Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
DFS (Depth First Search) in PythonIn this tutorial, we will learn about the Depth first search algorithm and implement with the Python programming language. We will discuss its fundamental and its simplicity. This algorithm is used to solve the graph related problem which will helpful in the many competitive exams. DFS is a traversal algorithm which is used to traverse all the elements or search an element in a graph or tree. Let's have a basic introduction of the DFS. Introduction to Depth First SearchThe DFS is an algorithm used to traverse the target node in a graph or tree data structure. The depth-first search derives from the word "depth". Its priorities depth and searches along one branch, as far as it can go - until the end of the branch. In Python, we can easily implement it using the recursion and other data structures like dictionaries and sets. Representation of a GraphBefore implementing the DFS algorithm, we will try to understand how to represent a graph in Python. There are several versions of the graph. A graph may have directed edges (defining the source and destination) between two nodes, or undirected edges. The directed graph can have the weights. It is completely depend upon the application to may use any of the versions of a graph. To implement the DFS, we will use the graph with the directed edges for the purpose of traversal through the entire graph. Python provides the multiple ways to represent a graph in Python; below are the most common ways.
Adjacency MatrixAdjacency Matrix is a square matrix of shape N x N (where N is the number of nodes in the graph). Each node represents a node; each of the columns represents a probable child of that node. Each (row, column) pair represents a potential edges. A non-zero value at the position (i, j) specifies the existence of an edge between i and j. If value is zero means there are no edges between i and j. The binary number can be used in the non-weighted graph (1 represents edge exist, and 0 represents it doesn't). For example a value 15 between at position (2, 3) represents there is edge exists between node 2 and 3 with the weight 15. We can represent the adjacency matrices using a 2-dimensional Numpy array. Adjacency ListIt is a list of the collection of the several lists. Each list represents a node in the graph, and stores all the neighbors/children of this node. We can use the dictionary to represent the adjacency list where the keys are the nodes of the graph, and their values are a list keeping the neighbors of these nodes. Let's take a simple example of graph and represent it using dictionary. 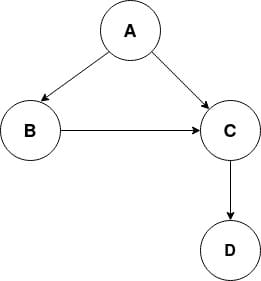
The above graph has given four edges. A -> B A -> C B -> C C -> D Let's create a Python dictionary to represent this graph. Now we have an idea how to represent the graph in Python. Let's implement the DFS algorithm. Implementing Depth First Search (A non-recursive approach)Let's consider the following graph for the DFS implementation. 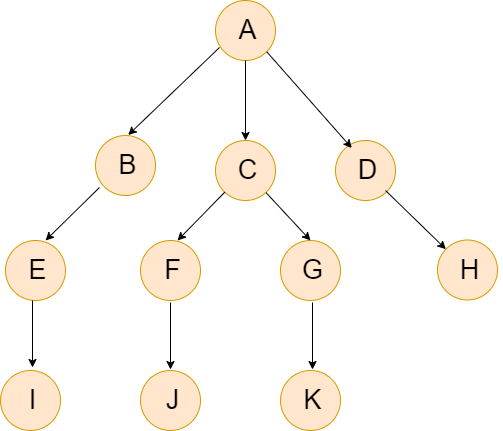
Let's define the graph as an adjacency list using the Python Dictionary. We can implement the DFS both recursion technique and non-recursion technique, iterative approach. In this section, we will understand the iterative approach. We will use a stack and a list to keep track of the visited nodes.
DFS PseudocodeBelow is the Pseudocode of the DFS. In the init() function, we run the DFS function on every node because most of the times, a graph may contain two different disconnect part. So it makes sure that we cover every vertex, can also run DFS algorithm on every node. Note - The above Pseudocode is for the recursive approach.Let's implement the DFS using the Python code. Example - Output: A D H C F J G K B E I The order of the traversal of the graph is in the 'Depth First' manner. DFS using a Recursive MethodThe recursive is a popular problem solving approach in which the same problem is divided into smaller instances. We will define the base case inside our program. Let's understand the below example. Example - Output: ['A', 'B', 'E', 'I', 'C', 'G', 'K', 'F', 'J', 'D', 'H'] The order of traversal is again in the Depth-first manner. ComplexityThe time complexity of the DFS is represented as O(V+E), where V shows the number of nodes and E is the number of edges. The space complexity is 0(V). Application of AlgorithmThe following are the real-life application of DFS.
ConclusionThis tutorial includes the concept of Depth-First Search in Python which is used to traverse the graph or tree. We have discussed both recursive and non-recursive methods to implement DFS in Python. We have also defined how to represent graph in Python. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










