When and How to Leverage Lambda Architecture in Big DataIn the current technology environment, numerous companies are attracted by Big data. However, in the past Big data utilized data stored in the Hadoop technology and had to deal with the issue of latency. An entirely new system could be used for large amounts of data and with high speeds to solve this issue completely. In this article, we'll attempt to make it easy to comprehend the structure, which makes it easy to use Big Data, which is nothing but Lambda Architecture. The design was developed in the hands of James Warren & Nathan Marz. Let's look at a few facts about Lambda Architecture. What is this Architecture all about?For better business decisions and to gain insight, systems are designed to handle the variety, speed, and volume. This is a novel method of Big Data created to analyse, process, and insulate this data which is difficult and huge for the conventional system. The hybrid architecture aids in supporting the Big Data system in real-time and batch processing of data. In this model, we can access both historical and new data. To get a better understanding of the movement of data in the past, information is transmitted to the data storage. The basic idea behind this architecture is built on Lambda calculus and is known as Lambda Architecture. The architecture was specifically designed to work with unchangeable data sets, specifically for the purpose of its manipulation. The technology can also solve the issue of arbitrary computing functions. In general, the problem can be divided into three levels:
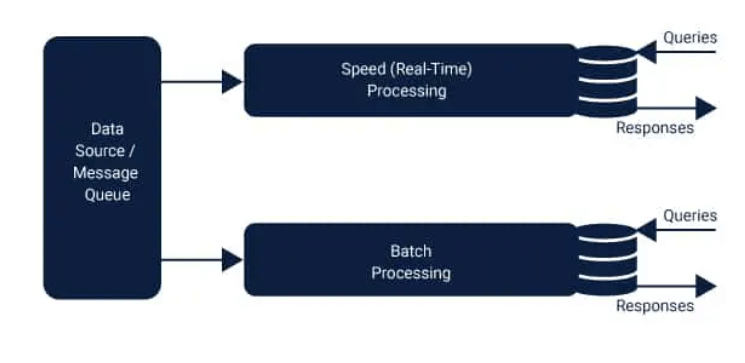
The image below will provide an understanding of the layers described above. Similar to Hadoop, this batch layer is referred to by the name of "Data Lake". It also functions as an archive for the past to store all data that has been fed into it. It also facilitates batch processing of data and aids in the generation of analysis results. To speed up the steaming and queuing of data, the speed layer is put into the picture. The function of this layer is to conduct analytic calculations on real-time data. The speed layer shares many features with the batch layer in that it can also calculate analogous analytics. The only difference is that the analysis is performed on data that is recent. Based on the speed of the data, the data could be as little as an hour outdated. The serving layer serves as the layer which combines the results from the two layers to produce the final. When data is transferred to the system, it is separated into speed and batch layers. The queries are answered through the integration of real-time view and batch view. While the batch layer performs two crucial roles.
The output of the batch layer is presented in the pattern of batch views, whereas the speed layer output is displayed in the form of live-time view patterns. The results are then passed to the layer serving. This indexing occurs in the serving layer so that requests can be made with low latency and in-demand. The speed layer, also known as the stream layer, is responsible for data that was not presented through batch views because due to the delay that the batch layers suffer. The layer only handles the most recent data, so it can provide an entire view by creating real-time views. In essence, we could say that in the Lambda structure, the data pipeline is separated into layers, and each is responsible for a specific task. In each layer, the provision is available to select the appropriate technology. For instance, in the Speed layer, one could select Apache Storm, Apache Spark streaming, or other technology. In the lambda structure, errors can be quickly rectified, as that it is necessary to return to the original version of the data. This can be accomplished because, in this case, data is never changed, but it is added in the event that the programmer inputs inaccurate data. They can delete and then recompute the data. Data Lake:The greatest benefit of this system is that it offers almost unlimited memory capacity as well as storage space. There is even an in-memory data store that has capacities of terabytes which is spread across all of the clusters. This type of architecture is reasonably cost-effective since it comes with built-in fault tolerance. With this huge data lake cluster, Data Lake can be built for any business. The entire data of the business is stored within the cluster and be shared via the cloud. The computational power of the architecture is able to be used to analyse the cluster. With this fault-resistant design, it is possible to reduce costs because a large number of duplicate ETL processes are prevented from interfacing with other systems. Applications of Lambda Architecture:The world is constantly undergoing new developments in the field of Big Data. Lambda architecture is built on log insertion and the analytics that accompany that. Most of the time, log messages are not contested and are produced at high speed, which is why they are often referred to as "fast data". There isn't a hard nor fast law that says that every log entry must receive an answer from the entity to which the data came since it's only a one-way pipeline. The processing of Big data is categorized into two pipelines data. One pipeline is where data is gathered in a huge quantity from various sources and stored in a distributed manner. The data is then analyzed to obtain the precise information needed to make better business decision-making. The procedure followed could be called a batch processing pipeline. In simple terms, the data pipeline architecture is designed to collect data and routes it through the data pipeline to provide insight into the analytical and intelligence of the business. It extracts and transforms data and then feeds it into databases. Another method of processing data using the Lambda architecture followed is an analysis of data while the data is in motion. This process is called the streaming data Pipeline. This is where the calculations are performed using live data. The framework we can use to do this is Apache Spark. The framework used for this is Apache Spark. Spark, it is possible to have the information separated into smaller batches, which stores them in memory and process the data and eventually remove the data from memory. The method used here can reduce the amount of latency since calculations are performed in memory. Merits of Lambda ArchitectureLambda architecture offers a variety of advantages, but the most significant ones are impermanence, fault tolerance, and it is used to perform re-computation or precomputation. The most significant advantages of this architecture are described in the following paragraphs:
In short, the benefits of this design are:
Disadvantages of Lambda ArchitectureSelecting a lambda framework for an enterprise that is preparing a data lake can have some negatives, too, especially in the event that certain aspects aren't taken into consideration. Certain of these points are listed in the following paragraphs:
A Unified Approach to Lambda ArchitectureAs mentioned above, one of the major drawbacks of the Lambda structure is its complexity. It's ongoing troublesome maintenance and installation because one must sync two systems that are distributed. To overcome these issues, there are three different methods that we will discuss below:
The image below will help you gain a better understanding of the issues mentioned above. The unification approach tackles the volume and velocity issues of Big Data as it utilizes a hybrid computing model. The model blends immediate and batch data with ease. An Outline of the ArchitectureBig data systems typically operate on raw and partially structured data. Organizations today require systems that have the capacity to process batch as well as real-time data. Lambda architecture is equipped to handle both processes. In the meantime, it is able to build impermanence in the process. The structure follows a solid set of guidelines, and it is an agonist of technology. Any technology can be integrated into it to accomplish the task since it's made up of different layers. Ready cloud components are accessible and can be used using the lambda structure. The architecture could be described as a pluggable system that can be used when a process is needed. Many data sources are plugged in or out based on the requirements. Real-Time Working Examples:Lambda architecture has proven itself many applications. A few of the examples that are working are listed in the following:
ConclusionSince the beginning of time, Big data technology has gained popularity. But when it comes to the requirements of a company such as Google or Facebook, the technology in place was not suited to the demands of the business. To satisfy their requirements, a standardized and flexible architecture was needed, leading to the creation of Lambda architecture. Following the introduction of this model, the proper planning must be taken to transfer the data into Data Lake. Since the architecture focuses on analytics, one could utilize the traditional transactional database to transfer the data into the cluster. Each year, more companies are moving to Big Data. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










