Linked List Deletion (Deleting a key at a given position)Linked lists are fundamental data structures that are essential in computer science. The deletion of a node at a particular point is a fundamental and often-used operation on linked lists. In this post, we will dig into the complexities of linked list deletion, investigating its relevance, underlying concepts, and a comprehensive Python implementation.
The Importance of RemovalDeletion of a linked list is critical for preserving the data structure's integrity and performance. Removing a node at a certain place requires altering the linkages between nodes to maintain the logical flow of data. Because linked lists may remove nodes dynamically, they can adapt to changing requirements, making them an effective tool for handling evolving datasets. Deletion at a Given Position: A Step-by-Step Approach1. Deleting the Head:The first possibility to explore is deleting the linked list's head. If the initial node is to be eliminated, changing the head to point to the next node effectively removes it from the list. This procedure has a temporal complexity of O(1) and is thus very efficient. Time Complexity: O(1) - constant time, as it involves a simple pointer update. Space Complexity: O(1) - constant space, as no additional data structures are used. Implementation This implementation includes:
Output 
2. Delete Other NodesA more detailed approach is necessary for nodes other than the head. The algorithm comprises traversing the list until the target location is reached, then diverting the following node's pointer to bypass the node to be destroyed. Time Complexity: O(n) - linear time, where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. Space Complexity: O(1) - constant space, as the algorithm uses a fixed amount of additional memory. Implementation This implementation includes:
Output: 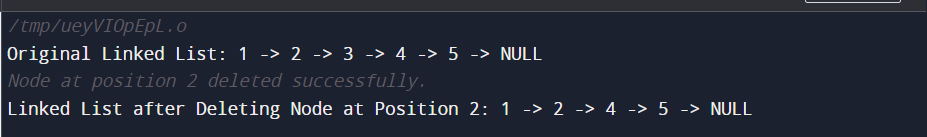
3. Handling Edge CasesEdge situations must be considered in robust linked list deletion solutions. These include attempting to delete a node from an empty list, attempting to delete a node at a non-existent location, and dealing with deletions that extend past the end of the list. Time Complexity: O(1) - constant time, as it involves basic conditional checks. Space Complexity: O(1) - constant space, as no additional memory is used. Implementation In this improved version:
Output: 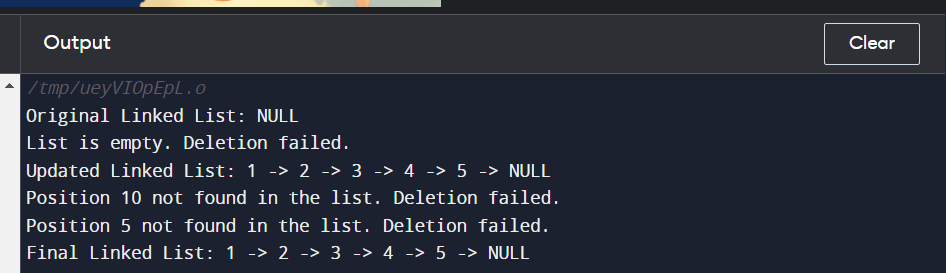
ConclusionFinally, linked list deletion at a specific point is a critical operation in the world of data structures. Understanding the ideas underlying this procedure, such as pointer updates and managing exceptional circumstances, is essential for any programmer or computer science enthusiast. Linked lists are a versatile and strong tool because of their ability to manage data dynamically through efficient deletion. We obtain insights into the underlying workings of these dynamic structures by investigating the complexities of linked list deletion, opening the door for more advanced data manipulation tasks. Mastering linked list deletion is an important step in your journey through the world of computer science, whether you are a newbie learning the ropes or an experienced developer honing your abilities. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









