Java Misc
How to Sort ArrayList in Java Java Stack How to Create Object in Java How to Print ASCII Value in Java How to Generate Random Number in Java How to Sort an Array in Java How to Download Java How to Compare Two Objects in Java How to Call a Method in Java How to Print Pattern in Java How to Create Singleton Class in Java How to Find Array Length in Java How to Read Character in Java How to Reverse a Number in Java Can We Overload main() Method in Java How to Convert Char Array to String in Java How to Run Java Program in CMD Using Notepad How to Sort String Array in Java How to Compare Dates in Java How to Take Multiple String Input in Java Using Scanner How to Remove Last Character from String in Java How TreeMap Works Internally in Java Java Program to Find Sum of Natural Numbers Java Program to Display Alternate Prime Numbers Java Program to Find Square Root of a Number Without sqrt Method Java Program to Swap Two Numbers Using Bitwise Operator Java Program to Break Integer into Digits Java Program to Find GCD of Two Numbers Java Program to Find Largest of Three Numbers Java Program to Calculate Area and Circumference of Circle Java Program to Check if a Number is Positive or Negative Java Program to Find Smallest of Three Numbers Using Ternary Operator What is Diamond Problem in Java Java Program to Check if a Given Number is Perfect Square Java Program to Display Even Numbers From 1 to 100 Java Program to Display Odd Numbers From 1 to 100 Java Program to Read Number from Standard Input How to Download Minecraft Java Edition Can We Override Static Method in Java How to Avoid Deadlock in Java How to Achieve Abstraction in Java How Garbage Collection Works in Java How to Take Array Input in Java How to Create Array of Objects in Java How to Create Package in Java How to Print in Java What is Framework in Java Why Java is Secure How to Iterate List in Java How to Use Eclipse for Java Which Package is Imported by Default in Java Could Not Find or Load Main Class in Java How to Compare Two Arrays in Java How to Convert String to JSON Object in Java Which is Better Java or Python How to Update Java C vs Java How to Get Value from JSON Object in Java Example How to Split a String in Java with Delimiter Structure of Java Program Why We Use Constructor in Java Java Create Excel File Java Interpreter javac is not Recognized Dynamic Array in Java Shunting yard algorithm Java Destructor Custom ArrayList in Java ArrayList vs HashMap Java Constant Java Tokens Java Xmx How to Enable Java in Chrome Java Semaphore Array to List in Java JIT in Java How to Clear Screen in Java Java IDEs Java Logger Reverse a String Using Recursion in Java Java Path Vs File Float Vs Double Java Stack vs Heap Java Abstraction vs Encapsulation Top 10 Java Books Public vs Private What is Java Used For Bitwise Operator in Java SOLID Principles Java Type Casting in Java Conditional Operator in Java Ternary Operator Java Java Architecture REPL in Java Types of Exception in Java Why String is Immutable or Final in Java Java vs Kotlin Set in Java Why non-static variable cannot be referenced from a static context in Java Java Developer Roles and Responsibilities Types of Classes in Java Marker Interface in Java Static Function in Java Unary Operators in Java What is Advance Java ArrayList Implementation Convert ArrayList to String Array Hashmap vs ConcurrentHashMap List vs ArrayList Map vs HashMap HashSet vs LinkedHashSet How TreeSet Works Internally LinkedHashMap vs HashMap Java Program to Solve Quadratic Equation Scope Resolution Operator in Java Composition in Java File Operations in Java NoClassDefFoundError in Java Thread Concept in Java Upcasting and Downcasting in Java Dynamic Polymorphism in Java Java Robot String Pool in Java What is constructor chaining in Java Add elements to Array in Java Advantages and disadvantages of Java Advantages of JavaBeans AWS SDK for Java with Apache Maven AWT and Swing in Java AWT Program in Java Boolean values in Java ByteStream Classes in Java CharacterStream Classes in Java Class and Interface in Java ClassCast Exception in Java Cloneable in Java Constructor overloading in Java Control Flow in Java Convert Java Object to Json using GSON Convert XML to JSON in Java How to avoid null pointer exception in Java Java constructor returns a value, but what Singleton Class in Java Doubly Linked List Program in Java Java 12 Association in Java Big data Java vs Python Branching Statements in Java Collections Sort in Java 8 List vs Set in Java How many days required to learn Java Implicitly Typecasting in Java Legacy Class in Java Character Array in Java Equals() and Hashcode() in Java Externalization in Java Identifiers in Java InvocationTargetException Java Pass by Value Mutable and Immutable in Java POJO Power Function in Java Primitive Data Types in Java String Array in Java Virtual Function in Java C vs C++ vs Java Java String Max Size nth Prime Number Java Convert Java object to JSON How to Calculate Date Difference in Java How to Improve Coding Skills in Java Java Email Validation Java Testing Tools Permutation and Combination in Java JavaCC Unique Number in Java Program JDBC MCQ OOPs MCQ Java Code for DES Pig Latin Program in Java Array Rotation in Java Equilibrium Index of an Array in Java Different Ways to Print Exception Message in Java Java Copy Constructor Example Why We Use Static Class in Java What is Core Java Set vs Map in Java How to Create a New Folder in Java Remove an Element from ArrayList in Java How to Create Test Cases for Exceptions in Java How to Convert JSON Array to ArrayList in Java How to Create a Class File in Java Java Spring Pros & Cons Java Stack Trace Array Slicing in Java Flutter vs Java Permutation of Numbers in Java Magic Number in Java Reference Data Types in Java Counter variable in Java How to take Character Input in Java using BufferedReader Class Java employee details program Java is case sensitive explain Ramanujan Number or Taxicab Number in Java Advanced Java Books in 2021 Fail Fast and Fail Safe Iterator in Java How to build a Web Application Using Java Is Java Interpreted or Compiled Java Big Data Frameworks Java Get Data From URL No Main Manifest Attribute Java missing return statement Java program to remove duplicate characters from a string JUnit test case example in Java List of logical programs in Java PermGen space Java Unsigned Right Shift Operator in Java Infix to Postfix Java Memory Leak in Java How To Write Test Cases In Java Java 32-Bit Download For Windows 10 FizzBuzz Program in Java Java Graph A Java Runtime Environment JRE Or JDK Must Be Available Java Does Not Open No Java Virtual Machine was Found Java Program Number to Word Types of Garbage Collector in Java No Suitable Driver Found For JDBC AVL Tree program in Java Fail-fast and Fail-safe in Java Find unique elements in array Java Highest precedence in Java Java Closure Java String Encoding Prim's algorithm Java Quartz scheduler java Red Black Tree Java GC Overhead Limit Exceeded Generating QR Code in Java Delegation Event Model in Java Java Pair Java Profilers Java XOR Java Flight Recorder Bucket Sort in Java Automorphic Number Program in Java Java Atomic Wait vs Sleep in Java Executor Framework Java Gregorian calendar Java int vs Integer Java What is truncation in Java Peterson Number in Java Sunny Number in Java Tech Number in Java Java HTTP Proxy Server Java Static Constructor How to prepare for Java Interview Java callback function Java 8 vs Java 11 Login Form Java Vaadin Framework Java EJB vs. Spring Fascinating Number in Java Keith Number in Java Neon Number in Java Spy Number in Java Types of Applets in Java Visitor Design Pattern Java Advantages of Python over Java ATM program Java Design Principles in Java JSON Validator Java Pseudocode Java Autobiographical Number in Java Emirp Number in Java Sphenic Number in Java Windows Programming Using Java Buzz Number Java Duck Number Java Evil Number Java ISBN Number Java Krishnamurthy Number Java Vert.x Java Bouncy Number in Java Mystery Number in Java Smith Number in Java Strontio Number in Java Xylem and Phloem Number in Java Complex Java Programs ORE Number Java PalPrime Number Java Twin Prime Numbers Twisted Prime Number Java Ugly number Java Achilles Number in Java Amicable Pair Number in Java Playfair Cipher Program in Java Java.lang.outofmemoryerror: java heap space Banker's Algorithm Java Kruskal Algorithm Java Longest Common Subsequence Travelling Salesman Problem & vs && in Java Jumping Number in Java Lead Number in Java Lucky Number in Java Middle Digit Number in Java Special Number in Java Passing Array to Function In Java Java Error Java Apps Lexicographical Order Java Adam Number in Java Bell Number in Java Reduce Java LRU Cache Implementation Goldbach Number in Java How to Find Number of Objects Created in Java Multiply Two Numbers Without Using Arithmetic Operator in Java Sum of Digits of a Number in Java Sum of Numbers in Java Power of a Number in Java Sum of Prime Numbers in Java Cullen Number in Java Mobile Number Validation in Java Fermat Number in Java Instantiation in Java Exception Vs Error in Java flatMap() Method in Java 8 How to Print Table in Java Java Create PDF Mersenne Number in Java Pandigital Number in Java Pell Number in Java Java Get Post Fork Join in Java Java Callable Example Blockchain Java Design of JDBC Java Anon Proxy Knapsack Problem Java Session Tracking in Java What is Object-Oriented Programming Literals in Java Square Free Number in Java What is an anagram in Java What is programming Iterate JSON Array Java Java Date Add Days Java Plot Javac Command Not Found Factorial Program in Java Using while Loop Frugal Number in Java Java Digital Signature Catalan Number in Java Partition Number in Java Powerful Number in Java Practical Number in Java Chromatic Number in Java Sublime Number in Java Advanced Java Viva Questions Getter and Setter Method in Java Example How to convert String to String array in Java How to Encrypt Password in Java Instance Variable in Java Java File Extension Java Pi Java Pop Types of Inheritance in Java Untouchable Number in Java AES 256 Encryption in Java Applications of Array in Java Example of Static Import in Java Hill Cipher Program in Java Lazy Loading in Java Rectangular Number in Java How to Print Table in Java Using Formatter IdentityHashMap Class in Java Java BF Java Logo Undulating Number in Java Java Obfuscator Java Switch String Applet Life Cycle in Java Banking Application in Java Duodecimal in Java Economical Number in Java Figurate Number in Java How to resolve IllegalStateException in Java Java Coding Software Java Create Jar Files Java Framework List Java Initialize array java lang exception no runnable methods Java Queue Nonagonal Number in Java SexagesimalFormatter in Java Sierpinski Number in Java Vigesimal in Java Java Color Codes JDoodle Java Online Java Compiler Pyramidal Number in Java Relatively Prime in Java Java Modulo Repdigit Numbers in Java Abstract Method in Java Convert Text-to-Speech in Java Java Editors MVC Architecture in Java Narcissistic Number in Java Hashing Algorithm in Java Java Escape Characters Java Operator Precedence Private Constructor in Java Scope of Variables in Java Groovy vs Java Java File Upload to a Folder Java Full Stack Java Developer Thread States in Java Java EE vs Node.js Java Image Loose Coupling in Java Java Top 10 Libraries Method Hiding in Java Java Tuple Dijkstra Algorithm Java Extravagant Number in Java Java Unicode New Line in Java Return Statement in Java Order of Execution of Constructors in Java Inheritance Cardinal Number in Java Hyperfactorial in Java Identifier Expected Error in Java Java Generate UUID Labeled Loop in Java Lombok Java Ordinal Number in Java Tetrahedral Number in Java Cosmic Superclass in Java Shallow Copy Java BiFunction Java 8 Equidigital Number in Java Fall Through in Java Java Reserved Keywords Java Vs Go Parking Lot Design Java Boyer Moore Java Java Security Framework Tetranacci Number in Java BFS Algorithm in Java CountDownLatch in Java Counting sort in Java CRC Program in Java FileNotFoundException in Java InputMismatchException in Java Java ASCII Table Spark Java Lock in Java Segment Tree in Java DTO Java Why main() method is always static in Java Bellman-Ford Algorithm Java BigDecimal toString() in Java .NET vs Java Java ZipFile Lazy Propagation in Segment Tree in Java Magnanimous Number in Java Binary Tree Java How to Create Zip File in Java Java Dot Operator Associativity of Operators in Java Fenwick Tree in Java How annotation works in Java How to Find Length of Integer in Java Java 8 filters List All Files in a Directory in Java TDD Java How to Get Day Name from Date in Java Zigzag Array in Java Class Definition in Java Find Saddle Point of a Matrix in Java Non-primitive data types in Java Pancake Number in Java Pancake Sorting in Java Print Matrix Diagonally in Java Sort Dates in Java Carmichael Numbers in Java Contextual Keywords in Java How to Open Java Control Panel How to Reverse Linked List in Java Interchange Diagonal Elements Java Program Java Set to List Level Order Traversal of a Binary Tree in Java Bully algorithm in Java Convert JSON File to String in Java Convert Milliseconds to Date in Java Copy Content/ Data From One File to Another in Java Constructor vs Method in Java Access Specifiers vs Modifiers Java vs PHP replace() vs replaceAll() in Java this vs super in Java Heap implementation in Java How to Check null in Java Java Arrays Fill Java Font Rotate Matrix by 90 Degrees in Java Exception Class in Java Transient variable in Java Web crawler Java Zigzag Traversal of a Binary Tree in Java Java Get File Size Internal Working of ArrayList in Java Java Program to Print Matrix in Z Form Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree in Java Group By in Java 8 Hashing Techniques in Java Implement Queue Using Array in Java Java 13 Features Package Program in Java Canonical Name Java Method Chaining in Java Orphaned Case Java Bottom View of a Binary Tree in Java Coercion in Java Dictionary Class in Java Left View of a Binary Tree in Java Pangram Program in Java Top View of a Binary Tree in Java Tribonacci Series in Java Hollow Diamond Pattern in Java Normal and Trace of a Matrix in Java Right View of a Binary Tree in Java Dining Philosophers Problem and Solution in Java Shallow Copy vs Deep Copy in Java Java Password Generator Java Program for Shopping Bill Lock Interface in Java Convert JSON to Map in Java Convert JSON to XML in Java Middle Node of a Linked List in Java Pernicious Number in Java Cohesion in Java How to get UTC time in Java Jacobsthal Number in Java Java BLOB Java Calculate Age JFC Java Tribonacci Number Java Bernoulli number in Java Cake Number in Java Compare time in Java Compare Two Sets in Java Crown Pattern in Java Convert List to Array in Java Aggregation vs Composition Morris Traversal for Inorder in Java Morris Traversal for Preorder in Java Package Naming Conversion in Java India Map Pattern in Java Ladder Pattern in Java ORM Tools in Java Odious Number in Java Rat in a Maze Problem in Java Sudoku in Java Christmas Tree Pattern in Java Double Hashing in Java Magic Square in Java Possible Paths from Top Left to Bottom Right of a Matrix in Java Palindrome Partitioning Problem in Java Rehashing in Java Round Robin Scheduling Program in Java Types of Statements in Java Compound Assignment Operator in Java Prime Points in Java Butterfly Pattern in Java Fish Pattern in Java Flag Pattern in Java Kite pattern in Java Swastika Pattern in Java Tug of War in Java Clone HashMap in Java Fibodiv Number in Java Heart Pattern in Java How to check data type in Java Java Array Clone Use of final Keyword in Java Factorial of a Large Number in Java Race Condition in Java Static Array in Java Water Jug Problem in Java Electricity Bill Program in Java Facts about null in Java Maximizing Profit in Stock Buy Sell in Java Permutation Coefficient in Java Convert List to String in Java List of Constants in Java MOOD Factors to Assess a Java Program Computing Digit Sum of All Numbers From 1 to n in Java Read PDF File in Java Finding Odd Occurrence of a Number in Java Java Indentation Zig Zag Star and Number Pattern in Java Check Whether a Number is a Power of 4 or not in Java Kth Smallest in an Unsorted Array in Java BlockingQueue in Java Next Greater Element in Java Star Numbers in Java 3N+1 Problem in Java Java Program to Find Local Minima in An Array Processing Speech in Java Java Output Formatting House Numbers in Java Java Program to Generate Binary Numbers Longest Odd-Even Subsequence in Java Java Subtract Days from Current Date Java Future Example Minimum Cost Path Problem in Java Diffie-Hellman Algorithm in Java Ganesha's Pattern in Java Hamming Code in Java Map of Map in Java Print Pencil Shape Pattern in Java Zebra Puzzle in Java Display Unique Rows in a Binary Matrix in Java Rotate A Matrix By 180 Degree in Java Dangling Else Problem in Java Java Application vs Java Applet Dutch National Flag Problem in Java Java Calculate Average of List compareToIgnoreCase Java Trimorphic Numbers in Java Arithmetic Exception in Java Java instanceof operator Java Localization Minimum XOR Value Pair in Java Iccanobif Numbers in Java Java Program to Count the Occurrences of Each Character Java Technologies List Java Program to Find the Minimum Number of Platforms Required for a Railway Station Shift Operators in Java Final Object in Java Java OCR Object Definition in Java Shadowing in Java Zipping and Unzipping Files in Java Display the Odd Levels Nodes of a Binary Tree in Java Java Variable Declaration Nude Numbers in Java Java Programming Challenges Java URL Encoder anyMatch() in Java 8 Sealed Class in Java Camel case in Java Career Options for Java Developers to Aim in 2022 Java Progress Bar Maximum Rectangular Area in a Histogram in Java Polygonal Number in Java Two Sorted LinkedList Intersection in Java Set Matrix Zeros in Java Find Number of Island in Java Balanced Prime Number in Java Minecraft Bedrock vs Java Minecraft arr.length vs arr[0].length vs arr[1].length in Java Future in Java 8 How to Set Timer in Java Construct the Largest Number from the Given Array in Java Java SHA Minimum Coins for Making a Given Value in Java Eclipse Shortcuts Java Empty Statement in Java Java Program to Implement Two Stacks in an Array Java Snippet Longest Arithmetic Progression Sequence in Java Types of Sockets in Java Java Program to Add Digits Until the Number Becomes a Single Digit Number Next Greater Number with Same Set of Digits in Java Split the Number String into Primes in Java Java Cron Expression Huffman Coding Java Java Snippet Class Why Java is So Popular Java Project idea Java Web Development Brilliant Numbers in Java Sort Elements by Frequency in Java Beautiful Array in Java Moran Numbers in Java Intersection Point of Two Linked List in Java Sparse Number in Java How to Check JRE Version Java Programming Certification Two Decimal Places Java Eclipse Change Theme Java how to Convert Bytes to Hex Decagonal Numbers in Java Java Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion Java Hexadecimal to Binary Conversion How to Capitalize the First Letter of a String in Java Java &0XFF Example Stream findFirst() Method in Java Balanced Parentheses in Java Caesar Cipher Program in Java next() vs nextLine() Java Split String by Comma Spliterator in java 8 Tree Model Nodes in Jackson Types of events in Java Callable and Future in Java How to Check Current JDK Version installed in Your System Using CMD How to Round Double and Float up to Two Decimal Places in Java Java 8 Multimap Parallel Stream in Java Java Convert Bytes to Unsigned Bytes Java SFTP Display List of TimeZone with GMT and UTC in Java Binary Strings Without Consecutive Ones in Java Convert IP to Binary in Java Java Macro Returning Multiple Values in Java Centered Square Numbers in Java ProcessBuilder in Java How to Clear Java Cache IntSummaryStatistics Class in Java Java ProcessBuilder Example Java Program to Delete a Directory Java Program to Print Even Odd Using Two Threads Java Variant MessageDigest in Java Alphabet Pattern in Java Java Linter Java Mod Example Stone Game in Java TypeErasure in Java How to Remove substring from String in Java Program to print a string in vertical in Java How to Split a String between Numbers and Letters String Handling in Java Isomorphic String in Java Java ImageIO Class Minimum Difference Subarrays in Java Plus One to Array Problem in Java Unequal Adjacent Elements in Java Java Parallel Stream Example SHA Hashing in Java How to make Java projects Java Fibers Java MD5 Hashing Example Hogben Numbers in Java Self-Descriptive Numbers in Java Hybrid Inheritance in Java Java IP Address (IPv4) Regex Examples Converting Long to Date in JAVA Java 17 new features GCD of Different SubSequences in Java Sylvester Sequence in Java Console in Java Asynchronous Call in Java Minimum Window Substring in Java Nth Term of Geometric Progression in Java Coding Guidelines in Java Couple Holding Hands Problem in Java Count Ones in a Sorted binary array in Java Ordered Pair in Java Tetris Game in Java Factorial Trailing Zeroes in Java Java Assert Examples Minimum Insertion To Form A Palindrome in Java Wiggle Sort in Java Java DOM Java Exit Code 13 Java JFileChooser What is LINQ NZEC in Java Box Stacking Problem K Most Frequent Elements in Java Parallel Programming in Java How to Generate JVM Heap Memory Dump Java Program to use Finally Block for Catching Exceptions Count Login Attempts Java Largest Independent Set in Java Longest Subarray With All Even or Odd Elements in Java Open and Closed Hashing in Java DAO Class in Java Kynea Numbers in Java UTF in Java Zygodromes in Java ElasticSearch Java API Form Feed in Java Java Clone Examples Payment Gateway Integration in Java What is PMD RegionMatches() Method in Java Repaint() Method in Java Serial Communication in Java Count Double Increasing Series in A Range in Java Longest Consecutive Subsequence in Java Smallest Subarray With K Distinct Numbers in Java String Sort Custom in Java Count Number of Distinct Substrings in a String in Java Display All Subsets of An Integer Array in Java Digit Count in a Factorial Of a Number in Java Valid Parentheses Problem in Java DAO Class in Java Median Of Stream Of Running Integers in Java Arrow Operator in Java Java Learning app Create Preorder Using Postorder and Leaf Nodes Array Display Leaf nodes from Preorder of a BST in Java Unicodes for Operators in Java XOR and XNOR operators in Java AWS Lambda in Java AWS Polly in Java SAML in Java SonarQube in Java UniRest in Java Override equals method in Java Undo and Redo Operations in Java Size of longest Divisible Subset in an Array in Java Sort An Array According To The Set Bits Count in Java Two constructors in one class in Java Union in Java What is New in Java 15 ART in Java Definite Assignment in Java Cast Operator in Java Diamond operator in Java Java Singleton Enum Size of longest Divisible Subset in an Array in Java Three-way operator | Ternary operator in Java GoF Design Pattern Java Java Programming Certification Shorthand Operator in Java What is new in Java 17 How to Find the Java Version in Linux What is New in Java 12 Exception in Thread Main java.util.NoSuchElementException no line Found How to reverse a string using recursion in Java Java Program to Reverse a String Using Stack Java Program to Reverse a String Using the Stack Data Structure Reverse Middle Words of a String in Java Sastry Numbers in Java Sum of LCM in Java Tilde Operator in Java 8 Puzzle problems in Java Maximum Sum Such That No Two Elements Are Adjacent in Java Reverse a String in Place in Java Reverse a string Using a Byte array in Java Reverse a String Using Java Collections Reverse String with Special Characters in Java get timestamp in java How to convert file to hex in java AbstractSet in java List vs Set vs Map in Java Birthday Problem in Java How to Calculate the Time Difference Between Two Dates in Java Number of Mismatching Bits in Java Palindrome Permutation of a String in Java Grepcode java.util.Date How to add 24 hrs to date in Java How to Change the Day in The Date Using Java Java ByteBuffer Size java.lang.NoSuchMethodError Maximum XOR Value in Java How to Add Hours to The Date Object in Java How to Increment and Decrement Date Using Java Multithreading Scenarios in Java Switch case with enum in Java Longest Harmonious Subsequence in Java Count OR Pairs in Java Merge Two Sorted Arrays Without Extra Space in Java How to call a concrete method of abstract class in Java How to create an instance of abstract class in Java Java Console Error 503 error handling retry code snippets Java Implementation Of Abstraction In Java How to avoid thread deadlock in Java Number of Squareful Arrays in Java One-Time Password Generator Code In Java Real-Time Face Recognition In Java Converting Integer Data Type to Byte Data Type Using Typecasting in Java How to Generate File checksum Value Index Mapping (or Trivial Hashing) With Negatives allowed in Java Shortest Path in a Binary Maze in Java customized exception in Java Difference between error and exception in Java How to solve deprecated error in Java Jagged Array in Java CloneNotSupportedException in Java with Examples Difference Between Function and Method in Java Immutable List in Java Nesting Of Methods in Java How to Convert Date into Character Month and Year Java How to Mock Lambda Expression in Java How to Return Value from Lambda Expression Java if Condition in Lambda Expression Java Chained Exceptions in Java Final static variable in Java Java File Watcher Various Operations on HashSet in Java Word Ladder Problem in Java Various Operations on Queue in Java Various Operations on Queue Using Linked List in Java Various Operations on Queue Using Stack in Java Get Yesterday's Date from Localdate Java Get Yesterday's Date by No of Days in Java Advantages of Lambda Expression in Java 8 Cast Generic Type to Specific type Java ConcurrentSkipListSet in Java Fail Fast Vs. Fail-Safe in Java Get Yesterday's Date in Milliseconds Java Get Yesterday's Date Using Date Class Java Getting First Date of Month in Java Gregorian Calendar Java Current Date How to Calculate Time Difference Between Two Dates in Java How to Calculate Week Number from Current Date in Java Keystore vs Truststore Leap Year Program in Java Online Java Compiler GDB Operators in Java MCQ Separators In Java StringIndexOutOfBoundsException in Java Anonymous Function in Java Default Parameter in Java Group by Date Code in Java How to add 6 months to Current Date in Java How to Reverse A String in Java Letter by Letter Java 8 Object Null Check Java Synchronized Types of Arithmetic Operators in Java Types of JDBC Drivers in Java Unmarshalling in Java Write a Program to Print Reverse of a Vowels String in Java ClassNotFound Exception in Java Null Pointer Exception in Java Why Does BufferedReader Throw IOException in Java Java Program to Add two Complex Numbers Read and Print All Files From a Zip File in Java Reverse an Array in Java Right Shift Zero Fill Operator in Java Static Block in Java Accessor and Mutator in Java Array of Class Objects in Java Benefits of Generics in Java Can Abstract Classes Have Static Methods in Java ClassNotFoundException Java Creating a Custom Generic Class in Java Generic Queue Java Getting Total Hours From 2 Dates in Java How to add 2 dates in Java How to Break a Date and Time in Java How to Call Generic Method in Java How to Increment and Decrement Date using Java Java Class Methods List Java Full Stack Developer Java.lang.NullPointerException Least Operator to Express Number in Java Shunting Yard Algorithm in Java Singleton Class in Java Switch Case Java Treeset Java Operations Types of Logical Operators in Java What is Cast Operator in Java What is Jersey in Java Alternative to Java Serialization API Development in Java Disadvantage of Multithreading in Java Find the row with the maximum number of 1s Generic Comparator in Java Generic LinkedList in Java Generic Programming in Java Example How Can I Give the Default Date in The Array Java How to Accept Date in Java How to add 4 years to Date in Java How to Check Date Equality in Java How to Modify HTML File Using Java Java 8 Multithreading Features Java Abstract Class and Methods Java Thread Dump Analyser Process vs. Thread in Java Reverse String Using Array in Java Types of Assignment Operators in Java Types of Bitwise Operators in Java Union and Intersection Of Two Sorted Arrays In Java Vector Operations Java Java Books Multithreading Advantages of Generics in Java Arrow Operator Java Generic Code in Java Generic Method in Java Example Getting a Range of Dates in Java Getting the Day from a Date in Java How Counter Work with Date Using Java How to Add Date in Arraylist Java How to Create a Generic List in Java Java Extend Multiple Classes Java Function Java Generics Design Patterns Why Are Generics Used in Java XOR Binary Operator in Java Check if the given string contains all the digits in Java Constructor in Abstract Class in Java Count number of a class objects created in Java Difference Between Byte Code and Machine Code in Java Java Program to Append a String in an Existing File Main thread in Java Store Two Numbers in One Byte Using Bit Manipulation in Java The Knight's Tour Problem in Java Business Board Problem in Java Business Consumer Problem in Java Buy as Much Candles as Possible Java Problem Get Year from Date in Java How to Assign Static Value to Date in Java Java List Node Java List Sort Lambda Java Program to Get the Size of a Directory Misc Operators in Java Reverse A String and Reverse Every Alternative String in Java Reverse a String in Java Using StringBuilder Reverse Alternate Words in A String Java Size of Empty Class in Java Titniry Operation in Java Triple Shift Operator in Java Types of Conditional Operators in Java View Operation in Java What is Linked list Operation in Java What is Short Circuit && And or Operator in Java What is the & Operator in Java Why to use enum in Java XOR Bitwise Operator in Java XOR Logical Operator Java Compile-Time Polymorphism in Java Convert JSON to Java Object Online Difference between comparing String using == and .equals() method in Java Difference Between Singleton Pattern and Static Class in Java Difference Between Static and Non-Static Nested Class in Java Getting Date from Calendar in Java How to Swap or Exchange Objects in Java Java Get Class of Generic Parameter Java Interface Generic Parameter Java Map Generic Java NLP Java Number Class Java Program for Maximum Product Subarray Java Program To Print Even Length Words in a String Logger Class in Java Manacher's Algorithm in Java Mutable Class in Java Online Java IDE Package getImplementationVersion() method in Java with Examples Set Default Close Operation in Java Sorting a Java Vector in Descending Order Using Comparator Types of Interfaces in Java Understanding String Comparison Operator in Java User-Defined Packages in Java Valid variants of main() in Java What is a Reference Variable in Java What is an Instance in Java What is Retrieval Operation in ArrayList Java When to Use the Static Method in Java XOR Operations in Java
What is Java?Java is a high-level, general-purpose, object-oriented, and secure programming language developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems, Inc. in 1991. It is formally known as OAK. In 1995, Sun Microsystem changed the name to Java. In 2009, Sun Microsystem takeover by Oracle Corporation. Editions of JavaEach edition of Java has different capabilities. There are three editions of Java:
Types of Java ApplicationsThere are four types of Java applications that can be created using Java programming:
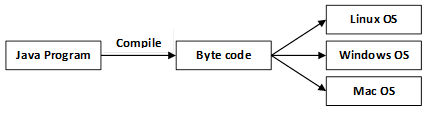
Java PlatformJava Platform is a collection of programs. It helps to develop and run a program written in the Java programming language. Java Platform includes an execution engine, a compiler and set of libraries. Java is a platform-independent language. Features of Java
OOPs (Object Oriented Programming System)Object-oriented programming is a way of solving a complex problem by breaking them into a small sub-problem. An object is a real-world entity. It is easier to develop a program by using an object. In OOPs, we create programs using class and object in a structured manner. Class: A class is a template or blueprint or prototype that defines data members and methods of an object. An object is the instance of the class. We can define a class by using the class keyword. Object: An object is a real-world entity that can be identified distinctly. For example, a desk, a circle can be considered as objects. An object has a unique behavior, identity, and state. Data fields with their current values represent the state of an object (also known as its properties or attributes). Abstraction: An abstraction is a method of hiding irrelevant information from the user. For example, the driver only knows how to drive a car; there is no need to know how does the car run. We can make a class abstract by using the keyword abstract. In Java, we use abstract class and interface to achieve abstraction. Encapsulation: An encapsulation is the process of binding data and functions into a single unit. A class is an example of encapsulation. In Java, Java bean is a fully encapsulated class. Inheritance: Inheritance is the mechanism in which one class acquire all the features of another class. We can achieve inheritance by using the extends keyword. It facilitates the reusability of the code. Polymorphism: The polymorphism is the ability to appear in many forms. In other words, single action in different ways. For example, a boy in the classroom behaves like a student, in house behaves like a son. There are two types of polymorphism: run time polymorphism and compile-time polymorphism.
Next TopicJava Tutorial
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










