Introduction to Dimensionality Reduction TechniqueWhat is Dimensionality Reduction?The number of input features, variables, or columns present in a given dataset is known as dimensionality, and the process to reduce these features is called dimensionality reduction. A dataset contains a huge number of input features in various cases, which makes the predictive modeling task more complicated. Because it is very difficult to visualize or make predictions for the training dataset with a high number of features, for such cases, dimensionality reduction techniques are required to use. Dimensionality reduction technique can be defined as, "It is a way of converting the higher dimensions dataset into lesser dimensions dataset ensuring that it provides similar information." These techniques are widely used in machine learning for obtaining a better fit predictive model while solving the classification and regression problems. It is commonly used in the fields that deal with high-dimensional data, such as speech recognition, signal processing, bioinformatics, etc. It can also be used for data visualization, noise reduction, cluster analysis, etc. 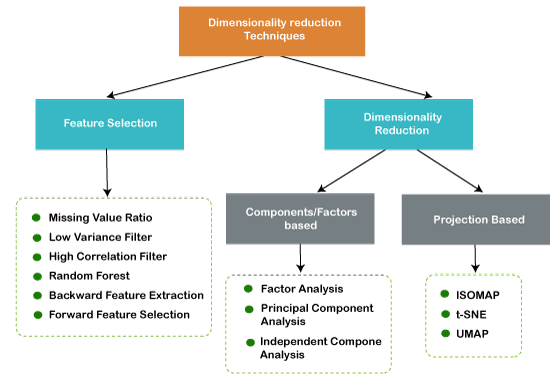
The Curse of DimensionalityHandling the high-dimensional data is very difficult in practice, commonly known as the curse of dimensionality. If the dimensionality of the input dataset increases, any machine learning algorithm and model becomes more complex. As the number of features increases, the number of samples also gets increased proportionally, and the chance of overfitting also increases. If the machine learning model is trained on high-dimensional data, it becomes overfitted and results in poor performance. Hence, it is often required to reduce the number of features, which can be done with dimensionality reduction. Benefits of applying Dimensionality ReductionSome benefits of applying dimensionality reduction technique to the given dataset are given below:
Disadvantages of dimensionality ReductionThere are also some disadvantages of applying the dimensionality reduction, which are given below:
Approaches of Dimension ReductionThere are two ways to apply the dimension reduction technique, which are given below: Feature SelectionFeature selection is the process of selecting the subset of the relevant features and leaving out the irrelevant features present in a dataset to build a model of high accuracy. In other words, it is a way of selecting the optimal features from the input dataset. Three methods are used for the feature selection: 1. Filters Methods In this method, the dataset is filtered, and a subset that contains only the relevant features is taken. Some common techniques of filters method are:
2. Wrappers Methods The wrapper method has the same goal as the filter method, but it takes a machine learning model for its evaluation. In this method, some features are fed to the ML model, and evaluate the performance. The performance decides whether to add those features or remove to increase the accuracy of the model. This method is more accurate than the filtering method but complex to work. Some common techniques of wrapper methods are:
3. Embedded Methods: Embedded methods check the different training iterations of the machine learning model and evaluate the importance of each feature. Some common techniques of Embedded methods are:
Feature Extraction:Feature extraction is the process of transforming the space containing many dimensions into space with fewer dimensions. This approach is useful when we want to keep the whole information but use fewer resources while processing the information. Some common feature extraction techniques are:
Common techniques of Dimensionality Reduction
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)Principal Component Analysis is a statistical process that converts the observations of correlated features into a set of linearly uncorrelated features with the help of orthogonal transformation. These new transformed features are called the Principal Components. It is one of the popular tools that is used for exploratory data analysis and predictive modeling. PCA works by considering the variance of each attribute because the high attribute shows the good split between the classes, and hence it reduces the dimensionality. Some real-world applications of PCA are image processing, movie recommendation system, optimizing the power allocation in various communication channels. Backward Feature EliminationThe backward feature elimination technique is mainly used while developing Linear Regression or Logistic Regression model. Below steps are performed in this technique to reduce the dimensionality or in feature selection:
In this technique, by selecting the optimum performance of the model and maximum tolerable error rate, we can define the optimal number of features require for the machine learning algorithms. Forward Feature SelectionForward feature selection follows the inverse process of the backward elimination process. It means, in this technique, we don't eliminate the feature; instead, we will find the best features that can produce the highest increase in the performance of the model. Below steps are performed in this technique:
Missing Value RatioIf a dataset has too many missing values, then we drop those variables as they do not carry much useful information. To perform this, we can set a threshold level, and if a variable has missing values more than that threshold, we will drop that variable. The higher the threshold value, the more efficient the reduction. Low Variance FilterAs same as missing value ratio technique, data columns with some changes in the data have less information. Therefore, we need to calculate the variance of each variable, and all data columns with variance lower than a given threshold are dropped because low variance features will not affect the target variable. High Correlation FilterHigh Correlation refers to the case when two variables carry approximately similar information. Due to this factor, the performance of the model can be degraded. This correlation between the independent numerical variable gives the calculated value of the correlation coefficient. If this value is higher than the threshold value, we can remove one of the variables from the dataset. We can consider those variables or features that show a high correlation with the target variable. Random ForestRandom Forest is a popular and very useful feature selection algorithm in machine learning. This algorithm contains an in-built feature importance package, so we do not need to program it separately. In this technique, we need to generate a large set of trees against the target variable, and with the help of usage statistics of each attribute, we need to find the subset of features. Random forest algorithm takes only numerical variables, so we need to convert the input data into numeric data using hot encoding. Factor AnalysisFactor analysis is a technique in which each variable is kept within a group according to the correlation with other variables, it means variables within a group can have a high correlation between themselves, but they have a low correlation with variables of other groups. We can understand it by an example, such as if we have two variables Income and spend. These two variables have a high correlation, which means people with high income spends more, and vice versa. So, such variables are put into a group, and that group is known as the factor. The number of these factors will be reduced as compared to the original dimension of the dataset. Auto-encodersOne of the popular methods of dimensionality reduction is auto-encoder, which is a type of ANN or artificial neural network, and its main aim is to copy the inputs to their outputs. In this, the input is compressed into latent-space representation, and output is occurred using this representation. It has mainly two parts:
Next TopicMachine Learning Algorithms
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









