Overfitting and Underfitting in Machine LearningOverfitting and Underfitting are the two main problems that occur in machine learning and degrade the performance of the machine learning models. The main goal of each machine learning model is to generalize well. Here generalization defines the ability of an ML model to provide a suitable output by adapting the given set of unknown input. It means after providing training on the dataset, it can produce reliable and accurate output. Hence, the underfitting and overfitting are the two terms that need to be checked for the performance of the model and whether the model is generalizing well or not. Before understanding the overfitting and underfitting, let's understand some basic term that will help to understand this topic well:
OverfittingOverfitting occurs when our machine learning model tries to cover all the data points or more than the required data points present in the given dataset. Because of this, the model starts caching noise and inaccurate values present in the dataset, and all these factors reduce the efficiency and accuracy of the model. The overfitted model has low bias and high variance. The chances of occurrence of overfitting increase as much we provide training to our model. It means the more we train our model, the more chances of occurring the overfitted model. Overfitting is the main problem that occurs in supervised learning. Example: The concept of the overfitting can be understood by the below graph of the linear regression output: 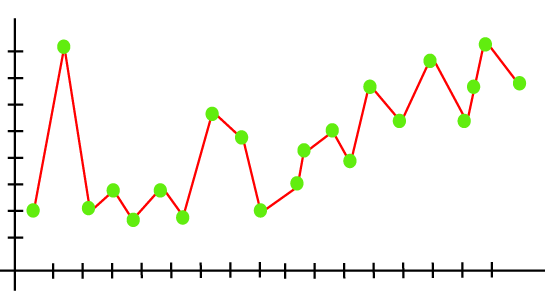
As we can see from the above graph, the model tries to cover all the data points present in the scatter plot. It may look efficient, but in reality, it is not so. Because the goal of the regression model to find the best fit line, but here we have not got any best fit, so, it will generate the prediction errors. How to avoid the Overfitting in ModelBoth overfitting and underfitting cause the degraded performance of the machine learning model. But the main cause is overfitting, so there are some ways by which we can reduce the occurrence of overfitting in our model.
UnderfittingUnderfitting occurs when our machine learning model is not able to capture the underlying trend of the data. To avoid the overfitting in the model, the fed of training data can be stopped at an early stage, due to which the model may not learn enough from the training data. As a result, it may fail to find the best fit of the dominant trend in the data. In the case of underfitting, the model is not able to learn enough from the training data, and hence it reduces the accuracy and produces unreliable predictions. An underfitted model has high bias and low variance. Example: We can understand the underfitting using below output of the linear regression model: 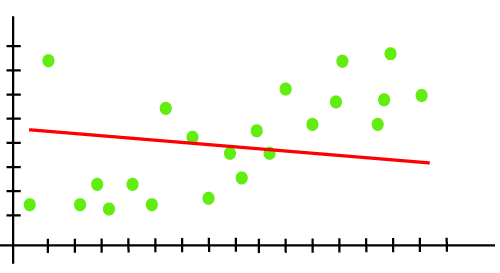
As we can see from the above diagram, the model is unable to capture the data points present in the plot. How to avoid underfitting:
Goodness of FitThe "Goodness of fit" term is taken from the statistics, and the goal of the machine learning models to achieve the goodness of fit. In statistics modeling, it defines how closely the result or predicted values match the true values of the dataset. The model with a good fit is between the underfitted and overfitted model, and ideally, it makes predictions with 0 errors, but in practice, it is difficult to achieve it. As when we train our model for a time, the errors in the training data go down, and the same happens with test data. But if we train the model for a long duration, then the performance of the model may decrease due to the overfitting, as the model also learn the noise present in the dataset. The errors in the test dataset start increasing, so the point, just before the raising of errors, is the good point, and we can stop here for achieving a good model. There are two other methods by which we can get a good point for our model, which are the resampling method to estimate model accuracy and validation dataset.
Next TopicPrincipal Component Analysis
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









