Automated Trading in PythonBecause Python accelerates the trading process, this method is known as automated or quantitative trading. Python's popularity is due to its powerful libraries, like Pyplot, TA-Lib, Scipy, NumPy, Zipline, Matplotlib, Pandas, etc. What is Automated Trading?Automated trading engages capital markets by executing pre-set procedures for accepting and leaving trades using a computer program. As a trader, one will combine in-depth statistical analysis with the creation of position characteristics like open orders, guaranteed stops and trailing stops. Auto trading allows us to make a large number of deals in a short period while also removing emotion from our investment choices. This is true because our constraints already include all of the trading rules. We can even utilize our pre-determined techniques to monitor trends and trade correspondingly to some algorithms. How does Automated Trading Work?We'll start by selecting a platform and defining the characteristics of our trading plan. We'll construct a set of terms and regulations based on our trading expertise, and our bespoke algorithm will use the information to conduct bets on our account. The scheduling of the deal, the cost at which it must be opened or closed, and the number are usually the determining considerations. 'Buy 100 Google shares whenever the 100-day moving average crosses the 250-day moving average,' for example. The established automated trading method will continuously watch financial market rates, and deals will be completed automatically if predefined conditions are reached. The goal is to conduct transactions more quickly and efficiently and profit from technical market happenings. Benefits of Automated SystemsThere are a lot of benefits to letting a computer watch the marketplace for trading activities and conduct the trades, including: Emotional Control During the buying and selling, automated trading systems reduce sentiments. By holding emotions under control, traders often have a better time adhering to the trading plan. Traders could not pause or challenge the trade because trade instructions are performed automatically when the trade regulations are met. Backtesting Backtesting determines the feasibility of a concept by applying trade laws to previous market data. When building a framework for automated trading, all rules must be precise, with no room for ambiguity. The machine cannot make educated guesses and must be given specific instructions. Traders can use past data to evaluate these specific rules before risking capital in trading. Maintaining Discipline Even in volatile times, discipline is maintained since market rules are formed, and trade operation is executed automatically. Emotional considerations such as being afraid of losing money or the urge to squeeze a bit more revenue out of a deal cause focus to be lost. Since the computer will carry out the trading strategy exactly as formed, automated trading aids in retaining discipline. Increasing the Speed of Order Entry Automated systems can produce bids as quickly as trade conditions are satisfied since computer systems react quickly to fluctuating market situations. Trading Diversification Trading numerous portfolios or tactics at once is possible with automated trading systems. This can disperse risk across multiple instruments while providing a buffer against losing trades. Necessary Elements for Automated Trading
Useful Packages/ Libraries in Python for Automated TradingPython has a major resource of libraries that we may use for various purposes like coding, machine learning, visualization, etc. We'll have to import financial information, do a numerical analysis, create trading strategies, draw graphs, and backtest data. The following libraries are required:
Setting Up Work EnvironmentInstalling Anaconda is the quickest way to get started with automated trading. The Python package Anaconda includes a variety of IDEs, including Spyder, Jupyter, __, ___, libraries for analysis, etc. Installing the Yahoo-Finance ModuleWe can retrieve the stock's previous data with the help of the Yahoo Finance module. Type the following command line in the terminal and hit enter to install Yahoo Finance: Code Importing the Required PackagesThe following step after installing yfinance is to import packages in our program to run trading algorithms. Due to the extensive data modification required for backtesting, we will use Pandas strictly throughout this course. Code Getting Stock Financial InformationFinancial data retrieval is also incredibly simple in yfinance. Simply use the company's ticker as an argument for the ticker function. The code below uses Tesla shares as an illustration: Code Output:
{'zip': '78725', 'sector': 'Consumer Cyclical', 'fullTimeEmployees': 99290, 'longBusinessSummary': 'Tesla, Inc. designs, develops, manufactures, leases, and sells electric vehicles, and energy generation and storage systems in the United States, China, and internationally? The company was formerly known as Tesla Motors, Inc. and changed its name to Tesla, Inc. in February 2017. Tesla, Inc. was incorporated in 2003 and is headquartered in Austin, Texas.', 'city': 'Austin', 'phone': '(512) 516-8177', 'state': 'TX', 'country': 'United States', 'companyOfficers': [], 'website': 'https://www.tesla.com', 'maxAge': 1, 'address1': '13101 Tesla Road', 'industry': 'Auto Manufacturers', 'ebitdaMargins': 0.20424, 'profitMargins': 0.13505, 'grossMargins': 0.27096, 'operatingCashflow': 13850999808, 'revenueGrowth': 0.805, 'operatingMargins': 0.1549, 'ebitda': 12702000128, 'targetLowPrice': 67, 'recommendationKey': 'buy', 'grossProfits': 13606000000, 'freeCashflow': 7054624768,...}
The print statement produces a Python dictionary, which we can use in analysis by getting the specific financial data we're looking for from Yahoo Finance. Let's take a few fiscal critical metrics as an example. The info dictionary contains all firm information. As a result, we may extract the desired elements from the dictionary by parsing it: Code Output: 0.85 759.19 728613322752 There is a tonne of more stuff in the info dictionary. By printing the info keys, we can view all of them: Code Output: dict_keys(['zip', 'sector', 'fullTimeEmployees', 'longBusinessSummary', 'city', 'phone', 'state', 'country', 'companyOfficers', 'website', 'maxAge', 'address1', 'industry', 'ebitdaMargins', 'profitMargins', 'grossMargins', 'operatingCashflow', 'revenueGrowth', 'operatingMargins', 'ebitda', 'targetLowPrice', 'recommendationKey', 'grossProfits', 'freeCashflow', 'targetMedianPrice', 'currentPrice', 'earningsGrowth', 'currentRatio', 'returnOnAssets',?) Retrieving Historical Market PricesContinuing with other resources the yf library has to offer. Additionally, we can utilise it to get market data from previous years. We will use historical Tesla stock prices in the example below over the past few years. It is a relatively easy assignment to complete, as demonstrated below: Code Output:
Open High Low Close Volume Dividends Stock Splits
Date
2010-06-29 3.800 5.000 3.508 4.778 93831500 0 0.0
2010-06-30 5.158 6.084 4.660 4.766 85935500 0 0.0
2010-07-01 5.000 5.184 4.054 4.392 41094000 0 0.0
2010-07-02 4.600 4.620 3.742 3.840 25699000 0 0.0
2010-07-06 4.000 4.000 3.166 3.222 34334500 0 0.0
We obtained the maximum quantity of daily prices currently available on Tesla because we have set period = max. A lesser range is also passable such as 1d = 1 day, 5d = 5 days, 1mo = 1 month, 2y = 2 year are all acceptable alternatives. As an alternative, we can specify our beginning and ending dates: Code Output:
Open High Low Close Volume \
Date
2010-06-29 3.800000 5.000000 3.508000 4.778000 93831500
2010-06-30 5.158000 6.084000 4.660000 4.766000 85935500
2010-07-01 5.000000 5.184000 4.054000 4.392000 41094000
2010-07-02 4.600000 4.620000 3.742000 3.840000 25699000
2010-07-06 4.000000 4.000000 3.166000 3.222000 34334500
... ... ... ... ... ...
2020-12-23 632.200012 651.500000 622.570007 645.979980 33173000
2020-12-24 642.989990 666.090027 641.000000 661.770020 22865600
2020-12-28 674.510010 681.400024 660.799988 663.690002 32278600
2020-12-29 661.000000 669.900024 655.000000 665.989990 22910800
2020-12-30 672.000000 696.599976 668.359985 694.780029 42846000
Additionally, we can jointly download historical prices for multiple stocks: Code Output: Date 2010-02-01 6.159000 6.243000 5.691000 5.943500 5.943500 2010-02-02 5.939500 5.949000 5.720000 5.906000 5.906000 2010-02-03 5.856000 5.980500 5.828000 5.955000 5.955000 2010-02-04 5.932000 6.016500 5.787000 5.797000 5.797000 2010-02-05 5.794000 5.882500 5.705000 5.869500 5.869500 ... ... ... ... ... ... 2020-12-23 160.250000 160.506500 159.208496 159.263504 159.263504 2020-12-24 159.695007 160.100006 158.449997 158.634506 158.634506 2020-12-28 159.699997 165.199997 158.634506 164.197998 164.197998 2020-12-29 165.496994 167.532501 164.061005 166.100006 166.100006 2020-12-30 167.050003 167.104996 164.123505 164.292496 164.292496 The program above generates a Pandas DataFrame with the various price information for the specified stocks. Then, we may choose a specific stock by printing the data frame interval prices. Amazon's historical market data will be available by AMZN: Important Words and PhrasesIt is important to comprehend what the data means and shows.
Calculating Returns per DayReturns are the gains or losses a stock experiences once a trader or investor has leveraged long or short positions. We merely employ the pct_change() function. Code Output:
[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed
Open High Low Close Adj Close \
Date
2010-06-29 3.800000 5.000000 3.508000 4.778000 4.778000
2010-06-30 5.158000 6.084000 4.660000 4.766000 4.766000
2010-07-01 5.000000 5.184000 4.054000 4.392000 4.392000
2010-07-02 4.600000 4.620000 3.742000 3.840000 3.840000
2010-07-06 4.000000 4.000000 3.166000 3.222000 3.222000
... ... ... ... ... ...
2020-12-23 632.200012 651.500000 622.570007 645.979980 645.979980
2020-12-24 642.989990 666.090027 641.000000 661.770020 661.770020
2020-12-28 674.510010 681.400024 660.799988 663.690002 663.690002
2020-12-29 661.000000 669.900024 655.000000 665.989990 665.989990
2020-12-30 672.000000 696.599976 668.359985 694.780029 694.780029
Date
2010-06-29 0.000000
2010-06-30 -0.002512
2010-07-01 -0.078472
2010-07-02 -0.125683
2010-07-06 -0.160938
...
2020-12-23 0.008808
2020-12-24 0.024444
2020-12-28 0.002901
2020-12-29 0.003465
2020-12-30 0.043229
Name: Adj Close, Length: 2646, dtype: float64
Moving AveragesMomentum-based trading strategies are built on the idea of moving averages. Moving period estimates are used by analysts in the field of finance to continuously evaluate statistical measures throughout a slidable time period. Let's move the window by 1 day to illustrate how we can calculate the rolling mean over a period of 55 days. Code Output: Date 2020-12-16 482.089091 2020-12-17 486.214364 2020-12-18 490.702364 2020-12-21 494.970909 2020-12-22 498.873819 2020-12-23 503.092000 2020-12-24 507.391455 2020-12-28 511.714546 2020-12-29 515.932546 2020-12-30 520.523092 Name: Adj Close, dtype: float64 Moving averages give us a smoother company performance profile by removing any data discrepancies or outliers. Plotting to See the DifferenceWe will plot both moving averages and adjusted closing prices for better clarity. Code Output: 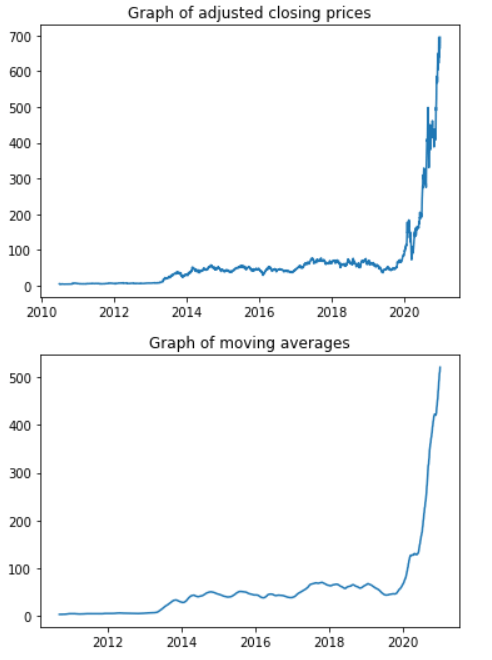
Plotting Them TogetherCode Output: 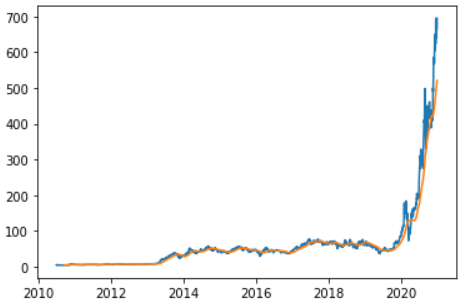
Next TopicPython Automation Project Ideas
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










