Sort an Array in Wave FormSorting arrays is a common task in computer science and programming. Often, the requirements are to simply sort the array in ascending or descending order. However, sometimes more complex arrangements are needed. One such arrangement is sorting the array elements in a wave pattern - alternating between large and small values. This wave sort presents an interesting problem, and the algorithm requires careful swapping after sorting to achieve the wave effect. In this article, we will look at the wave sort technique to rearrange an unsorted array of integers in a wave fashion. We will go through the algorithm step-by-step. Code examples in Python. 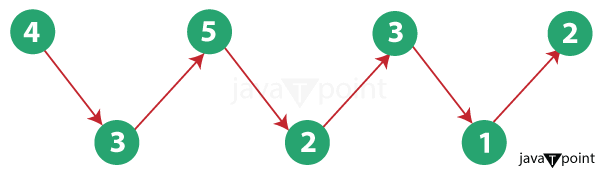
What is Wave Form?Waveform sorting refers to arranging the elements of an array in a sequence such that elements alternatively change from large to small and then small to large. Visualizing the final sorted array in a graph will look like a wave with crests and troughs. For example, consider the array [3, 6, 5, 10, 7, 20]. If we sort this array in wave form, we should get [5, 3, 10, 6, 20, 7]. We can observe the following properties:
Therefore, waveform sorting aims to rearrange elements in this fashion rather than in simple ascending or descending order. The algorithm involves sorting the array normally and then swapping adjacent elements pairwise. This results in small and large values exchanging positions in each pair, creating the wave pattern. The wave-sorted array has applications where generating data in wave patterns is required. For example, while testing functions that process alternating large and small values. It is also sometimes used in mathematics for specific sequences. Overall, waveform sorting creates an unusual arrangement of data that switches between crests and troughs in a wave-like visual pattern. Advantages of using Wave Form in Sorting
So, in summary, the alternating pattern, stability, in-place operation, easy coding, optimal time/space complexity and parallelism make wave form sorting useful over conventional sorting techniques in certain cases. The wave pattern has its unique applications. Applications and Uses of Wave Form
So, in summary, generating alternating test data, processing wave signals, creating patterns and sequences, analyzing cyclical data, balancing loads, testing edge cases etc., are some applications where wave form sorting provides benefits over other sorting techniques. The alternating wave pattern has unique use cases. Python Implementation of Wave FormAlgorithm
Approach
Example Input: arr[] = [10, 90, 49, 2, 1, 5, 23] Sort: [1, 2, 5, 10, 23, 49, 90] After swap: [2, 1, 10, 5, 90, 23, 49] (wave form) Time Complexity - O(nLogn) for sort() + O(n) for swap loop => O(nLogn) Space Complexity - O(1) as it's done in place without any extra space. So, in summary, initializing 'i' for accessing alternates, swapping adjacent pairs, and performing it in-place results in an efficient wave sort algorithm with optimal time and space complexity. Output: 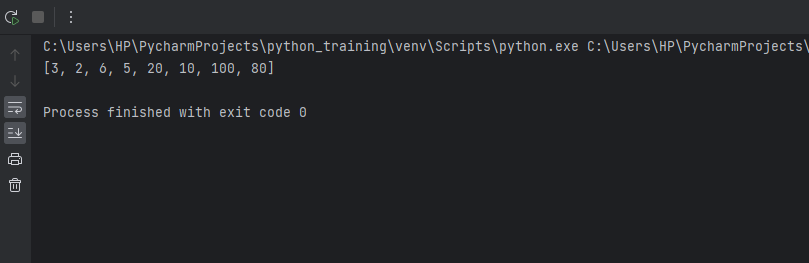
Explanation:
Conclusion:In this article, we explored the technique of sorting an unsorted array of integers in a wave pattern. This wave sorting rearranges the elements into alternating crests and troughs instead of just ascending or descending order. We looked at a simple and efficient algorithm that first sorts the array normally, then swaps adjacent elements pairwise to achieve the wave effect. The algorithm has an optimal time complexity of O(nLogn) and constant O(1) space complexity. Code examples were provided in Python to demonstrate implementation. The Python program leveraged built-in sort and in-place swapping to implement the wave sort efficiently. Wave form sorting has some interesting applications in computing and mathematics. Some use cases include generating alternating test data, processing wave signals, creating dithering effects, balancing loads and analyzing waveforms. It provides a different data arrangement compared to typical sorting. In summary, the wave sort algorithm provides an unusual reordering of array elements from small to large to small and so on in a wave pattern. With its unique applications, this technique can be useful to standard sorting methods in certain scenarios. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










