GUI to Shut Down, Restart, and Log off the computer using Tkinter in PythonAs we know, Python is a standard scripting language because of its multipurpose features. In the following tutorial, we will understand how to build a GUI application in order to Shut Down, Restart and Log off the computer with the help of the tkinter and the os modules in the Python programming language. But before we get started, let us have a quick overview of the os module. Understanding the os module in briefThe os module is a built-in Python module that allows users to interact with the Operating System. The os module in Python offers functions to work with directories, manipulate their contents, and work with the system. In order to start interacting with the underlying Operating System, we are first required to import the os module. The syntax of the same is shown below: File: test.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the import statement to import the os module. Let us now understand how to shut down, restart, and log off the computer system using the os module. The os module offers the system() method to execute the command (a string) in a subshell. This method is executed by calling the Standard C function system(), which has the same restrictions. If the command produces any output, it is forwarded to the interpreter's standard output stream. The particular shell of the Operating System is opened whenever this method is utilized, and the command is executed on it. Let us now consider the syntax of the system() method of the os module. Syntax: Parameter(s): 1. command: The command is a string-type parameter that informs which command to execute. Return Value: The return value on the Unix Operating System is the process's exit status. In contrast, the return value on the Windows Operating System is the value returned by the system shell after running the command. Now that we have understood what the os.system() method does, it is time to understand how we will use it to shut down, restart, and log off the computer system. We will use the system's shutdown command followed by the argument /s to shut down the system, /r to restart the system, or /l to log off the system. We can also use the /t argument followed by some integer value to set the timer for executing the operation. Let us consider the following syntax illustrating the same. Syntax: Prerequisites of the ProjectThere are some libraries and modules that we will need in the creation of the GUI to Shut down, restart, and log off the computer in Python. These libraries are briefly described as follows:
Since the Tkinter library along with the os and webbrowser modules comes preinstalled with Python, there is no need to install it externally. However, we can install the pillow (PIL) library using the PIP installer by typing the following command in a command prompt or terminal. Syntax: Once the installation is complete, we can verify whether the pillow library is installed properly or not by creating a new python program file and importing the pillow (PIL) module. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the same. File: verify.py Now, let us save the file and run the following command in a command prompt or terminal. Syntax: The library has been installed successfully if the program does not return any importing error. In case any exception is raised, try reinstalling the library and consider checking their official documentation. Let us now start building the project. Building the GUI to Shut Down, Restart, and Log off the computer using Tkinter in PythonWe have divided the complete project code for creating this GUI Application in Python into several steps for better understanding. These steps are shown below: Step 1: Importing the necessary modules Step 2: Defining the required functions to execute different operations Step 3: Creating the main window of the application. Step 4: Adding necessary widgets to the window and setting the event triggers. Let us understand the steps mentioned above in a more elaborate way. Importing the necessary modulesAt first, we will start by importing all the required modules, which include all the widgets and modules from the tkinter module, the Image and ImageTk modules from the PIL module, the os module and the webbrowser module. Let us consider the following snippet of code illustrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have imported all the widgets and modules from the tkinter module to work with Graphical User Interface. We then imported the Image and ImageTk modules from the PIL module to add images to the program and use them in the Tkinter application. We then imported the os module to use the system commands. At last, we have imported the webbrowser module to add a website link to the application. Defining the necessary functions to execute different operationsNow that we have imported all the required modules for the project, it is time for us to define some functions to execute different operations. These functions include displaying the information, executing the desired command, canceling the action, and accessing help. Let us now understand the implementation of these functions in detail. Function to Display the Information The first function we define will allow us to display the information. This function will check the selected key in the options menu and display the information related to the selected option for the user. The following is the snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as display_info() with a variable-length argument. Within this function, we have iterated through the keys in the MENU dictionary using the for-loop. We have then used the set() method to display the information in the label from the INFO list for the selected option. Function to Execute the Desired Command We will now define a function to execute the system's shutdown command with different arguments per the requirement. This function will use the system() method of the os module to execute the system's shutdown command with the appropriate argument for the selected option from the menu. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as execute_command(). Within this function, we have iterated through the keys available in the MENU dictionary and checked if the selected option is equal to the key in the MENU. If so, we have used the system() method to execute the system's shutdown command, followed by the argument available as the value for that respective key. Function to cancel the action We will now define a function to cancel or terminate the action. We will use the destroy() method to close the application. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as cancel(). Within this function, we have used the destroy() method along with gui_root, the object of the Tk() class to close the application. Function to access the help We will now define a function to open the URL providing help and support. We will use the open() method of the webbrowser module to open the required URL. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as help(). Within this function, we have used the open() method of the webbrowser module to access the URL providing the help and support. Creating the main window of the applicationNow that we have defined all the necessary functions to execute the operations, it is time for us to create the main window where the widgets will be added. We will create the window using the Tk() class of the tkinter module. We will also set the title, size, position, background color, and icon. Let us consider the following snippet of code illustrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have created the main window by instantiating the Tk() class as gui_root. We then used the title() method to set the title of the window. We have also set the size and position of the window using the geometry() method and disabled the resizable option for better UI by setting the values of the parameters of the resizable() method to 0. We have configured the background color of the window with the help of the config() method. At last, we have used the iconbitmap() method to set the icon of the window. Adding the necessary widgets to the window and setting the event triggersSince the main window of the application is created successfully, we will add all the necessary widgets to the window and set the event triggers. These widgets include frames to structure other widgets, labels to display important information, entry fields to insert data, and buttons to manipulate the entered data and call the functions. Let us now understand the addition of these widgets in detail. Adding Frames & Images We will start by adding the frames to the main window. These frames will help structure the other widgets. These frames can be created using the Frame() widget of the tkinter module. We will also import some images to the program using the Image and ImageTk module of the PIL module. These images will display some information in the application. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have added some frames to the window using the Frame() widget and set their master parameters to gui_root, the object of the Tk() class. We then used the pack() method to set the position of these frames. We then used the open() method of the Image module and the PhotoImage() method of the ImageTk module to import the images from the directory for the Tkinter application. Adding the widget to the heading_frame Frame We will now add a label to this Frame using the Label() widget to display the heading. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Label() widget to add an image as the label to the application. We then used the pack() method to set the position of this label. Adding the widgets to the menu_frame Frame We will now define a dictionary to display a set of options to be performed through the application. We will also define a list to display the information associated with each option. We will then add the widgets like the labels to display some information and an options menu for the user to select the operation to be performed using the Label() and OptionMenu() widgets. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a dictionary as MENU, displaying the options and the arguments to perform the associated operation. We have then defined a list as INFO displaying the information regarding each operation. We have then created an object of the List() function for the MENU dictionary. We have then created some objects of the StringVar class and set the initial values of these objects. We have added some labels using the Label() widget setting their master parameters to the menu_frame frame. We have then used the OptionMenu() widget to create a drop down menu to display the keys of the MENU dictionary and set their master parameters to the menu_frame frame. We have also used the config() method to configure the width, background color, and anchor of the menu. At last, we have used the grid() method to set the position of the labels and option menu in the grid format. Adding the widgets to the buttons_frame frame We will now add the necessary buttons to this frame. We will use the Button() widget to add the buttons to the application that will allow the user to execute the operation, cancel the action, and access the help. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Button() widget to add the buttons to the application and set the master parameter to the buttons_frame frame. We have then set the command parameter of these widgets to the functions we defined earlier. We have also used the Label() widget to add an empty label to the application and set the master parameter to the buttons_frame frame. At last, we have used the grid() method to set the position of these buttons and the label in the grid format. Running the Application We will now use the mainloop() method along with the object of the Tk() class to run the application. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: appToClose.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the mainloop() method with gui_root, the object of the Tk() class, to run the application. Hence, the project code is now complete. We will save this python program file and run the following command in the command prompt or terminal to see the output. Syntax: But before we see the output, the complete project code of the 'GUI to Shut down, Restart, and Log off the computer using Tkinter' is shown below. The Complete Project CodeThe following is the project code for the 'GUI to Shut down, Restart, and Log off the computer using Tkinter in Python'. File: appToClose.py Output: 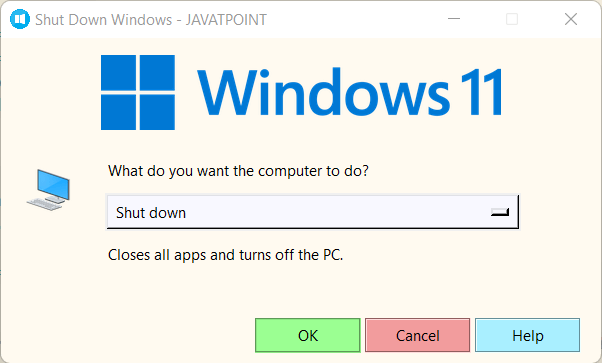
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










