Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
In-place Operators in PythonPython provides a set of in-place operators in Python. In-place operators allow you to perform arithmetic, logical, and bitwise operations on variables updating their values in place. These operators are denoted by combining the assignment operator (=) with another operator. It enhances the program's performance and saves memory. In this article, we will explore the various in-place operators available in Python, along with examples. 1. iadd() - In-place AdditionThe iadd(x, y) operator performs an in-place addition operation. It updates the value of the variable with the result. It is represented by the += symbol. Output: Original, a = 5 Updated, a = 9 The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place addition. 2. isub() - In-place SubtractionThe isub(x, y) operator performs an in-place subtraction operation. It updates the value of the variable with the result. It is represented by the -= symbol. Output: Original, a = 5 Updated, a = 1 The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place subtraction. 3. imul() - In-place MultiplicationThe imul(x, y) operator performs an in-place multiplication operation. It updates the value of the variable with the result. It is represented by the *= symbol. Output: Original, a = 5 Updated, a = 20 The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place multiplication. 4. itruediv() - In-place True DivisionThe itruediv(x, y) operator performs an in-place true division operation. It updates the value of the variable with the result. It is represented by the /= symbol. Output: Original, a = 5 Updated, a = 1.25 The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place true division. 5. iand(), ior(), ixor() - In-place Bitwise AND, Bitwise OR, Bitwise XORThe iand(x, y) operator performs an in-place Bitwise AND operation. It is represented by the &= symbol. The ior(x, y) operator performs an in-place Bitwise OR operation. It is represented by the |= symbol. The ixor(x, y) operator performs an in-place Bitwise XOR operation. It is represented by the ^= symbol They all update the value of the variable with the result. Output: Original, a = 5 Original, c = 3 Original, d = 2 Updated, a = 4 Updated, c = 7 Updated, d = 6 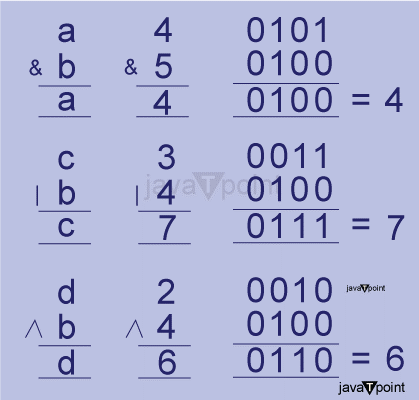
The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place AND, OR, and XOR operations. 6. imod() and ifloordiv() - In-place Modulo and Floor DivisionThe imod(x, y) operator performs an in-place modulo operation. It is represented by the %= symbol. The ifloordiv(x, y) operator performs an in-place floor division operation. It is represented by the //= symbol. They update the value of the variable with the result. Output: Original, a = 5 Original, c = 15 Updated, a = 1 # Remainder when 5 is divided by 4 Updated, c = 3 # Floor value of the result The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place modulo and floor division operations. 7. ilshift() and irshift() - In-place Left Shift and Right ShiftThe ilshift(x, y) operator performs an in-place left-shift operation. It is represented by the <<= symbol. The irshift(x, y) operator performs an in-place right-shift operation. It is represented by the >> = symbol. They update the value of the variable with the result. Output: Original, a = 20 Original, b = 25 Updated, a = 80 Updated, b = 6 
The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place modulo and floor division operations. 8. ipow() - In-place ExponentiationThe ipow(x, y) operator performs an in-place exponentiation operation. It is represented by the **= symbol. It updates the value of the variable with the result. Output: Original, a = 10 Updated, a = 100 The above code demonstrates how to perform an in-place exponentiation operation. 9. imatmul() - In-place Matrix MultiplicationThe imatmul() operator performs an in-place matrix multiplication operation. It updates the value of the variable with the result. It is represented by the @= symbol. Output: Original, a = [[1 2] [3 4]] Updated, a = [[19 22] [43 50]] 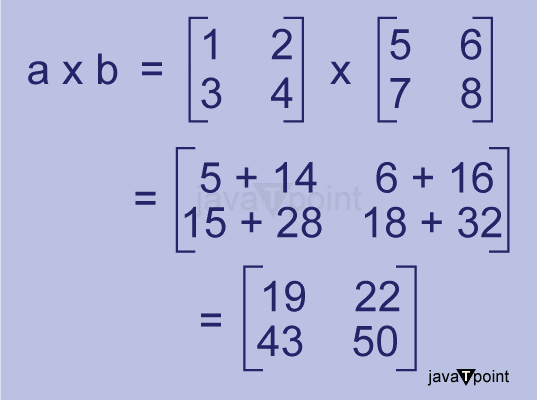
The above code demonstrates how to perform an in-place matrix multiplication operation. 10. iconcat() - In-place ConcatenationThe iconcat(x, y) performs an in-place concatenation operation. It is represented by the += symbol and used to concatenate strings, lists, and other sequences. It updates the value of the variable with the concatenated result. Output: Original, s = Hello Updated, s = Hello World Original, numbers = [1, 2, 3] Updated, numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] The above code demonstrates how to perform in-place concatenation operation. CONCLUSIONIn conclusion, in-place operators allow you to perform different operations in place means updating the value of the variable without creating a new variable or object. They provide an efficient way to perform operations, save memory, and make your code more readable. By using these in-place operators, you can streamline your code and improve its performance. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









