Compound Interest GUI Calculator using PythonThe Programming language like Python provides different options for developing a GUI, short for Graphical User Interface. Among all the GUI methods, Tkinter is the most commonly utilized one. In the following tutorial, we will learn the method of creating a simple Compound Interest GUI Calculator application with the help of the Tkinter package in the Python programming language. But before we get started with the coding section, let us briefly understand the Compound Interest and how we can calculate it using Python. Understanding the Compound InterestCompound Interest is the Interest paid on both the principal as well as Interest compounded at standard intervals. At standard intervals, the accumulated Interest is clubbed with the current principal amount, and then the Interest is estimated for the new principal. The new principal is equivalent to the sum of the initial principal and the Interest accumulated so far. We can calculate the Compound Interest in two steps. At first, we will calculate the final amount by multiplying the initial principal amount by one plus the annual interest rate raised to the number of compound periods minus one. For the next step, we will subtract the total initial amount of the loan from the resulting value. This will give us Compound Interest or CI. Thus, in order to calculate the annual compound interest, we will multiply the actual amount of the loan, investment, or principal, by the annual interest rate. We will then add that amount to the principal, then multiply it by the interest rate again to get the compounding interest of the second year. Let us now consider the above statement mathematically: 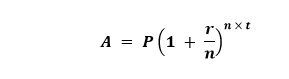
Where,
The above formula represents the total amount at the end of the time period and includes the compounded interest and the principal. Moreover, we can estimate the compound interest by subtracting the principal from this amount. The formula for calculating the compound interest is as follows: Let us now consider the above mathematical statement using an example. Example: Input Values P = 7500 If we put the above values into the formula, we will get the following: 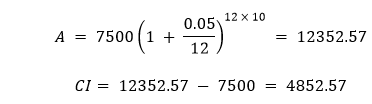
Thus, the Total Amount is , and Compound Interest is . Let us now consider the following example code demonstrating the implementation of the above formula in Python: Example: Output: Enter the Principal Amount: 7500 Enter the Rate of Interest: 0.05 Enter the Number of times that interest is compounded per unit t: 12 Enter the Time Period: 10 Compound Interest (C.I.): 4852.571233 Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as compound_interest() that accepts some parameters like principal, rate_of_interest, number, and time. We have used the above formula to calculate the amount for compound interest and then calculated the compound interest by subtracting the principal amount from the total amount. At last, we have returned the compound interest as ci. We have then defined another function as main_function() that asks input like principal, rate of interest, number of time, and time period from the user and stored them in the variable p, r, n, and t. We have then called the compound_interest() function providing the values from the variables and storing the result in a new variable, ci. We have then printed the result for the user. At last, we have called the main_function() to execute the program. We will now modify this function in order to utilize it with the Tkinter library to build a Graphical User Interface for the calculation of Compound Interest. Creating the Compound Interest GUI Calculator using TkinterWe will create the GUI for the project using the following steps: Step 1: We will import the required modules. Step 2: We will then define some functions for the application. Step 3: We will then create the main window (container). Step 4: We will then add any number of widgets to the main windows. Let us now understand these steps in detail. Importing the required modulesFirst of all, we will import the Tkinter library to construct the GUI for the application. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: We have imported the required widgets and methods from the Tkinter library in the above snippet of code. Defining the necessary functions for the ApplicationWe will require some important functions for this GUI application that will help us run the program. The first function will allow us to reset the entry fields that a user will fill whenever the user presses the Reset Button. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as reset(). Within this function, we have deleted all the entries written in the entry fields using the delete() method specifying (0, END) as its parameter in order to delete the entire text. We have then used the focus_set() method to the entry field we will define for the principal amount later in this tutorial. We will now define another function that will calculate the compound interest for the entered values. We will slightly modify the previous compound_interest() function for this function. The following snippet of code demonstrates the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as compound_interest(). We retrieved the values from the entry fields and stored them as float values in different variables. We have then calculated the compound interest of the entered value and inserted the resultant value in the result entry field. Creating the main window for the applicationNow that we have successfully created the functions we need for the application, we will work on the GUI section. We will create the main window for the application where all the necessary widgets will be displayed in the section. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we defined the main function. We have created an object of the Tk() class within this function. We have then defined the title for the as GUI window using the title() method. We have then defined the geometry for the window using the geometry() method and disabled the resizable option by setting the (0, 0) as the parameters in the resizable() method. At last, we have used the configure() method and set the background color to #f0c33c for the application. Adding Widgets to the Main Window Now that we have created the main window for the project. It is time for us to add some widgets to it in order to display data to the users. We will start by adding a label displaying the heading on the main window with the help of the Label() widget. The following is the snippet of code demonstrating the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Label() widget to create a label for the main window. We have specified the guiWindow as its parameter. We have also set the text to be displayed along with the font style and size, foreground color, and background color. We have then used the place() method to place the label on the screen. Now, let us create other labels to display necessary information like principal amount, rate of interest, number of times, time period, and compound interest using the Label() widget. The following is the snippet of code demonstrating the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined different labels using the Label() widget specifying the guiWindow as their parameters along with the text these labels will display, background, and foreground color. Now that we have created the labels, it is time for us to place them on the main window. We will be using the place() method specifying the coordinates where the label will be displayed. Let us consider the following snippet of code illustrating the same. File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the place() method on the labels we created earlier. We have specified the x- and y-coordinates for the placement of these labels. We will now use the Entry() widget to add some entry fields to the main window to allow the user to enter the required values to calculate the compound interest. We will also define an entry field where the result will be displayed. Let us consider the snippet of code shown below illustrates the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Entry() widget to define the entry fields for the user to enter the required data. We have also defined an entry field to display the result for the user. Now, let us place these entry fields on the main window using the place() method. The following snippet of code demonstrates the same: File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the place() method to place the above fields on the window. We have specified the x- and y-coordinates for their placements. We will now create some buttons that will trigger the functions for their execution. We will use the Button() widgets for the same and specify its command parameter to the function we defined earlier. We will be creating two buttons - The first button is the CALCULATE button that will execute the calculation of the Compound Interest for the given data. The second button is the RESET button, which will reset all the entries and the result. File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Button() widget to create the CALCULATE and RESET buttons. We have used the command parameter and set the target to the compound_interest() and reset() functions. Now that we have created the buttons, it is time for us to place them on the main window using the place() method. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the place() method to place the above buttons on the main window on the specified coordinates. At last, we will use the mainloop() method to run the Tkinter event loop. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the same. File: ciCalci.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the mainloop() method to run the Tkinter event loop. Thus, the coding of the 'Compound Interest GUI Calculator' project is finally completed. We can now save the file and run the program to see if it works. To run the program, we can type the following command in the command-line shell or terminal: Command: But before we see the output, here is a complete project code. The Complete Project CodeThe following program file is a complete code for the 'Compound Interest GUI Calculator' project. File: ciCalci.py Output: 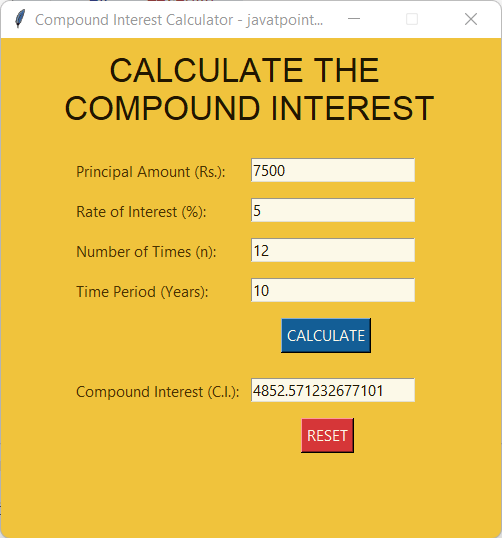
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










