Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
Python random randrange()The Python random module allows generating random numbers. The generated numbers are a sequence of pseudo-random numbers, which are based on the used function. There are different types of functions used in a random module to generate random numbers, such as random.random(), random.randint(), random.choice(), random.randrange(start, stop, width), and many more. Here, we will discuss the randrange() function of the random module. The randrange() function is used to generate a random number between the specified range in its parameter. It accepts three parameters: starting number, stop number, and width, which is used to skip a number in the range. Syntax of random.randrange()The random.randrange() function returns a random integer number within the given range, i.e., start and stop. The random.randrange() function takes three parameters as an input start, stop, and width. Out of these three parameters, the two parameters start and width are optional.
The randrange(start, stop, width) function does not include the end parameter while generating the random integer number. The stop parameter is exclusive, and it not gets generated in a random number. Look at this random.randrange(3, 30, 3) function that will generate any random integer value between 3 to 30 like 3, 6, 9, 12, …27. But this function never includes 30 while generating a random number. Generating a random in an application always been important, and it has several real-time uses in day-to-day life. For example, generating and sending a random number to a customer as an OTP (one-time-password) for making a safe transaction. Another example of generating a random number is used while playing the ludo game to generate a random dice number. Examples 1: random.randrange() generate a random integers number within the given rangeLet's see an example where we are generating a random integer number within a given range. This example shows all the different forms of random.randrange() function. Output: 
Example 2: Generate a random integer number range (multiple) of nLet's generate the random integer number between 5 to 100, which is a range of 5 such as 5, 10, 25, …, 90, 95. Output: 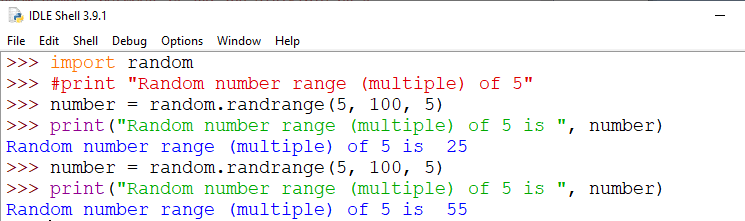
Example 3: Generate the random integer number of a specific lengthYou can also generate a random integer number of a specific length. If you want to generate a random number of length 3, input the start and stop parameter in randrange() function as least number of 3 digit length (100) and least number of 4 digit length (1000) because it generates a random number of 3 digit form 100 to 999 where 4 digits (1000) is excluded. Example: Generate a random number of 3 digit using random.randrange() Output: First random number of length 3 is: 813 Second random number of length 3 is: 770 Example 4: Generate a random negative integer number:Let's see an example that generates a random negative integer number between -50 to -10. Output: Random negative integer number between -50 to -10 Random negative integer number between -50 to -10 is: -43 Example 5: Generate random positive or negative integer numberOutput: -5 0 Note that the parameter start and stop, which is passed in random.randrange() function must be in increasing order, such as random.randrange(5, 10) or random.randrange(-20, -10). The start parameter always be smaller than the stop parameter; otherwise, this function generates an error as "Traceback (most recent call last) and raise ValueError empty range for randrange()".For example: Look at this example in which we are violating the rule by passing the start parameter greater than the stop parameter in random.randrange() function, which generates an error message as: Output: 
Some of the other functions of Python's random module that are used to generate numbers randomly are:
random.choice()Python random module has a choice() function used to choose a random element from a list or other sequence. A random.choice() function is used to returns a random element from the list of values. Syntax of ramdom.choice() or Here the parameter sequence can be string, list, tuple, and random.choice() only a single random element. In the random.choices() function k is the number of elements to be returned. Suppose we don't mention the value for k parameter the random.choices() returns a single item from the sequence or list. Example 1: In this example, we are providing on sequence (list) as a parameter and returning a single random element. Output: random item from list is: 10 Example 2: The random.choices() function is mostly used for returning random elements with various possibilities. This function also takes weight (k) the number of random choices. For example, we want to print 3 random movies name from list of 5 movies. Output: random movies from list are: ['Avengers', 'Black Panther', 'Titanic'] random.randint()Python random.randint() function is used to generate a random integer number within the specified range. Syntax: The random.randint() function takes two parameters start, which is a starting range, and stop, which is an end range. Both parameters (start, stop) are included while generating a random number. Example of random.randint() generating a list of random integer This example will create a list of multiple random integers using the randint() function. Generating a list of 5 random integers between 1 and 100, both values are inclusive. Output: Printing list of 5 generated random numbers [65, 82, 3, 39, 40] However, there may be a possibility that the random.randint() function returns a duplicate number in the output result. To avoid the duplicate random integer number in a result, use random.sample() function. random.sample()In the above example, there may be a possibility that random.randint() generates the duplicate random number from the list. If you want to generate unique random numbers from a list, use random.sample() function. The random.sample() function generates unique elements from a set, list, and other sequences. Python's random.sample() function allows random sampling of more than one element within a range from the list without duplicating. Example of a random.sample() to generate random elements from a list without duplicates: In this example, we will generate 10 random integers from the range 0 to 100. Output: [15, 17, 16, 66, 34, 85, 71, 82, 97, 48] If you want to generate a list of random numbers and each of them must be multiple of 'n', then use the step parameter of range() function. For example, generating 10 random integers which are multiple of 5 from the range 0 to 100 using random.sample(range(0, 100, 5), 10). Output: [75, 40, 20, 55, 15, 10, 5, 90, 95, 70] List sort()The Python sort() function is used to sort the random integer numbers of the list in ascending order (by default). We can also sort the list value in descending order by specifying its order reverse = True. The default value of reverse is False. Example 1: sort() sorting list elements in ascending order In this example, we will generate a random list of 5 numbers in a range of 50 to 100 with the width of 5 and sort them using sort() function. Output: Before sorting random integers list [90, 80, 60, 55, 85] After sorting random integers list [55, 60, 80, 85, 90] Example 2: sort() sorting list elements in descending order In this example, we will sort the list elements in descending order using randomList.sort(reverse=True). Output: Before sorting random integers list [70, 50, 80, 90, 85] After sorting random integers list [90, 85, 80, 70, 50]
Next TopicPermutation and Combination in Python
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









