Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
Python New LineGenerally, when we print a string using a print statement, we use another print statement to print another string in a new line. When we write a print statement, after its execution, automatically, the cursor is shifted to a new line. Why does this happen? Can't we print a string in a new line without using a new print statement? The code becomes absurd if we keep writing new print statements for every string. The answer to both the above questions is an escape sequence character called the 'Python new line character' represented by '\n'. This article discusses new line character with examples. Basic understanding:Character: '\n' Function: Shifts the cursor to a new line.
Syntax:
Need of '\n':Suppose we are trying to print "Hello" in the first line, '!' in the next line and "world" in the line after that and if we use a normal print statement: Output: 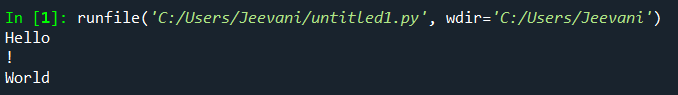
It took 3 lines of code to print 3 words. The code will be longer if we want to print more strings. Now, if we use '\n': Output: 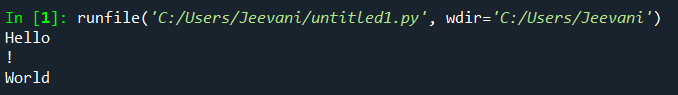
It just took one line. We can print any number of strings using '\n' in multiple lines and still keep the code simple and small. More about '\n':Why is the print statement not printing '\n' like a normal string? How does Python recognize '\n'? We have a few predefined characters in Python succeeding a back slash character ('\'), called the 'Escape sequences'. Python recognizes the '\' and immediately understands that it is not a part of the string and executes it based on its succeeding character. Using a backslash before a character helps the character escape normal string execution. Examples: \t, \r, \n etc. Declaring a string with '\n': Output: 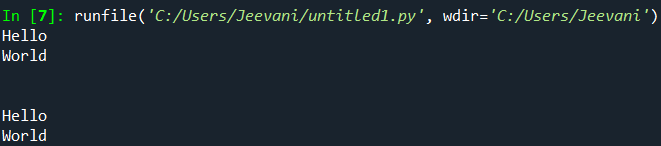
Understanding: In the above example:
How does the print statement automatically shift to a new line?In Python, the syntax of the print statement: print (values, sep = '', end = '\n', file = file, flush = flush) Here, the end is an optional parameter. It specifies the last character we want the string to end with. By default, '\n' is assigned to the end, which is why, after the execution of a print statement, it will shift the cursor to the next line when we don't give any argument to the end. If we give an argument to the end: Output: 
Understanding: We assigned '!' to the end. Hence, after the execution of the first print statement, the second print statement is not shifted to a new line and follows "!" in the same line. Another way to print a string in a new line:There is one more way we can shift to a new line. First, we can use multiple print statements. Second, we can use the '\n' character. We can achieve this using 'Multi-line strings' in Python. We use single quotes or double quotes to print a single-line string. In Python, we can print multiple lines of strings using either 3 double quotes ("""strings""") or three single quotes (''' string'''). Syntax: Python recognizes that the string is a multi-line string by the quotes ''' or """. Example: Output: 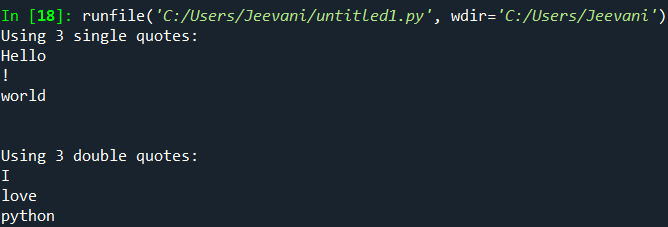
Understanding: We wrote two multi-line strings using single quotes and double-quotes.
Summary:We can print a string in a new line in 3 ways in Python:
These three ways might be useful for different needs, but programmers mostly use '\n' to print a new line because it is the most commonly accepted method due to its simplicity. Using '\n,' we can:
Next Topic__init__ in python
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









