Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
Sklearn Logistic RegressionIn this tutorial, we will learn about the logistic regression model, a linear model used as a classifier for the classification of the dependent features. We will implement this model on the datasets using the sklearn logistic regression class. What is logistic regression?Predictive analytics and classification frequently use this kind of machine learning regression model, also referred to as a logit model. Depending on the given dataset of independent features, the logistic regression model calculates the probability that an event will occur, such as voting or not voting. Given that the result is a probability of happening an event, the dependent feature's range is 0 to 1. In the logistic regression model, the odds of winning the probability of success of an event divided by the probability of failure-are transformed using the logit formula. The following formulas are used to represent this logistic function, which is sometimes referred to as the log odds or the natural logarithm of odds: 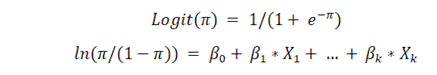
Logit(pi) is the dependent or target feature in the equation of the logistic regression model, while x is the independent feature. The most frequent method for estimating the coefficients in this linear model is by using the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). To find the best fit for the log odds, this approach iteratively evaluates various values of the coefficients. The log-likelihood function is created after each of these iterations, and logistic regression aims to maximise this function to get the most accurate parameter estimate. The conditional probabilities for every class of the observations can be computed, logged, and added together to produce a forecast probability once the best coefficient (or coefficients, if there are multiple independent features) has been identified. If the classification is binary, a probability of less than 0.5 predicts 0, and a probability of more than 0 indicates 1. Once the logistic regression model has been computed, it is recommended to assess the linear model's goodness of fit or how well it predicts the classes of the dependent feature. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test is a well-liked technique for evaluating model fit. Sklearn Logistic Regression ExampleSklearn Logistic RegressionParameters:
Sklearn Logistic Regression ClassifierCode Output: [0 0] [[9.81764058e-01 1.82359281e-02 1.43020498e-08] [9.71660947e-01 2.83390229e-02 2.99214023e-08]] 0.9733333333333334 Logistic Regression CV ExampleCode Output: [0 0] [[9.91624054e-01 8.37594552e-03 2.92559111e-11] [9.85295789e-01 1.47042107e-02 1.03510087e-10]] 0.9866666666666667 Scikit-learn Logistic Regression CoefficientsIn this part, we will learn how to use the sklearn logistic regression coefficients. A number to which we multiply the value of an independent feature is referred to as the coefficient of that feature. Here, a feature's size and direction are expressed using logistic regression. Code Output: The size of the complete dataset is: 150 [[-0.35041623 0.91723236 -2.23583834 -0.97778255] [ 0.56061567 -0.44283218 -0.21739708 -0.64651405] [-0.21019944 -0.47440019 2.45323542 1.6242966 ]] Sklearn Logistic Regression Feature ImportanceIn this part, we will study sklearn's logistic regression's feature importance. A method called "feature importance" assigns a weight to each independent feature and, based on that value, concludes how valuable the information is in forecasting the target feature. Code Output: [ 1.96365376 -0.11875128 -0.32930302 1.23664458 -1.40461804] Feature: 0, weight: 1.9636537611525497 Feature: 1, weight: -0.1187512810730595 Feature: 2, weight: -0.32930302369908127 Feature: 3, weight: 1.236644582783369 Feature: 4, weight: -1.4046180417231233 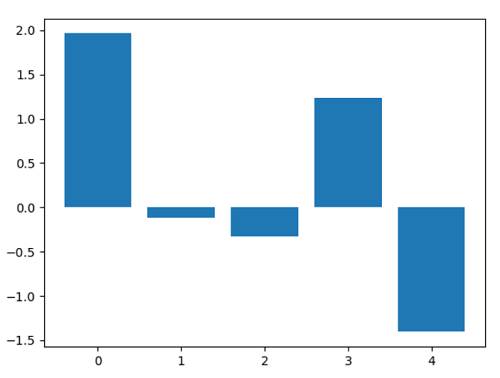
Sklearn Logistic Regression Cross-ValidationCode Output: Cross-validation accuracy scores of each split is: [0.80666667 0.80666667 0.81333333 0.86666667 0.78666667 0.8 0.78 0.82 0.80666667 0.83333333] mean and standard deviation of the scores is: 0.812 0.023247461032216934
Next TopicWhat is Sklearn in Python
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










