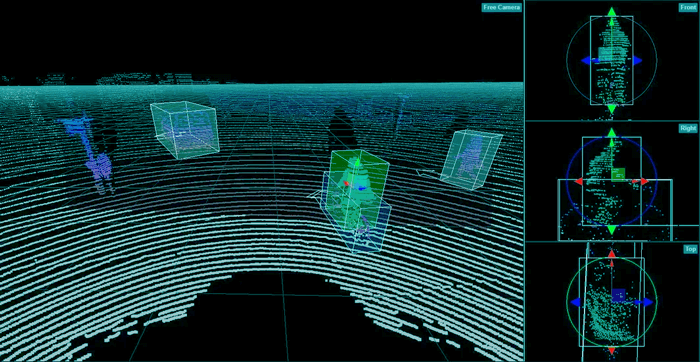
LiDAR: Light Detection and Ranging for 3D ReconstructionWhat is LiDAR?LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, is a system that maps various structures, like height, density, etc, of any object around a region. It is also known as Active Laser Scanning. It can be used in various industries. For instance, it is used in vegetation also. This system can directly measure the height and density of the vegetation on the ground, which helps scientists study vegetation over a huge area. It uses light in a pulsed laser form (in the form of optical pulses or light flashes), which can measure distance. These light pulses and other data points build precise 3-D information about any object related to the environment. It is faster than the RADAR or camera in detecting objects and calculating distance as it is unparalleled in dimensions and depth. Working of LiDARLiDAR ranges the pulsed light to measure the distance to a target position. It is measured by sending a laser and recording the time taken from the source light pulse, and the reflected light pulse. As it is an active system, it generates energy by itself. In the LiDAR system, the light is released from a rapid-firing laser. Firstly, the light travels from the source, moves to the ground, and then reflects the light from the things to be observed. Then, the reflected light energy returns to the LiDAR sensor. The Light Detection and Ranging system calculates the time from the source point to the destination. Then, the time calculated is used to calculate the distance between both points, which further calculates the elevation (the distance above the sea level). These measurements are measured with the help of the LiDAR system components consisting of the GPS system used to get the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the light energy and the Inertial Measurement Unit, which is used to determine the directions of the plane in the sky. The LiDAR system is also used to measure the detailed features of the environment, like the scattering of particles, absorption, or emission in the atmosphere. The systems need specific wavelengths to determine these kinds of features in the environment. The LiDAR system can also measure rain droplets, the amount and intensity of rainfall, and different types of molecules like methane, aerosol, etc. Many LiDAR systems give three-dimensional surfaces in the object space. It does not need any special spectral for observing the 3-D objects. It can be used to make 3-D structures or models in autonomous scenes. For example, the scenarios in driverless cars can be observed using the LiDAR system. Some scanning processes do this. 
Process of the LiDAR SystemThe LiDAR systems give out laser beams ranging up to 150,000 pulses per second. Generally, the beams emitted out in a circular movement, just like RADAR, along with the up and down motion of the laser. The LiDAR devices follow a basic process including a few steps:
Some Other Applications of LiDARLiDAR is a wide technology and is used in various fields and areas. This includes:
LiDAR data and Computer VisionLiDAR data can be useful for computer vision and supervised machine learning. To make it more effective, the LiDAR data must be labeled. It isn't easy to scale the data as it is huge. Scientists and artificial intelligence engineers face challenges while handling this kind of data. Because of the huge size of the data, it isn't easy to convert it into structured data and train the data that can understand the optical world. Challenges faced by LiDAR
Next TopicMeta-Learning in Machine Learning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









