Array in Data StructureIn this article, we will discuss the array in data structure. Arrays are defined as the collection of similar types of data items stored at contiguous memory locations. It is one of the simplest data structures where each data element can be randomly accessed by using its index number. In C programming, they are the derived data types that can store the primitive type of data such as int, char, double, float, etc. For example, if we want to store the marks of a student in 6 subjects, then we don't need to define a different variable for the marks in different subjects. Instead, we can define an array that can store the marks in each subject at the contiguous memory locations. Properties of arrayThere are some of the properties of an array that are listed as follows -
Representation of an arrayWe can represent an array in various ways in different programming languages. As an illustration, let's see the declaration of array in C language - 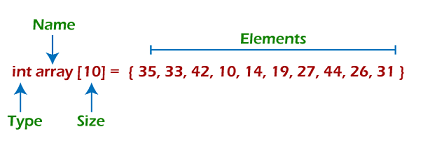
As per the above illustration, there are some of the following important points -
Why are arrays required?Arrays are useful because -
Memory allocation of an arrayAs stated above, all the data elements of an array are stored at contiguous locations in the main memory. The name of the array represents the base address or the address of the first element in the main memory. Each element of the array is represented by proper indexing. We can define the indexing of an array in the below ways -
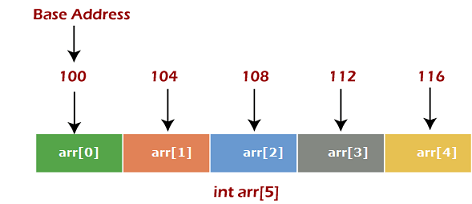
In the above image, we have shown the memory allocation of an array arr of size 5. The array follows a 0-based indexing approach. The base address of the array is 100 bytes. It is the address of arr[0]. Here, the size of the data type used is 4 bytes; therefore, each element will take 4 bytes in the memory. How to access an element from the array?We required the information given below to access any random element from the array -
The formula to calculate the address to access an array element - Here, size represents the memory taken by the primitive data types. As an instance, int takes 2 bytes, float takes 4 bytes of memory space in C programming. We can understand it with the help of an example - Suppose an array, A[-10 ..... +2 ] having Base address (BA) = 999 and size of an element = 2 bytes, find the location of A[-1]. L(A[-1]) = 999 + 2 x [(-1) - (-10)] = 999 + 18 = 1017 Basic operationsNow, let's discuss the basic operations supported in the array -
Traversal operationThis operation is performed to traverse through the array elements. It prints all array elements one after another. We can understand it with the below program - Output 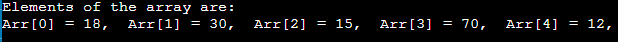
Insertion operationThis operation is performed to insert one or more elements into the array. As per the requirements, an element can be added at the beginning, end, or at any index of the array. Now, let's see the implementation of inserting an element into the array. Output 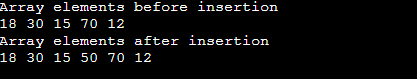
Deletion operationAs the name implies, this operation removes an element from the array and then reorganizes all of the array elements. Output 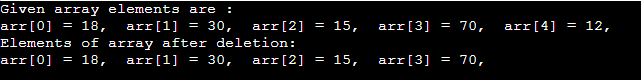
Search operationThis operation is performed to search an element in the array based on the value or index. Output 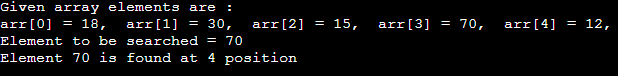
Update operationThis operation is performed to update an existing array element located at the given index. Output 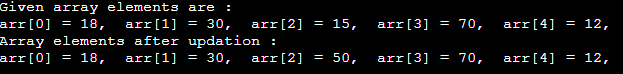
Complexity of Array operationsTime and space complexity of various array operations are described in the following table. Time Complexity
Space Complexity In array, space complexity for worst case is O(n). Advantages of Array
Disadvantages of Array
ConclusionIn this article, we have discussed the special data structure, i.e., array, and the basic operations performed on it. Arrays provide a unique way to structure the stored data such that it can be easily accessed and can be queried to fetch the value using the index.
Next Topic2D Array
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









