Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) in Machine LearningLinear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is one of the commonly used dimensionality reduction techniques in machine learning to solve more than two-class classification problems. It is also known as Normal Discriminant Analysis (NDA) or Discriminant Function Analysis (DFA). This can be used to project the features of higher dimensional space into lower-dimensional space in order to reduce resources and dimensional costs. In this topic, "Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) in machine learning”, we will discuss the LDA algorithm for classification predictive modeling problems, limitation of logistic regression, representation of linear Discriminant analysis model, how to make a prediction using LDA, how to prepare data for LDA, extensions to LDA and much more. So, let's start with a quick introduction to Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) in machine learning. Note: Before starting this topic, it is recommended to learn the basics of Logistic Regression algorithms and a basic understanding of classification problems in machine learning as a prerequisiteWhat is Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)?Although the logistic regression algorithm is limited to only two-class, linear Discriminant analysis is applicable for more than two classes of classification problems. Linear Discriminant analysis is one of the most popular dimensionality reduction techniques used for supervised classification problems in machine learning. It is also considered a pre-processing step for modeling differences in ML and applications of pattern classification. Whenever there is a requirement to separate two or more classes having multiple features efficiently, the Linear Discriminant Analysis model is considered the most common technique to solve such classification problems. For e.g., if we have two classes with multiple features and need to separate them efficiently. When we classify them using a single feature, then it may show overlapping. 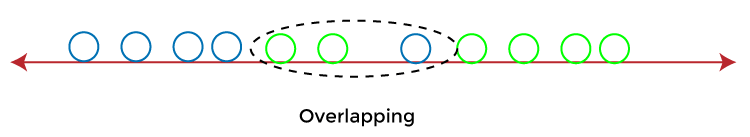
To overcome the overlapping issue in the classification process, we must increase the number of features regularly. Example:Let's assume we have to classify two different classes having two sets of data points in a 2-dimensional plane as shown below image: 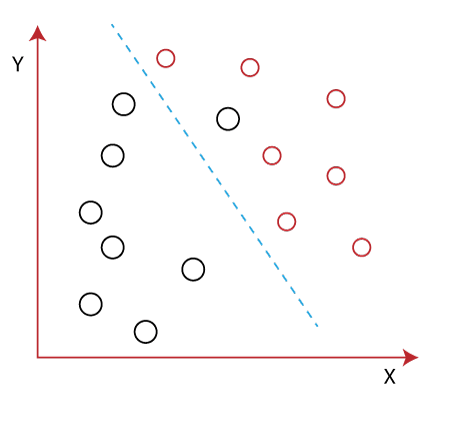
However, it is impossible to draw a straight line in a 2-d plane that can separate these data points efficiently but using linear Discriminant analysis; we can dimensionally reduce the 2-D plane into the 1-D plane. Using this technique, we can also maximize the separability between multiple classes. How Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) works?Linear Discriminant analysis is used as a dimensionality reduction technique in machine learning, using which we can easily transform a 2-D and 3-D graph into a 1-dimensional plane. Let's consider an example where we have two classes in a 2-D plane having an X-Y axis, and we need to classify them efficiently. As we have already seen in the above example that LDA enables us to draw a straight line that can completely separate the two classes of the data points. Here, LDA uses an X-Y axis to create a new axis by separating them using a straight line and projecting data onto a new axis. Hence, we can maximize the separation between these classes and reduce the 2-D plane into 1-D. 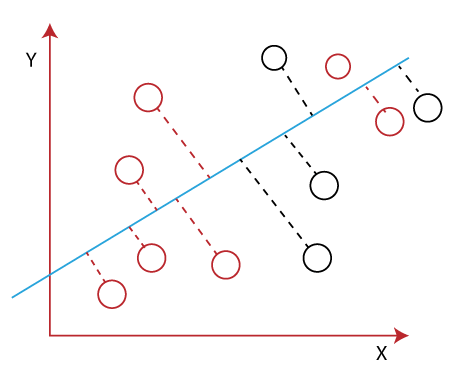
To create a new axis, Linear Discriminant Analysis uses the following criteria:
Using the above two conditions, LDA generates a new axis in such a way that it can maximize the distance between the means of the two classes and minimizes the variation within each class. In other words, we can say that the new axis will increase the separation between the data points of the two classes and plot them onto the new axis. Why LDA?
Drawbacks of Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)Although, LDA is specifically used to solve supervised classification problems for two or more classes which are not possible using logistic regression in machine learning. But LDA also fails in some cases where the Mean of the distributions is shared. In this case, LDA fails to create a new axis that makes both the classes linearly separable. To overcome such problems, we use non-linear Discriminant analysis in machine learning. Extension to Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)Linear Discriminant analysis is one of the most simple and effective methods to solve classification problems in machine learning. It has so many extensions and variations as follows:
Real-world Applications of LDASome of the common real-world applications of Linear discriminant Analysis are given below:
Difference between Linear Discriminant Analysis and PCABelow are some basic differences between LDA and PCA:
How to Prepare Data for LDABelow are some suggestions that one should always consider while preparing the data to build the LDA model:
Next TopicStacking in Machine Learning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









