Representation of stack in data structureAn abstract data type (ADT) called a stack is used to store data linearly. The only end of a stack via which we may add or remove data is the top of the stack. Abstract Data TypeAn object's behavior may be described by a set of values and a set of actions, and this behavior is known as an abstract data type (ADT). The definition of ADT merely specifies the actions that must be taken, not how they must be carried out. It is unclear what algorithms will be utilized to carry out the operations and how the data will be structured in memory. Because it provides an implementation-independent view, it is dubbed "abstract." Abstraction is the technique of presenting only the basics while obscuring the nuances. 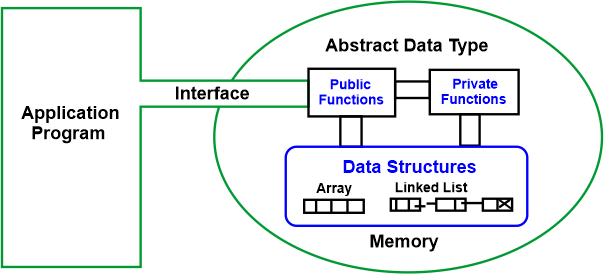
The user of a data type does not need to be aware of how that data type is implemented. For instance, we have been using primitive values such as int, float, and char data types only with the understanding that these data types can operate and be performed on without being aware of how they are implemented. Therefore, a user just has to be aware of what a data type is capable of, not how it will be used. Consider ADT as a "black box" that conceals the internal organization and design of the data type. We will now define the three ADTs: List, Stack, and Queue. Stack ADT
LIFO (Last in First Out)We will insert the data pieces into the data structure using the Last In First Out method, or LIFO. We will highlight the most current data items here. It implies that the last component will emerge first. Example from real life: 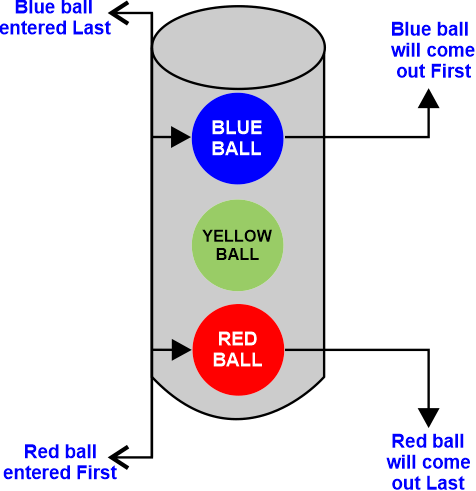
The following elements should be taken into account in this example:
Book Example:The quantity of books stacked one on top of the other
The stack-based data structure is based on the LIFO concept. Push and pop are the two major operations we use on it. Data items are pushed into the stack using the push operation and removed from the stack using the pop operation. The top pointer in the stack data structure points to the value that is present at the top of the stack. The underflow situation is the state in which the stack initially links to the null pointer when it is empty. We have provided the stack's capacity; let's say n, in the stack. The data values must be added to the stack one at a time until the top of the stack is filled to its maximum size. Overflow refers to the situation when it exceeds the capacity. Where LIFO is employed:Data Structures: Some data structures, such as Stacks and various Stack variations, process data using the LIFO method. Get the newest information: When data is taken from an array or data buffer, computers may employ LIFO. The LIFO technique is utilized when it is necessary to retrieve the most recent data entered. Let us see a program in C to better understand the working of LIFO using struct: Output 10 pushed into stack 20 pushed into stack 30 pushed into stack 30 Popped from stack Top element is : 20 Elements present in stack : 20 10 ........................................................... Process executed in 3.22 seconds Press any key to continue. Explanation: In the above C program for LIFO representation, we can see first 10 is pushed and then 20 is pushed into the stack follow by 30 into the stack, then when performing pop function the element which was entered in the stack in the last is pop out first.
Next TopicAdvantages of Threaded Binary Tree
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









